| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- GPT 역할 부여하기
- aws eks
- kiali
- Ingress
- grafana
- Istio
- GPT 멀티챗
- 랭그래프 목차만들기
- vagrant
- CNI
- K8S
- Jenkins
- 타빌리
- Ambient
- service mesh
- Kind
- loadbalancer
- vpc cni
- argocd
- Streamlit 활용한 챗봇만들기
- docker
- 멀티에이전트 RAG
- Observability
- 스트림릿 활용한 GPT
- prometheus
- CICD
- envoy
- WSL
- Kubernetes
- PuMuPDF
- Today
- Total
WellSpring
Istio 6주차 - 10~11장, 부록 D - 운영, 튜닝 본문
목차
※ 본 게재 글은 gasida님의 'Istio' 스터디 강의 및 실습예제와 'Istio in Action' 서적을 참고하여 작성하였습니다.
[ 10장 환경 설치 ]
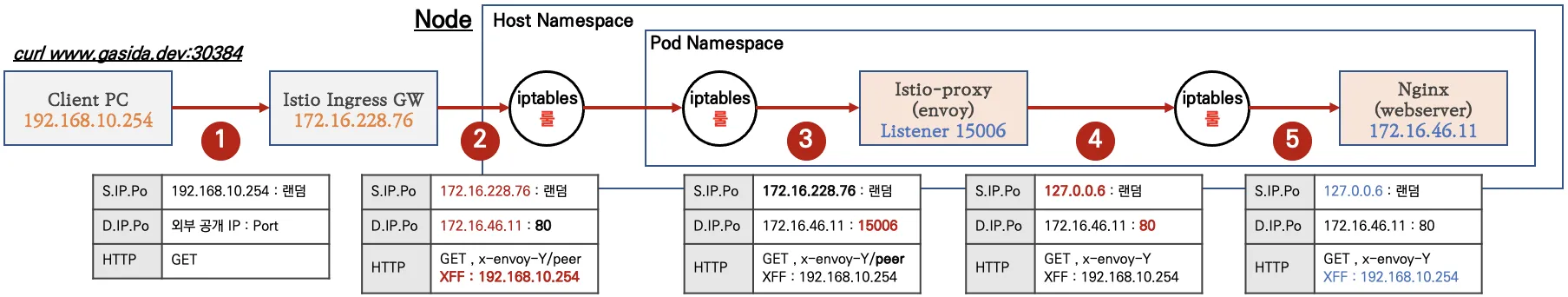
▶ [실습 환경 구성] k8s(1.23.17) 배포 : NodePort(30000 HTTP, 30005 HTTPS)
☞ 늘어난 서비스 갯수를 반영한 테스트 환경 구성으로 기존 subnet '/24' -> '/22'를 사용함.
#
git clone https://github.com/AcornPublishing/istio-in-action
cd istio-in-action/book-source-code-master
pwd # 각자 자신의 pwd 경로
code .
# 아래 extramounts 생략 시, myk8s-control-plane 컨테이너 sh/bash 진입 후 직접 git clone 가능
kind create cluster --name myk8s --image kindest/node:v1.23.17 --config - <<EOF
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30000 # Sample Application (istio-ingrssgateway) HTTP
hostPort: 30000
- containerPort: 30001 # Prometheus
hostPort: 30001
- containerPort: 30002 # Grafana
hostPort: 30002
- containerPort: 30003 # Kiali
hostPort: 30003
- containerPort: 30004 # Tracing
hostPort: 30004
- containerPort: 30005 # Sample Application (istio-ingrssgateway) HTTPS
hostPort: 30005
- containerPort: 30006 # TCP Route
hostPort: 30006
- containerPort: 30007 # kube-ops-view
hostPort: 30007
extraMounts: # 해당 부분 생략 가능
- hostPath: /Users/gasida/Downloads/istio-in-action/book-source-code-master # 각자 자신의 pwd 경로로 설정
containerPath: /istiobook
networking:
podSubnet: 10.10.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 10.200.0.0/22
EOF
# 설치 확인
docker ps
# 노드에 기본 툴 설치
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane sh -c 'apt update && apt install tree psmisc lsof wget bridge-utils net-tools dnsutils tcpdump ngrep iputils-ping git vim -y'
# (옵션) kube-ops-view
helm repo add geek-cookbook https://geek-cookbook.github.io/charts/
helm install kube-ops-view geek-cookbook/kube-ops-view --version 1.2.2 --set service.main.type=NodePort,service.main.ports.http.nodePort=30007 --set env.TZ="Asia/Seoul" --namespace kube-system
kubectl get deploy,pod,svc,ep -n kube-system -l app.kubernetes.io/instance=kube-ops-view
## kube-ops-view 접속 URL 확인
open "http://localhost:30007/#scale=1.5"
open "http://localhost:30007/#scale=1.3"
# (옵션) metrics-server
helm repo add metrics-server https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/metrics-server/
helm install metrics-server metrics-server/metrics-server --set 'args[0]=--kubelet-insecure-tls' -n kube-system
kubectl get all -n kube-system -l app.kubernetes.io/instance=metrics-server
▶ [실습 환경 구성] istio 1.17.8 설치 - Docs , Install , profile
# myk8s-control-plane 진입 후 설치 진행
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane bash
-----------------------------------
# (옵션) 코드 파일들 마운트 확인
tree /istiobook/ -L 1
혹은
git clone ... /istiobook
# istioctl 설치
export ISTIOV=1.17.8
echo 'export ISTIOV=1.17.8' >> /root/.bashrc
curl -s -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=$ISTIOV sh -
cp istio-$ISTIOV/bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/istioctl
istioctl version --remote=false
# demo 프로파일 컨트롤 플레인 배포
istioctl install --set profile=demo --set values.global.proxy.privileged=true -y
# 보조 도구 설치
kubectl apply -f istio-$ISTIOV/samples/addons
# 빠져나오기
exit
-----------------------------------
# 설치 확인 : istiod, istio-ingressgateway, crd 등
kubectl get istiooperators -n istio-system -o yaml
kubectl get all,svc,ep,sa,cm,secret,pdb -n istio-system
kubectl get cm -n istio-system istio -o yaml
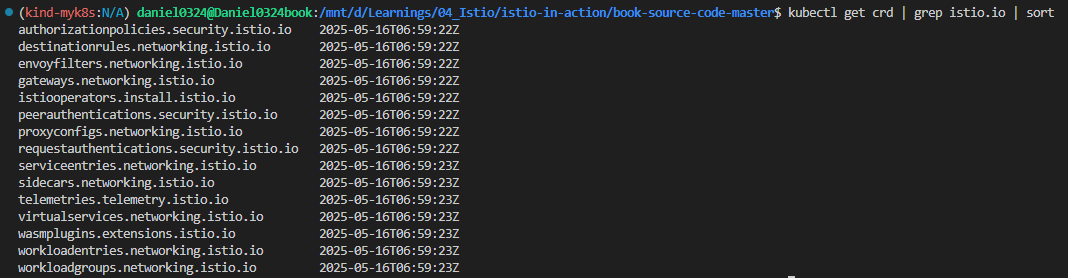
kubectl get crd | grep istio.io | sort
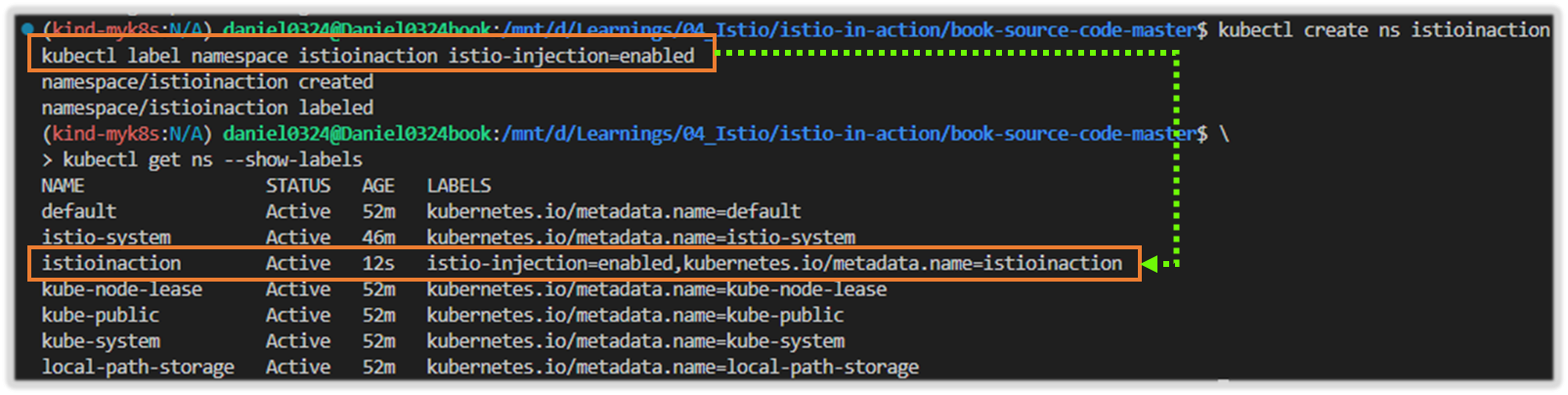
# 실습을 위한 네임스페이스 설정
kubectl create ns istioinaction
kubectl label namespace istioinaction istio-injection=enabled
kubectl get ns --show-labels
# istio-ingressgateway 서비스 : NodePort 변경 및 nodeport 지정 변경 , externalTrafficPolicy 설정 (ClientIP 수집)
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 80, "targetPort": 8080, "nodePort": 30000}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 443, "targetPort": 8443, "nodePort": 30005}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -p '{"spec":{"externalTrafficPolicy": "Local"}}'
kubectl describe svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway
# NodePort 변경 및 nodeport 30001~30003으로 변경 : prometheus(30001), grafana(30002), kiali(30003), tracing(30004)
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system prometheus -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 9090, "targetPort": 9090, "nodePort": 30001}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system grafana -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 3000, "targetPort": 3000, "nodePort": 30002}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system kiali -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 20001, "targetPort": 20001, "nodePort": 30003}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system tracing -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 80, "targetPort": 16686, "nodePort": 30004}]}}'
# Prometheus 접속 : envoy, istio 메트릭 확인
open http://127.0.0.1:30001
# Grafana 접속
open http://127.0.0.1:30002
# Kiali 접속 1 : NodePort
open http://127.0.0.1:30003
# (옵션) Kiali 접속 2 : Port forward
kubectl port-forward deployment/kiali -n istio-system 20001:20001 &
open http://127.0.0.1:20001
# tracing 접속 : 예거 트레이싱 대시보드
open http://127.0.0.1:30004[ 실행 결과 - 점검 사항 ]
1) 설치 CRD 리스트 확인
2) Istio-system 라벨링 확인
10장 데이터 플레인 트러블 슈팅하기
☞ This chapter covers Troubleshooting the data plane
- 잘못 설정한 워크로드 트러블슈팅하기 Troubleshooting a misconfigured workload
- istioctl과 키알리로 잘못된 설정 감지 및 방지하기 Detecting and preventing misconfigurations using istioctl and Kiali
- istioctl을 사용해 서비스 프록시 설정 조사하기 Using istioctl to investigate the service proxy configuration
- 엔보이 로그 이해하기 Making sense of Envoy logs
- 텔레메트리를 사용해 앱에 대한 통찰력 얻기 Using telemetry to gain insights into apps
▶ 들어가며* : 데이터 플레인 문제 해결
- 잘 알다시피 네트워크를 통해 통신할 때는 많은 것이 잘못될 수 있다.
- 이스티오가 존재하는 주요 이유는 무언가 잘못됐을 때 네트워크 통신을 조명하고 타임아웃, 재시도, 서킷 브레이커 같은 복원 기능을 배치함으로써 애플리케이션이 네트워크 문제에 자동으로 대응할 수 있도록 하기 위함이다.
- 서비스 프록시는 네트워크에서 일어나는 일을 매우 자세히 보여주지만, 프록시 자신이 예기치 못하게 작동하면 어떻게 될까?
- 그림 10.1은 요청 처리에 참여하는 구성 요소들을 보여준다.
- istiod, 데이터 플레인이 원하는 상태 desired state 로 동기화되도록 보장한다.
- 인그레스 게이트웨이. 트래픽을 클러스터로 허용한다.
- 서비스 프록시, 접근 제어 기능을 제공하고, 다운스트림에서 로컬 애플리케이션으로 흐르는 트래픽을 처리한다.
- 애플리케이션 그 자체, 요청을 처리하고, 또 다른 업스트림 서비스로 체인을 이어나가는 다른 서비스에 요청하는 것 등을 한다.
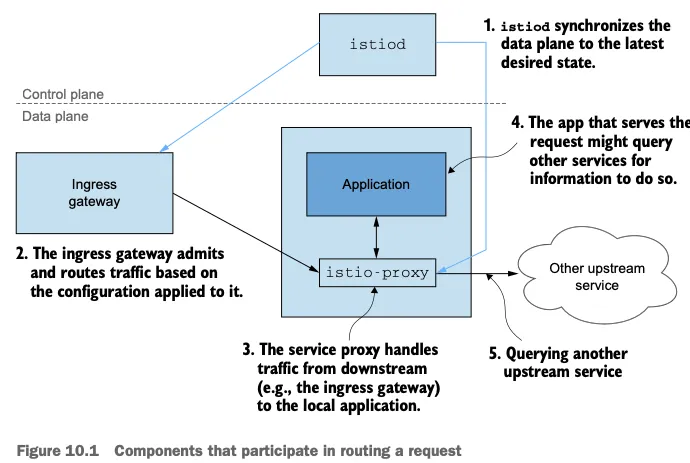
- 따라서 예기치 못한 문제는 이 체인의 어떤 구성 요소와도 관련 있을 수 있다.
- 모든 구성 요소를 디버깅하는 것은 시간이 많이 필요한데, 앱이 클러스터나 시스템 전체에 영향을 줄 때는 그럴 시간이 없다.
- 이번 장에서는 오류 시나리오를 해결하기 위해 프록시와 관련 설정을 살펴보는 도구를 활용해본다.
10.1 가장 흔한 실수: 잘못 설정한 데이터 플레인
☞ https://netpple.github.io/docs/istio-in-action/Istio-ch10-troubleshooting
▶ The most common mistake: A misconfigured data plane : 환경 설정하기 (실습~)
- 이스티오는 서비스 프록시 설정을 사람이 읽을 수 있는 형식인 VirtualService, DestinationRule 등과 같은 CRD로 누출한다.
- 이 리소스들은 엔보이 설정으로 변환돼 데이터 플레인에 적용된다.
- 새 리소스를 적용한 후 데이터 플레인의 동작이 예상과 다를 때 가장 일반적인 원인은 우리가 설정을 잘못한 것이다.
- 데이터 플레인을 잘못 설정했을 때 트러블슈팅하는 방법을 보여주기 위해 다음 예제를 준비한다.
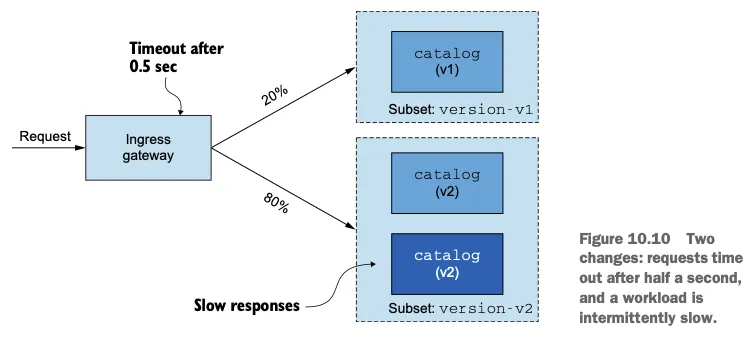
- 이스티오 인그레스 게이트웨이로 트래픽을 허용하는 Gateway 리소스와 그림 10.2처럼 요청 중 20% 부분집합 version-v1으로, 나머지 80%를 version-v2로 라우팅하는 VirtualService리소스를 사용할 것이다.
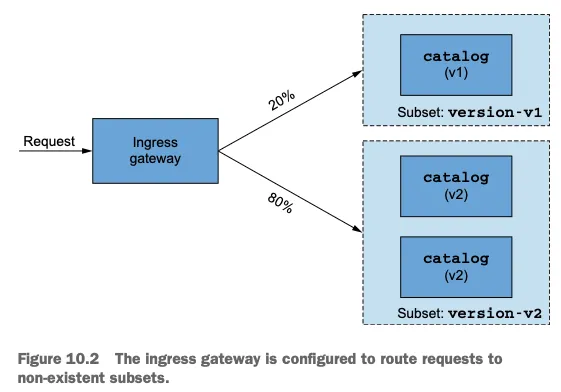
- ‘여기까지는 괜찮다’고 생각할 수 있지만, 그렇지 않다.
- DestinationRule 리소스가 없으면 인그레스 게이트웨이는 부분집합 version-v1과 version-v2에 대한 클러스터 정의가 없으므로, 모든 요청은 실패할 것이다.
- 이는 트러블슈팅을 해보기에 좋은 문제다!
- 먼저 이스티오는 배포했지만 (2장 참조) 다른 애플리케이션 구성 요소는 배포해두지 않았다고 해보자.
- 앞 장들부터 계속해오고 있다면, 다음과 같이 남아 있는 Deployment, Service, Gateway, VirtualService 를 정리 후 샘플 애플리케이션 배포하자.
# 샘플 애플리케이션 배포
kubectl apply -f services/catalog/kubernetes/catalog.yaml -n istioinaction # catalog v1 배포
kubectl apply -f ch10/catalog-deployment-v2.yaml -n istioinaction # catalog v2 배포
kubectl apply -f ch10/catalog-gateway.yaml -n istioinaction # catalog-gateway 배포
kubectl apply -f ch10/catalog-virtualservice-subsets-v1-v2.yaml -n istioinaction
# Gateway
cat ch10/catalog-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: catalog-gateway
namespace: istioinaction
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
servers:
- hosts:
- "catalog.istioinaction.io"
port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
# VirtualService
cat ch10/catalog-virtualservice-subsets-v1-v2.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: catalog-v1-v2
namespace: istioinaction
spec:
hosts:
- "catalog.istioinaction.io"
gateways:
- "catalog-gateway"
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
subset: version-v1
port:
number: 80
weight: 20
- destination:
host: catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
subset: version-v2
port:
number: 80
weight: 80
# 확인
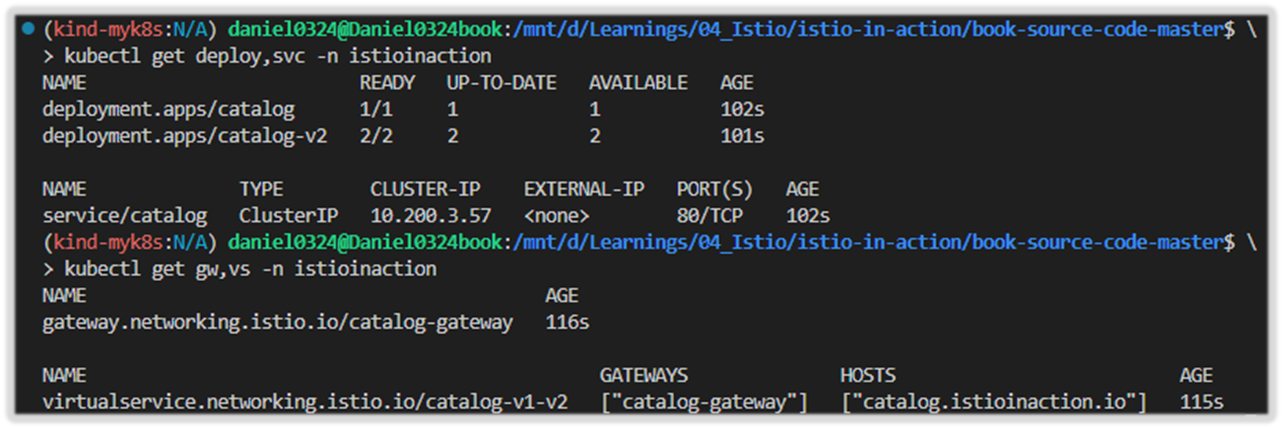
kubectl get deploy,svc -n istioinaction
kubectl get gw,vs -n istioinaction
- 통신 확인 : 부분집합 설정 누락으로 503 ‘Service Unavailable’ 출력 - Envoy
# 로그 확인 : NC - NoClusterFound : Upstream cluster not found.
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f
[2025-05-09T01:54:51.145Z] "GET /items HTTP/1.1" 503 NC cluster_not_found - "-" 0 0 0 - "172.18.0.1" "curl/8.7.1" "90a7d941-cbc4-91ae-9da1-bc95695d5c50" "catalog.istioinaction.io:30000" "-" - - 10.10.0.7:8080 172.18.0.1:64130 - -
# 반복 호출 시도
for i in {1..100}; do curl http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items -w "\nStatus Code %{http_code}\n"; sleep .5; done
Status Code 503
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
1) gw 및 Virtual Service 배포
2) 부하 테스트 결과 확인 ** 부하를 주기 전에 반드시 OS의 hosts 파일에 요청 URL을 등록해 주자!!
127.0.0.1 catalog.istioinaction.io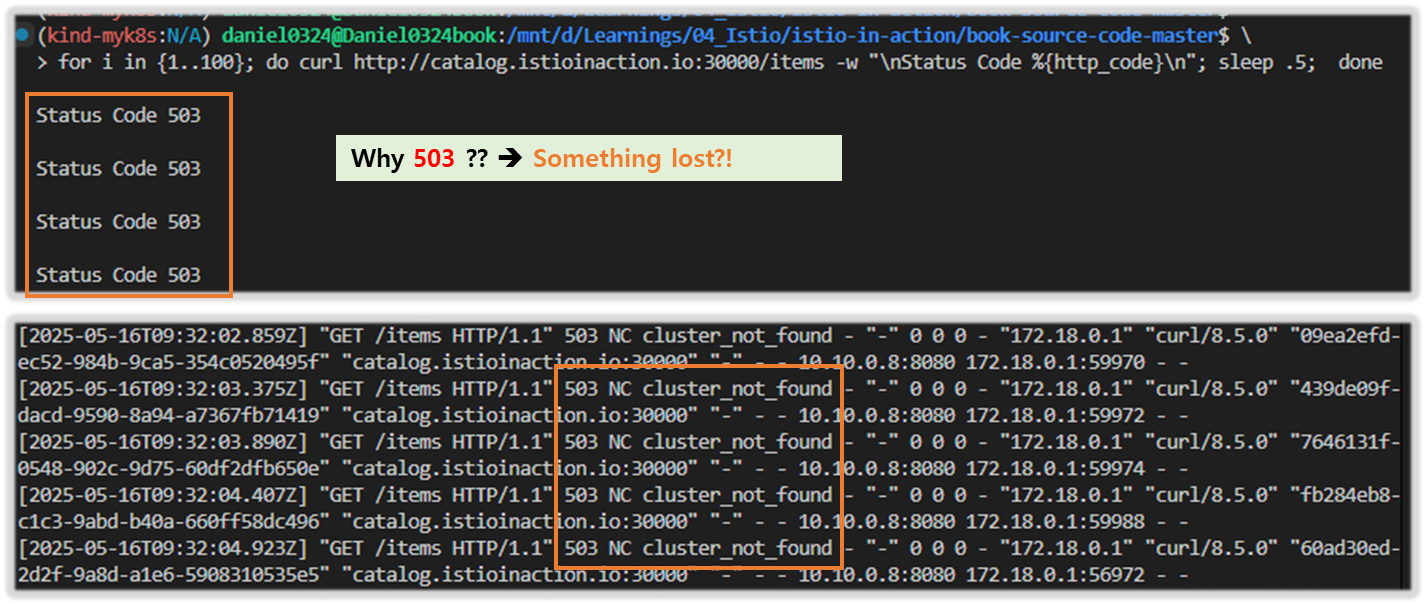
3) 다음 Traffic 테스트 를 위해서 curl URL 을 걸어두자!!
while true; do curl -s http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items/ -I | head -n 1 ; date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ; sleep 0.5; echo; done
[참고] Envoy response flag - 링크
HTTP and TCP
• UH: No healthy upstream hosts in upstream cluster in addition to 503 response code.
• UF: Upstream connection failure in addition to 503 response code.
• UO: Upstream overflow (circuit breaking) in addition to 503 response code.
• NR: No route configured for a given request in addition to 404 response code, or no matching filter chain for a downstream connection.
• URX: The request was rejected because the upstream retry limit (HTTP) or maximum connect attempts (TCP) was reached.
• NC: Upstream cluster not found.
• DT: When a request or connection exceeded max_connection_duration or max_downstream_connection_duration.
HTTP only
• DC: Downstream connection termination.
• LH: Local service failed health check request in addition to 503 response code.
• UT: Upstream request timeout in addition to 504 response code.
• LR: Connection local reset in addition to 503 response code.
• UR: Upstream remote reset in addition to 503 response code.
• UC: Upstream connection termination in addition to 503 response code.
• DI: The request processing was delayed for a period specified via fault injection.
• FI: The request was aborted with a response code specified via fault injection.
• RL: The request was ratelimited locally by the HTTP rate limit filter in addition to 429 response code.
• UAEX: The request was denied by the external authorization service.
• RLSE: The request was rejected because there was an error in rate limit service.
• IH: The request was rejected because it set an invalid value for a strictly-checked header in addition to 400 response code.
• SI: Stream idle timeout in addition to 408 response code.
• DPE: The downstream request had an HTTP protocol error.
• UPE: The upstream response had an HTTP protocol error.
• UMSDR: The upstream request reached max stream duration.
• OM: Overload Manager terminated the request.
• DF: The request was terminated due to DNS resolution failure.
10.2 데이터 플레인 문제 식별하기
▶ 들어가며
- 일상적인 운영에서는 보통 데이터 플레인 문제를 처리할 것이다.
- 바로 데이터 플레인 디버깅에 뛰어드는 습관이 생길 수도 있지만, 컨트롤 플레인 문제를 추정 원인에서 빠르게 배제하는 것이 중요하다.
- 컨트롤 플레인의 주요 기능이 데이터 플레인을 최신 설정으로 동기화하는 것임을 감안하면, 첫 단계는 컨트롤 플레인과 데이터 플레인이 동기화된 상태인지 확인하는 것이다.
10.2.1 데이터 플레인이 최신 상태인지 확인하는 방법
- How to verify that the data plane is up to date
- 데이터 플레인 설정은 설계상 궁극적으로 일관성을 가진다. The data-plane configuration is eventually consistent by design.
- 즉, 환경(서비스, 엔드포인트, 상태)이나 설정의 변화는 컨트롤 플레인과 적절히 동기화하기 전까지는 데이터 플레인에 즉시 반영되지 않는다.
- 예를 들어 앞 장들에서 봤듯이 컨트롤 플레인은 특정 서비스의 개별 엔드포인트 IP 주소를 데이터 플레인으로 보낸다. (서비스 내의 각 파드 IP 주소와 대강 동일)
- 이런 엔드포인트 중 어느 하나가 비정상이 되면, 쿠버네티스가 이를 인지하고 파드를 비정상으로 표시하는 데 시간이 걸린다.
- 어느 시점에 컨트롤 플레인도 문제를 인지하고 엔드포인트를 데이터 플레인에서 제거한다.
- 따라서 컨트롤 플레인은 최신 설정으로 돌아오며, 프록시 설정도 다시 일관된 상태가 된다.
- 그림 10.3은 데이터 플레인을 업데이트하기 위해 발생하는 이벤트를 시각화한다.
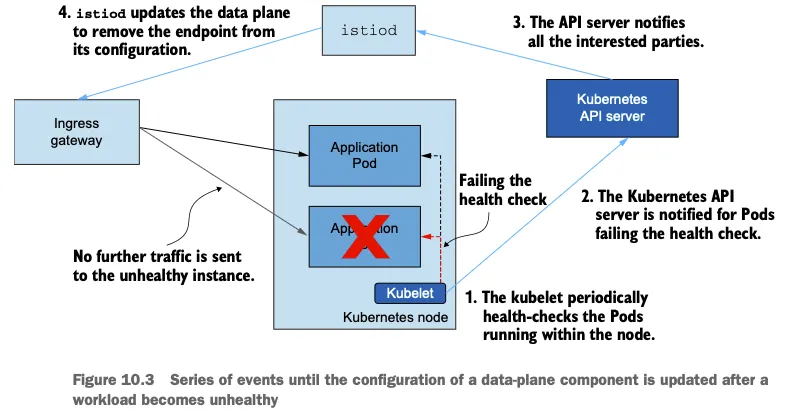
- kubelet은 주기적으로 노드 내에서 실행 중인 파드의 상태를 확인한다.
- 쿠버네티스 API서버는 상태 확인을 실패한 파드를 통보받는다.
- API 서버가 모든 이해 당사자들에게 알린다.
- istiod가 데이터 플레인을 업데이트해 설정에서 엔드포인트를 제거한다.
- 건강하지 않은 인스턴스로 더 이상 트래픽을 전송되지 않는다.
☞ 워크로드와 이벤트 개수가 늘어나는 대규모 클러스터 에서는 데이터 플레인을 동기화하는 데 필요한 시간도 비례해 늘어난다. 대규모 클러스터에서 성능을 개선하는 방법은 11장에서 살펴볼 것이다.
※ istioctl proxy-status 로 데이터 플레인이 최신 설정과 동기화했는지 확인하자.
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-status
NAME CLUSTER CDS LDS EDS RDS ECDS ISTIOD VERSION
catalog-6cf4b97d-l44zk.istioinaction Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-ltkhs 1.17.8
catalog-v2-56c97f6db-d74kv.istioinaction Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-ltkhs 1.17.8
catalog-v2-56c97f6db-m6pvj.istioinaction Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-ltkhs 1.17.8
istio-egressgateway-85df6b84b7-2f4th.istio-system Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-ltkhs 1.17.8
istio-ingressgateway-6bb8fb6549-hcdnc.istio-system Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-ltkhs 1.17.8
- SYNCED : istiod가 보낸 마지막 설정을 엔보이가 확인했다.
- NOT SENT : istiod가 아무것도 엔보이로 보내지 않았다. 보통은 istiod가 보낼 것이 없기 때문이다.
- STALE : istiod가 엔보이에 업데이트를 보냈지만 확인받지 못했다. 이는 다음 중 하나를 나타낸다.
- istiod가 과부하됐거나, 엔보이와 istiod 사이의 커넥션 부족 또는 끊김이거나, 이스티오의 버그다.
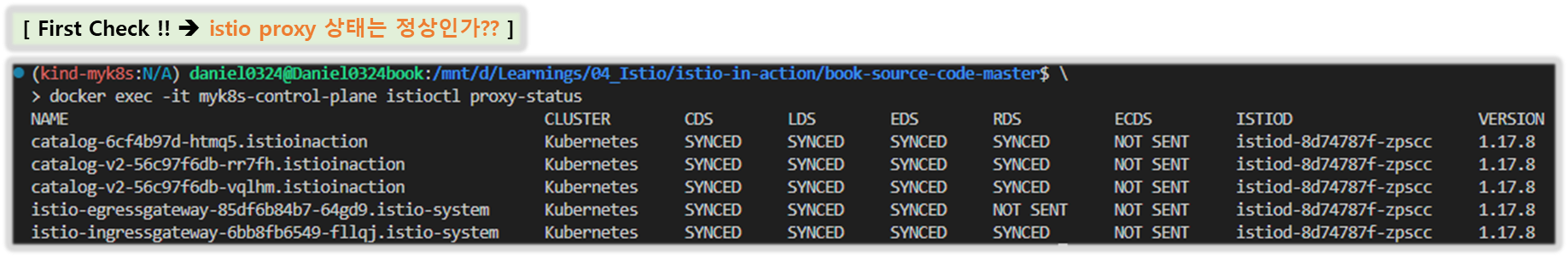
- 그런데 우리의 출력에는 설정을 받지 못한 stale 상태의 워크로드가 없다.
- 따라서 컨트롤 플레인에 문제가 있을 가능성은 낮으므로 데이터 플레인 구성 요소를 조사해야 한다.
- 데이터 플레인 구성 요소에서 가장 일반적인 문제는 잘못된 워크로드 설정이다.
- 키알리를 사용하면 설정을 빠르게 검증할 수 있다.
10.2.2 키알리로 잘못된 설정 발견하기
- Discovering misconfigurations with Kiali
- 대시보드에 Overview 에 istioinaction 네임스페이스에 경고 표시 확인 → 클릭 시 Istio Config 로 이동 ⇒ 클릭 시 내장 편집기에서 경고 메시지 확인 - Docs
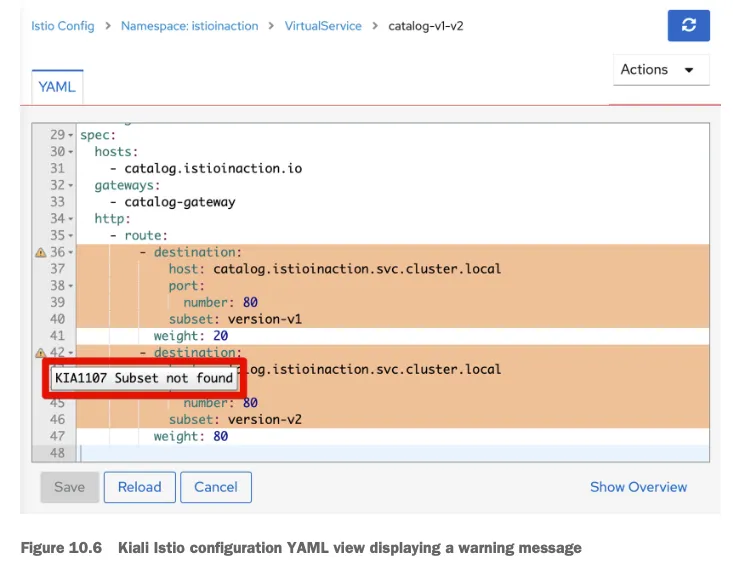
☞ 경고 아이콘 위로 마우스를 올리면 경고 메시지 ‘KIA1107 Subnet not found’를 보여준다.
자세한 건 키알리 공식 문서 참고 - Docs
- 예를 들어 다음은 KIA1107 경고의 해결책 부분이다.
- 존재하지 않은 부분집합을 가리키는 루트를 수정하자. 아마 부분집합 이름의 오타를 수정하거나 DestinationRule 에서 빠트린 부분집합을 정의하자.
- 키알리 검증은 도움이 되므로, 워크로드가 예상대로 동작하지 않을 때 취하는 첫 초지 중 하나여야 한다.
- 다음 조치는 또 다른 검증 모음을 제공하는 istioctl을 사용하는 것이다.
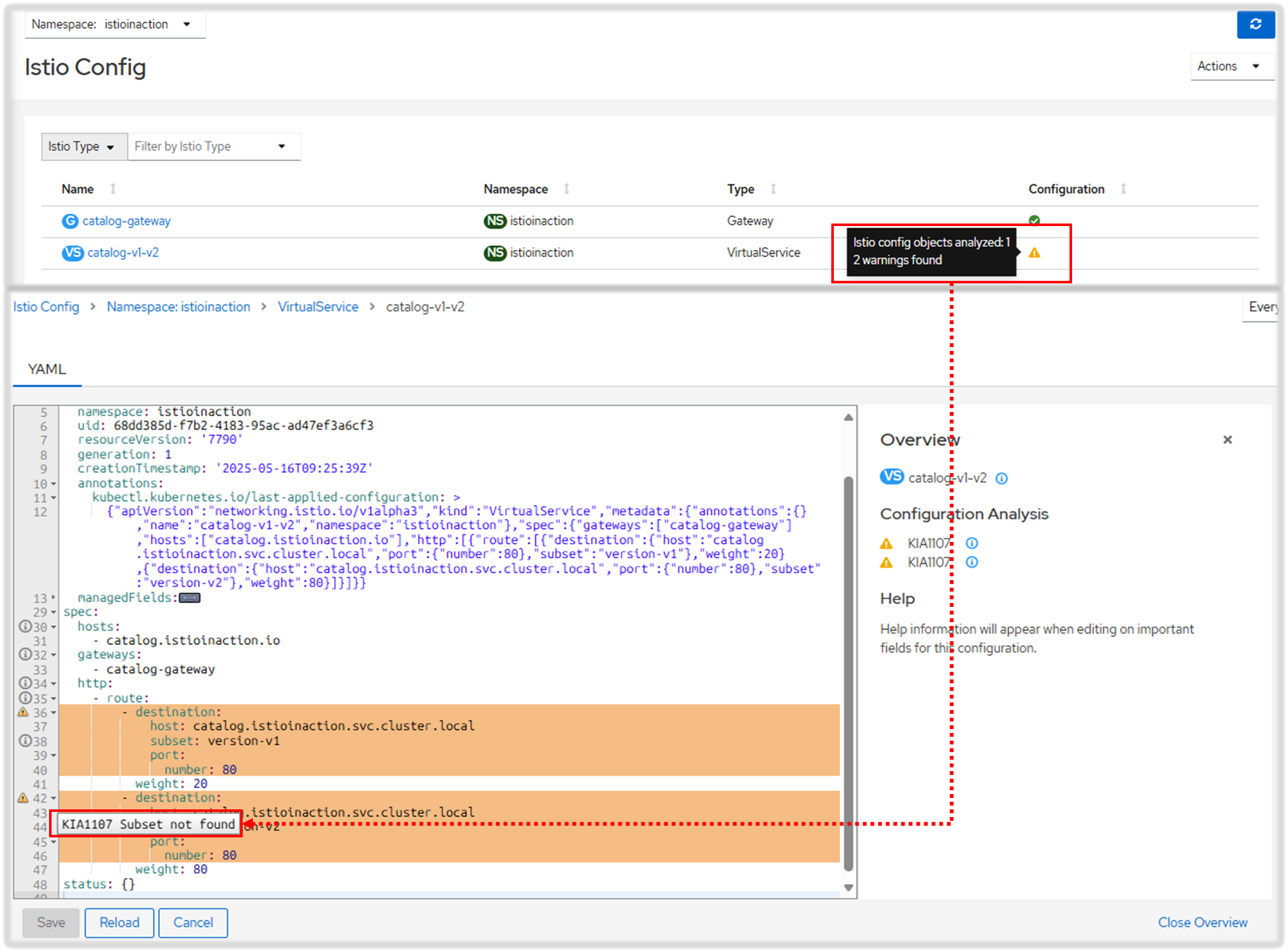
10.2.3 istioctl로 잘못된 설정 발견하기*
- Discovering misconfigurations with istioctl
잘못 설정된 워크로드를 자동으로 트러블슈팅하는 데 가장 유용한 istioctl 명령어 두 가지는 istioctl analyze 와 istioctl describe 이다.
☞ istioctl 로 이스티오 설정 분석하기 ANALYZING ISTIO CONFIGURATIONS WITH ISTIOCTL
- istioctl analyze 명령어는 이스티오 설정을 분석하는 강력한 진단 도구다.
- 이미 문제가 발생한 클러스터에 실행하거나, 리소스를 잘못 구성하는 것을 방지하고자 클러스터에 적용하기 전에 설정이 유효한지 검사할 수 있다.
- analyze 명령어는 여러 분석기를 실행하는데, 각 분석기는 특정 문제를 감지하는 데 특화되어 있다.
- analyze 명령어는 쉽게 확장할 수 있어 이스티오와 함께 발전할 수 있다.
- 감지된 문제를 살펴보자 - IstioDocs , 0101
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl analyze -h
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl analyze --list-analyzers
...
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl analyze -n istioinaction
Error [IST0101] (VirtualService istioinaction/catalog-v1-v2) Referenced host+subset in destinationrule not found: "catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local+version-v1"
Error [IST0101] (VirtualService istioinaction/catalog-v1-v2) Referenced host+subset in destinationrule not found: "catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local+version-v2"
Error: Analyzers found issues when analyzing namespace: istioinaction.
See https://istio.io/v1.17/docs/reference/config/analysis for more information about causes and resolutions.
# 이전 명령어 종료 코드 확인
echo $? # (참고) 0 성공
79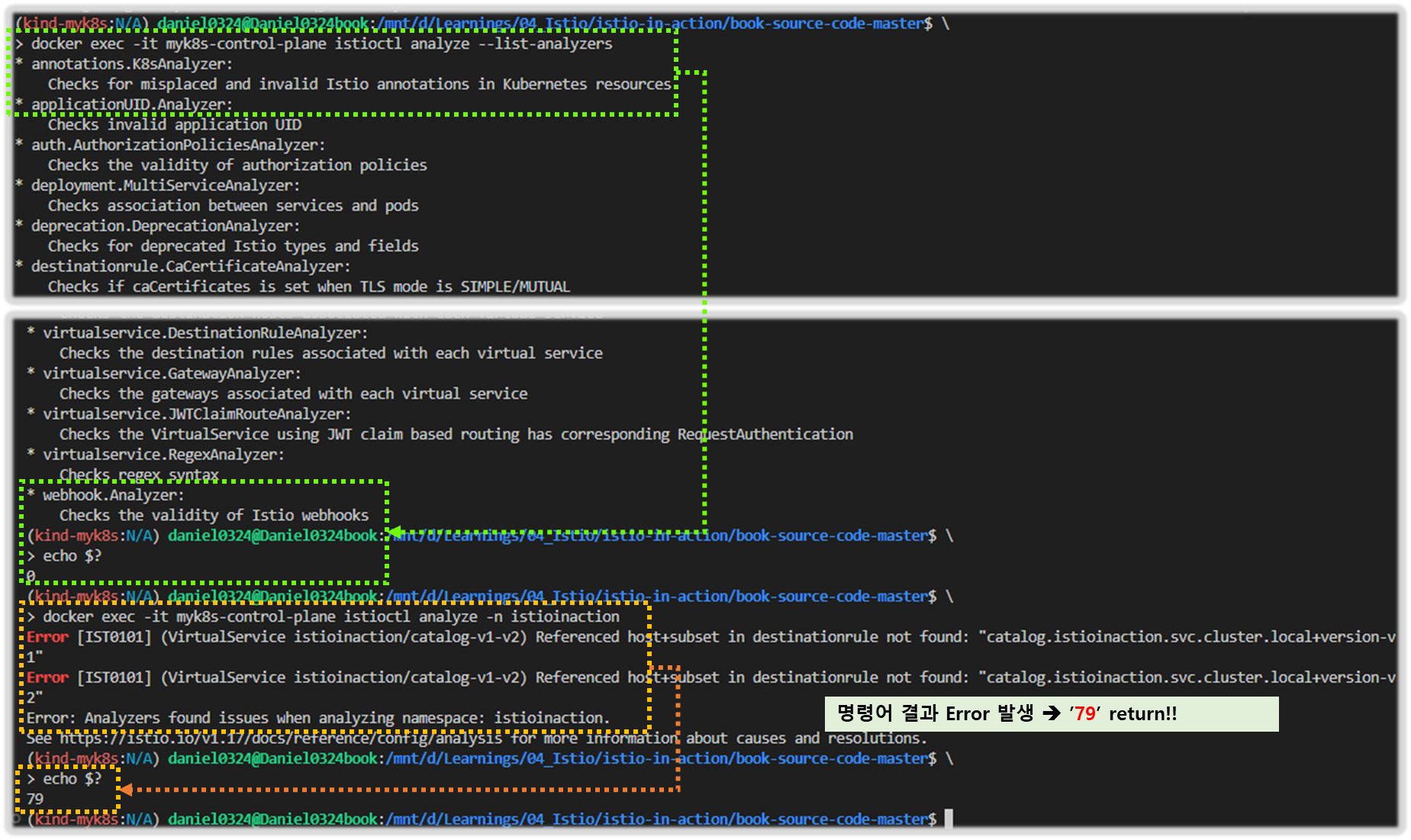
☞ 워크로드별로 설정 오류 찾기 DETECTING WORKLOAD-SPECIFIC MISCONFIGURATIONS
- describe는 워크로드별 설정을 기술하는데 사용한다.
- describe는 워크로드 하나에 직간접적으로 영향을 미치는 이스티오 설정을 분석해 요약 내용을 출력한다.
- 이 요약은 다음과 같은 워크로드 관련 질문에 답변을 제공한다.
- 이 워크로드는 서비스 메시의 일부인가?
- 어떤 VirtualService 와 DestinationRule 이 적용되는가?
- 상호 인증 트래픽을 요구하는가?
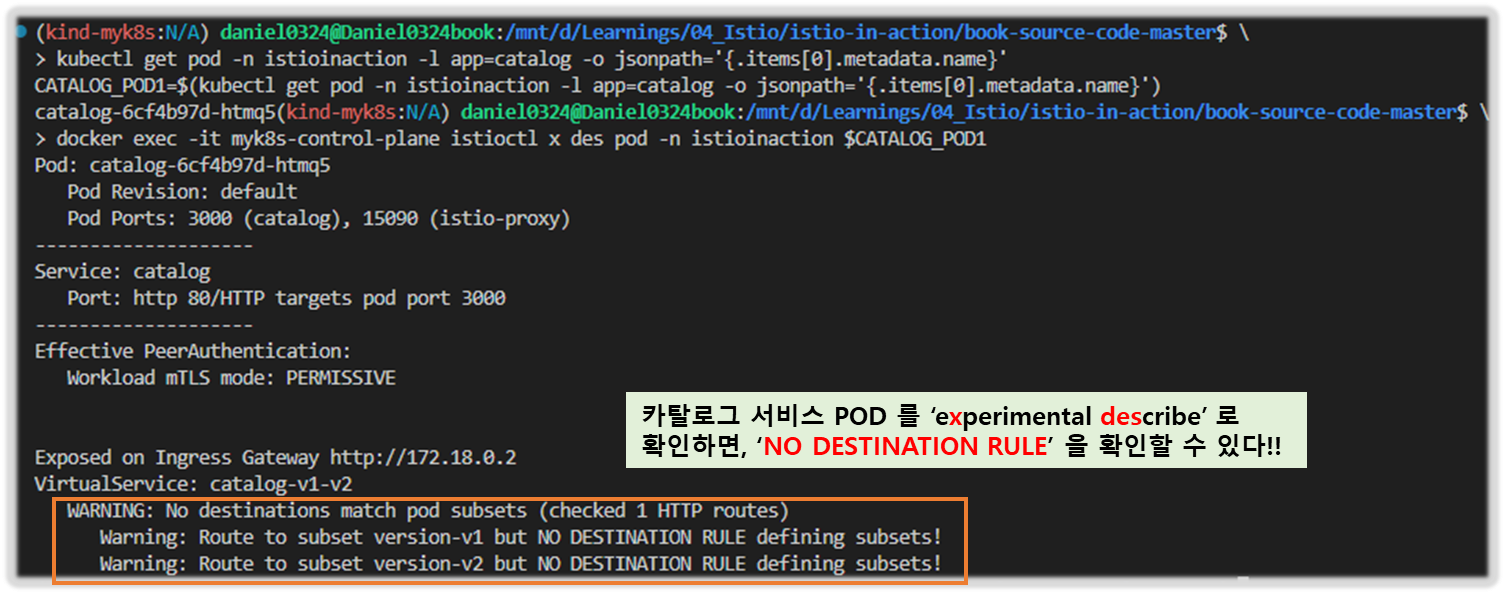
▶ 실행해보자 !! ( Virtual Service 부분에서 WARNING 내용을 자세히 보자!! - "No Destination Rule ~~ " )
#
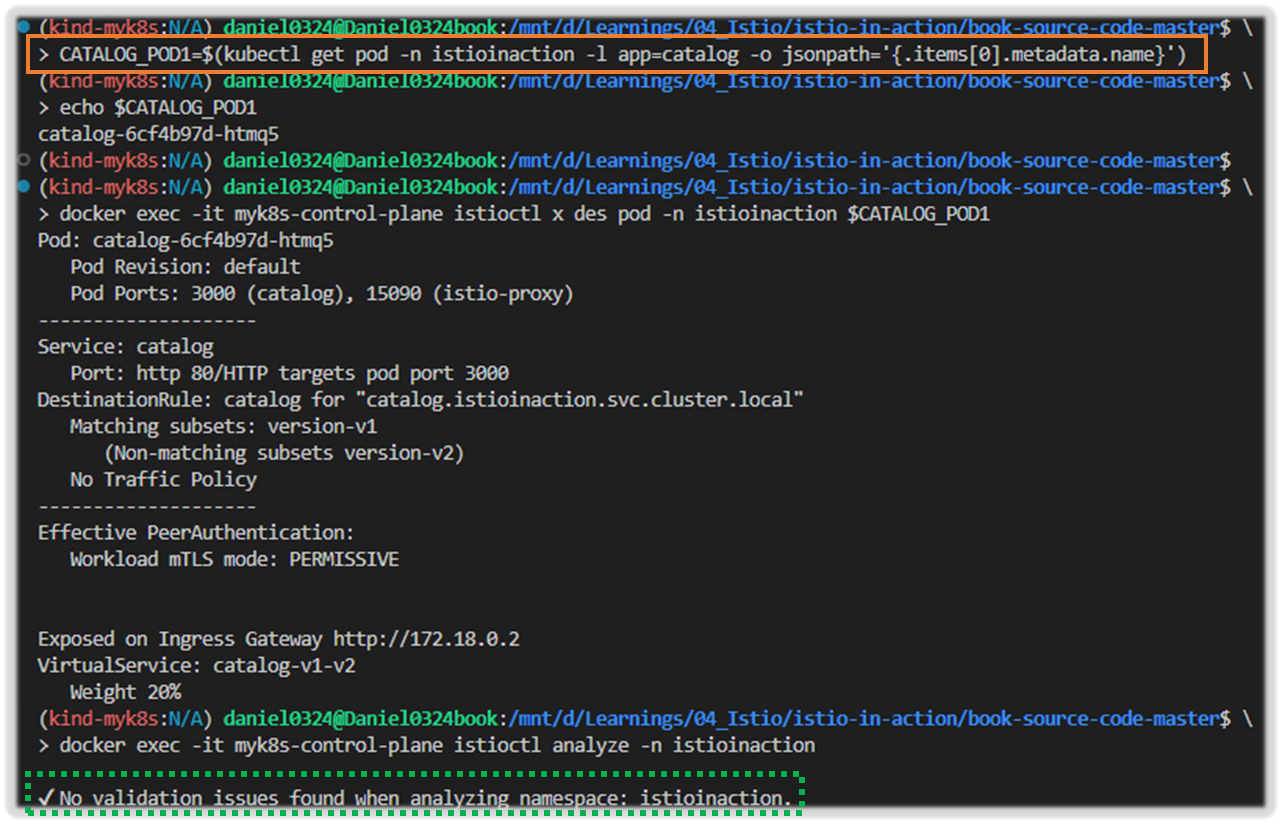
kubectl get pod -n istioinaction -l app=catalog -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}'
CATALOG_POD1=$(kubectl get pod -n istioinaction -l app=catalog -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
# 단축키 : experimental(x), describe(des)
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl experimental describe -h
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl x des pod -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD1
Pod: catalog-6cf4b97d-l44zk
Pod Revision: default
Pod Ports: 3000 (catalog), 15090 (istio-proxy)
--------------------
Service: catalog
Port: http 80/HTTP targets pod port 3000
--------------------
Effective PeerAuthentication:
Workload mTLS mode: PERMISSIVE
Exposed on Ingress Gateway http://172.18.0.2
VirtualService: catalog-v1-v2
WARNING: No destinations match pod subsets (checked 1 HTTP routes)
Warning: Route to subset version-v1 but NO DESTINATION RULE defining subsets!
Warning: Route to subset version-v2 but NO DESTINATION RULE defining subsets!
# 문제 해결 후 확인
cat ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml
kubectl apply -f ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml
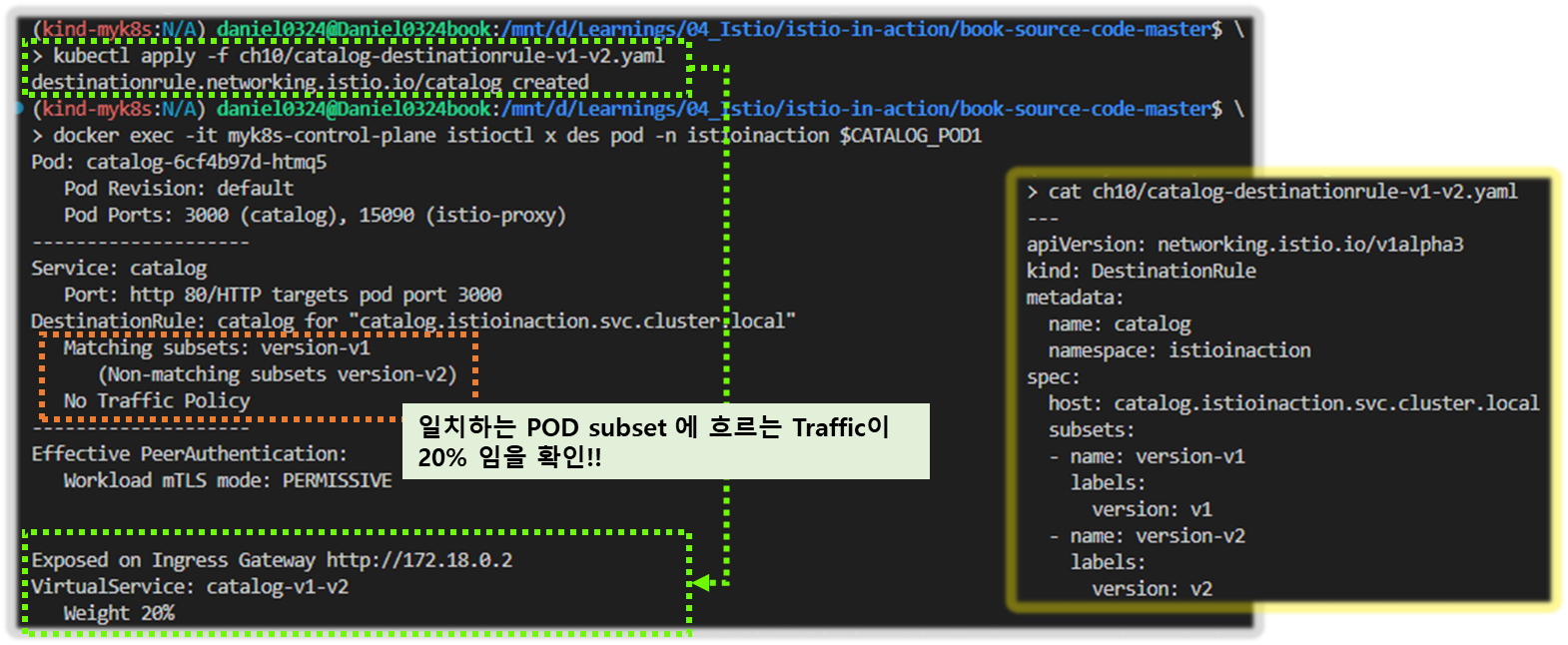
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl x des pod -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD1
Pod: catalog-6cf4b97d-l44zk
Pod Revision: default
Pod Ports: 3000 (catalog), 15090 (istio-proxy)
--------------------
Service: catalog
Port: http 80/HTTP targets pod port 3000
DestinationRule: catalog for "catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local"
Matching subsets: version-v1 # 일치하는 부분집합
(Non-matching subsets version-v2) # 일치하지 않은 부분집합
No Traffic Policy
--------------------
Effective PeerAuthentication:
Workload mTLS mode: PERMISSIVE
Exposed on Ingress Gateway http://172.18.0.2
VirtualService: catalog-v1-v2 # 이 파드로 트래픽을 라우팅하는 VirtualService
Weight 20%
# 다음 점검 방법을 위해 오류 상황으로 원복
kubectl delete -f ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml
- 하위 명령어 analyze 와 describe 모두 설정에서 흔한 오류를 식별하느 데 도움이 되며, 보통은 해결책을 제시하기에 충분한다.
- 이 명령어로 드러나지 않은 문제나 해결 지침을 충분히 제공하지 않은 문제는 더 깊이 파고들 필요가 있다. 그것은 다음 절에서 할 일이다.
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
▶ 도전과제1 istioctl analyze와 istioctl describe를 CI/CD 파이프라인에서 istio 설정 검증 활용 해보기
- 명령어 활용 예시
# 로컬 YAML 파일 검증
istioctl analyze --use-kube=false samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
# 라이브 클러스터와 YAML 파일 조합 검증
istioctl analyze samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml samples/bookinfo/networking/destination-rule-all.yaml
# 특정 경고 억제
istioctl analyze --namespace default --suppress "IST0102=Namespace default"
# 모든 네임스페이스 분석
istioctl analyze --all-namespaces
# 디렉토리 내 모든 YAML 파일 분석
istioctl analyze --recursive my-istio-config/
- GitHub Actions 예시 ( By GPT - 실습 확인 필요 )
name: Istio YAML 분석
on:
push:
paths:
- 'istio-configs/**.yaml'
pull_request:
jobs:
istio-analyze:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout repository
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install istioctl
run: |
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=1.22.0 sh -
export PATH="$PATH:./istio-1.22.0/bin"
echo "PATH=$PATH:./istio-1.22.0/bin" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name: Run istioctl analyze
run: |
# --use-kube=false를 지정하면 클러스터 없이도 로컬 파일만으로 분석 가능
istioctl analyze ./istio-configs --use-kube=false --output json > analyze-report.json || true
cat analyze-report.json
- name: Fail if issues found
run: |
if grep -q '"Level":"Error"' analyze-report.json; then
echo "Istio analyze found errors"
exit 1
finame: Istio YAML Validation
on:
pull_request:
branches:
- main
jobs:
validate-istio:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
# 리포지토리 체크아웃
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
# Istio 설치
- name: Install istioctl
run: |
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=1.25.2 sh -
mv istio-1.25.2/bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/
istioctl version
# YAML 파일 검증
- name: Run istioctl analyze
run: |
istioctl analyze --use-kube=false ./istio-config/*.yaml
continue-on-error: false
# 클러스터 접근 설정 (필요한 경우)
- name: Setup kubeconfig
run: |
echo "${{ secrets.KUBECONFIG }}" > kubeconfig
export KUBECONFIG=kubeconfig
# 라이브 클러스터 분석
- name: Run istioctl analyze with cluster
run: |
istioctl analyze ./istio-config/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
# 파드 구성 확인 (배포 후)
- name: Run istioctl describe
run: |
POD_NAME=$(kubectl get pods -l app=ratings -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
istioctl describe pod $POD_NAME
- istioctl describe 사용 : 디버깅용으로 로그 출력에 사용
...
- name: Describe Istio service
run: |
istioctl x describe svc reviews.default.svc.cluster.local || true
- GitLab CI 예시
# .gitlab-ci.yml
stages:
- lint
- build
- deploy
variables:
ISTIO_VERSION: "1.20.0" # 사용하는 Istio 버전에 맞게 조정
istioctl_analyze:
stage: lint
image:
name: gcr.io/google.com/cloudsdk/cloud-sdk:latest # kubectl, istioctl이 포함된 이미지 사용 (또는 커스텀 이미지)
entrypoint: [""] # Entrypoint를 재정의하여 쉘 스크립트 실행
before_script:
# istioctl 다운로드 및 설치 (만약 이미지에 포함되어 있지 않다면)
- apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl
- curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=$ISTIO_VERSION sh -
- export PATH=$PWD/istio-$ISTIO_VERSION/bin:$PATH
script:
- echo "Analyzing Istio YAML files..."
# 모든 Istio 관련 YAML 파일이 있는 디렉토리를 지정
# 여기서는 project/istio-config/ 아래에 모든 Istio 설정 파일이 있다고 가정
- istioctl analyze project/istio-config/
# 또는 특정 파일만 지정
# - istioctl analyze project/istio-config/gateway.yaml project/istio-config/virtualservice.yaml
- if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then
echo "Istio configuration analysis failed. Please check the reported errors."
exit 1
fi
- echo "Istio configuration analysis passed."
only:
- merge_requests # PR/MR 시에만 실행
- main # main 브랜치 커밋 시에도 실행
- Jenkins 파이프라인
pipeline {
agent any
environment {
ISTIO_VERSION = '1.22.0'
ISTIOCTL_PATH = "${env.WORKSPACE}/istio-${ISTIO_VERSION}/bin"
}
stages {
stage('Checkout') {
steps {
git 'https://your-repo-url.com/your-istio-config-repo.git'
}
}
stage('Install istioctl') {
steps {
sh '''
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=${ISTIO_VERSION} sh -
export PATH=$PATH:${ISTIOCTL_PATH}
'''
}
}
stage('Run istioctl analyze') {
steps {
sh '''
export PATH=$PATH:${ISTIOCTL_PATH}
istioctl analyze ./istio-configs --use-kube=false --output json > analyze-report.json || true
cat analyze-report.json
if grep -q '"Level":"Error"' analyze-report.json; then
echo "Istio analyze found errors"
exit 1
fi
'''
}
}
}
}
10.3 엔보이 설정에서 수동으로 잘못된 설정 발견하기
Discovering misconfigurations manually from the Envoy config 앞 선 방법이 부족 할 때는 엔보이 설정 전체를 수동으로 조사해야 한다.
10.3.1 엔보이 관리(admin) 인터페이스 Envoy administration interface
- 엔보이 관리 인터페이스는 프록시의 특정 부분(로그 수준 증가 등)을 수정하는 기능과 엔보이 설정을 노출한다.
- 이 인터페이스는 모든 서비스 프록시에서 포트 15000으로 접근 할 수 있다.
#
kubectl port-forward deploy/catalog -n istioinaction 15000:15000
open http://localhost:15000
# 현재 적재한 엔보이 설정 출력 : 데이터양이 많다!
curl -s localhost:15000/config_dump | wc -l
13952
- 출력은 너무 커서 기본적으로 사람이 읽을 수 없다!! - Youtube Link

- 이런 이유로 istioctl은 출력을 작은 뭉치로 필터링하는 도구를 제공해 가독성을 높이고 이해를 돕는다.
- 엔보이 관리 인터페이스 https://www.envoyproxy.io/docs/envoy/latest/operations/admin
10.3.2 istioctl 로 프록시 설정 쿼리하기 Querying proxy configurations using istioctl
- istioctl proxy-config 명령어를 사용하면 엔보이 xDS API를 기반으로 워크로드의 프록시 설정을 가져오고 필터링할 수 있다. 하위 명령어 참고.
- cluster : 클러스터 설정을 가져온다
- endpoint : 엔드포인트 설정을 가져온다
- listener : 리스너 설정을 가져온다
- route : 루트 설정을 가져온다
- secret : 시크릿 설정을 가져온다
1. 요청을 라우팅하기 위한 엔보이 API의 상호작용 THE INTERACTION OF ENVOY APIS TO ROUTE A REQUEST
- 그림 10.8은 요청 라우팅을 설정하는 엔보이 API를 보여준다. Figure 10.8 shows the Envoy APIs that configure the routing of a request.
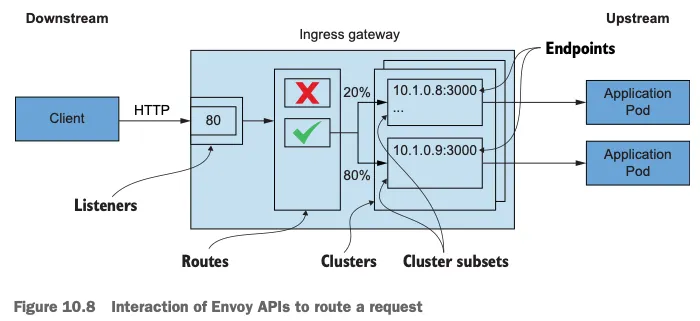
- 이 API는 프록시에 다음과 같은 영향을 미친다.
- 엔보이 리스너 listeners 는 네트워크 설정(다운스트림 트래픽을 프록시로 허용하는 IP 주소 및 포트 등)을 정의한다.
- 허용된 커넥션에 HTTP 필터 filter 체인이 만들어진다. 체인에서 가장 중요한 필터는 라우터 필터로, 고급 라우팅 작업을 수행한다.
- 엔보이 루트 routes 는 가상 호스트를 클러스터에 일치시키는 규칙 집합이다. 루트는 순서대로 처리된다.
- 일치하는 첫 번째 항목이 트래픽을 워크로드 클러스터로 라우팅하는 데 사용된다.
- 루트는 정적으로 설정할 수 도 있지만, 이스티오에서는 RDS를 사용해 동적으로 설정한다.
- 엔보이 클러스터 clusters 에서, 각 클러스터에는 유사한 워크로드에 대한 엔드포인트 그룹이 있다.
- 부분집합 Subsets 은 클러스터 내에서 워크로드를 더 분할하는 데 사용하며 덕분에 정밀한 트래픽 관리가 가능해진다.
- 엔보이 엔드포인트는 요청을 처리하는 워크로드의 IP 주소를 나타낸다.
- 다음 절에서는 인그레스 게이트웨이의 리스너, 루트, 클러스터, 엔드포인트 설정을 쿼리하고 수동으로 검증해본다.
- 이를 통해 트래픽을 catalog 워크로드로 라우팅하도록 올바르게 설정했는지 확인할 수 있다.
2. 엔보이 리스너 설정 쿼리하기 QUERYING THE ENVOY LISTENER CONFIGURATION
- 먼저 인그레스 게이트웨이 NodePort 30000 포트로 도착하는 트래픽이 클러스터로 허용되는지 부터 확인하자.
- 트래픽을 허용하는 것은 엔보이 리스너의 역할로, 이스티오에서는 Gateway 리소스를 설정한다.
- 게이트웨이의 리스너 설정을 쿼리하고 80 포트에서 트래픽이 허용되는지 확인하자
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config listener deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
ADDRESS PORT MATCH DESTINATION
0.0.0.0 8080 ALL Route: http.8080 # 8080 포트에 대한 요청은 루트 http.8080에 따라 라우팅하도록 설정된다
0.0.0.0 15021 ALL Inline Route: /healthz/ready*
0.0.0.0 15090 ALL Inline Route: /stats/prometheus*
## 리스터는 8080 포트에 설정돼 있다.
## 그 리스너에서 트래픽은 http.8080 이라는 루트에 따라 라우팅된다.
- 루트 http.8080이 80 포트가 아니라 8080포트에서 리스닝하도록 설정됐다는 사실이 놀라울 수 있다.
- 포트 8080이 올라는 포트인지 확인하자.
#
kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -o yaml | grep "ports:" -A10
ports:
- name: status-port
nodePort: 30840
port: 15021
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 15021
- name: http2
nodePort: 30000
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080- 트래픽이 nodePort 30000 포트에 인입 시, istio-ingressgateway 서비스는 인그레스 게이트웨이(파드)에 tcp 8080 포트로 전달(도달)하게 됨.
- 만약 k8s 클러스터 내부에서 clusterIP혹은 서비스명으로 tcp 80 요청 시 → 인그레스 게이트웨이(파드)에 tcp 8080 포트로 전달(도달)하게 됨.
- 그 트래픽을 인그레스 게이트웨이로 허용하는 리스너가 존재함을 확인했다.
- 또한 이 리스너의 라우팅은 루트 http.8080이 수행한다는 사실도 확인했다.
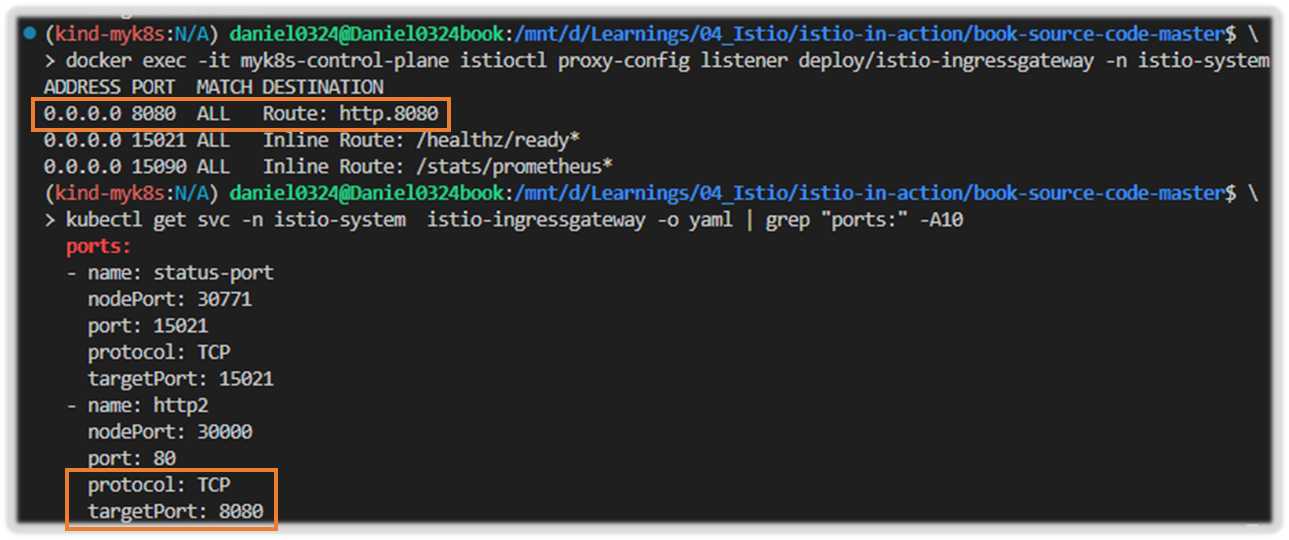
3. 엔보이 루트 설정 쿼리하기 QUERYING THE ENVOY ROUTE CONFIGURATION
- 엔보이 루트 설정은 트래픽을 라우팅할 클러스터를 결정하는 규칙 집합을 정의한다. The Envoy route configuration defines the set of rules that determine the cluster where traffic is routed.
- 이스티오는 엔보이 루트를 VirtualService 리소스로 설정한다. 한편, 클러스터는 디스커비리로 자동 설정되거나 DestinationRule 리소스로 정의된다.
- http.8080 루트의 트래픽을 어느 클러스터로 라우팅할지 알아내기 위해 설정을 쿼리해보자.
- 이 요약은 호스트 catalog.istioinaction.io 의 트래픽 중 URL이 경로 접두사 /*과 일치하는 것이 istioinaction 네임스페이스의 catalog 서비스에 있는 catalog VirtualService 로 라우팅됨을 보여준다.
# http.8080 루트의 트래픽을 어느 클러스터로 라우팅할지 알아내기 위해 설정을 쿼리
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config routes deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system --name http.8080
NAME DOMAINS MATCH VIRTUAL SERVICE
http.8080 catalog.istioinaction.io /* catalog-v1-v2.istioinaction
## 호스트 catalog.istioinaction.io 의 트래픽 중 URL이 경로 접두사 /*과 일치하는 것이 istioinaction 네임스페이스의 catalog 서비스에 있는 catalog VirtualService 로 라우팅됨을 보여준다.
# 세부 정보 확인
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config routes deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system --name http.8080 -o json
...
"routes": [
{
"match": {
"prefix": "/" # 일치해야 하는 라우팅 규칙
},
"route": {
"weightedClusters": {
"clusters": [ # 규칙이 일치할 때 트래픽을 라우팅하는 클러스터
{
"name": "outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",
"weight": 20
},
{
"name": "outbound|80|version-v2|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",
"weight": 80
}
],
"totalWeight": 100
},
...- 클러스터 출력 : {DIRECTION} | {PORT} | {SUBSET} | {FQDN} ⇒ 루트가 일치할 때 트래픽을 수신하는 클러스터가 둘임을 보여줌.
- outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
- outbound|80|version-v2|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
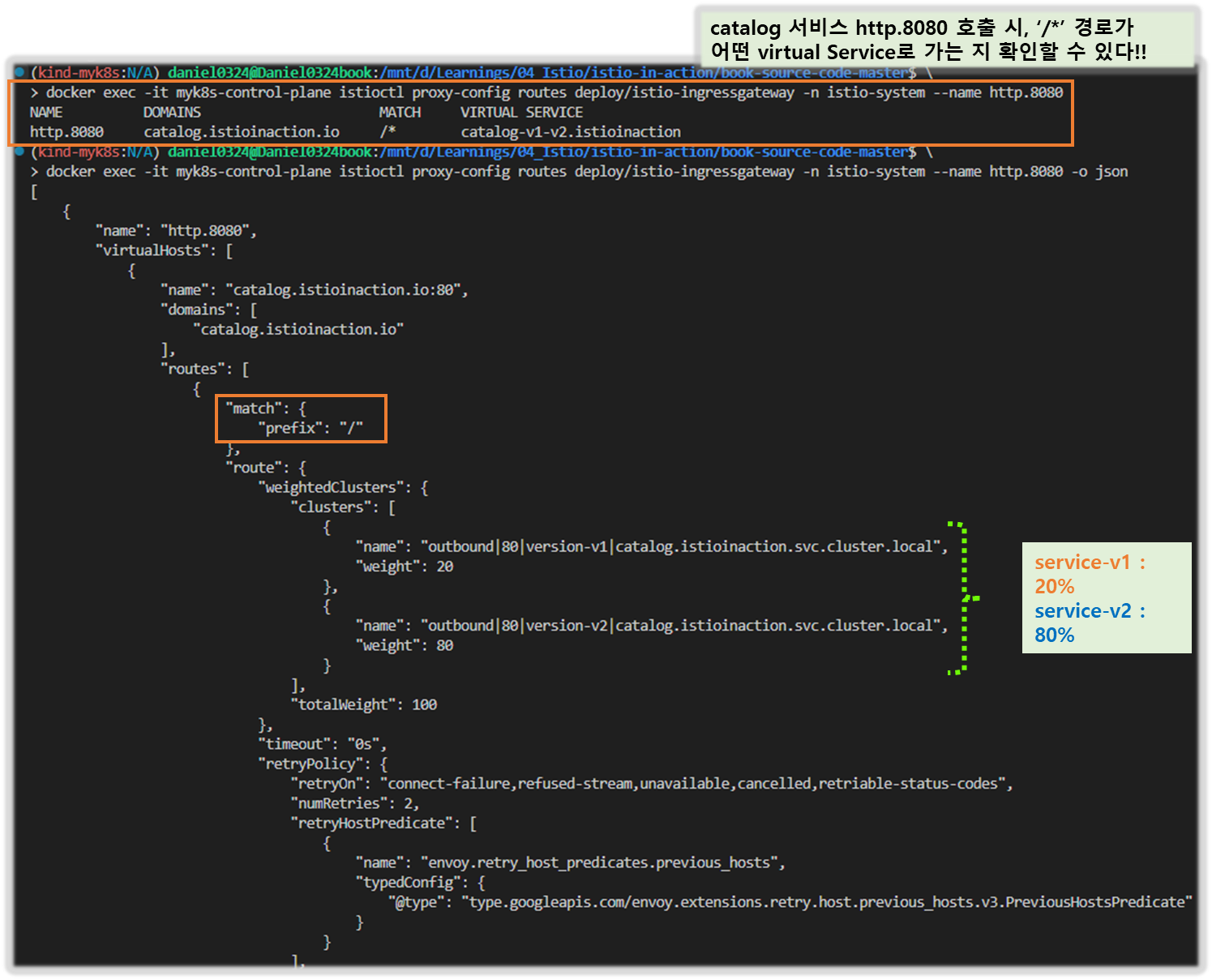
4. 엔보이 클러스터 설정 쿼리하기 QUERYING THE ENVOY CLUSTER CONFIGURATION
- 엔보이 클러스터 설정은 요청을 라우팅할 수 있는 백엔드 서비스를 정의한다. The Envoy cluster configuration defines the backend services to which requests can be routed.
- 클러스터는 부하를 여러 인스턴스나 엔드포인트에 분산한다.
- 이 엔드포인트(보통 IP 주소)는 최종 사용자 트래픽을 처리하는 개별 워크로드 인스턴스를 나타낸다.
- istioctl을 사용하면 인그레스 게이트웨이가 알고 있는 클러스터를 쿼리할 수 있지만, 클러스터가 많다.
- 라우팅할 수 있는 모든 백엔드 서비스마다 하나씩 설정되기 때문이다.
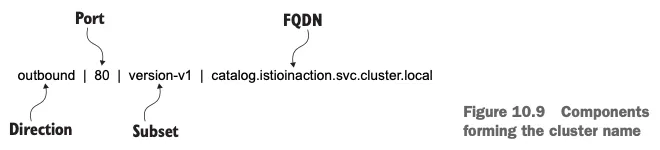
- istioctl proxy-config clusters 의 플래그 direction, fqdn, port, subent 을 사용하면 특정 클러스터만 출력할 수 있다.
- 플래그에서 사용할 정보는 그림 10.9와 같이 앞서 가져온 클러스터 이름에 포함돼 있다.
- 클러스터 중 하나를 쿼리해보자.
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config clusters deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system \
--fqdn catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local --port 80
SERVICE FQDN PORT SUBSET DIRECTION TYPE DESTINATION RULE
catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 80 - outbound EDS
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config clusters deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system \
--fqdn catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local --port 80 --subset version-v1
▷ 부분 집합 subset version-v1 이나 version-v2 용 클러스터는 없었다! ⇒ 이 부분 집합에 대한 클러스터가 없으면 요청은 실패한다.
- 정상 설정 전에 istioctl analyze 명령어를 사용해서, 설정할 yaml 파일이 식별한 서비스 메시 오류를 고칠 수 있는지 확인해보자. ( 경로확인 : /istiobook/book-source-code-master/ch10 )
# 해당 파일이 없을 경우 'copy & paste'로 작성 후 진행 하자
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane cat /istiobook/ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: catalog
namespace: istioinaction
spec:
host: catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- name: version-v1
labels:
version: v1
- name: version-v2
labels:
version: v2
# istioctl analyze 명령어를 사용해서, 설정할 yaml 파일이 식별한 서비스 메시 오류를 고칠 수 있는지 확인
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl analyze /istiobook/ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml -n istioinaction
✔ No validation issues found when analyzing /istiobook/ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml.
- 리소스 적용의 영향을 시뮬레이션해보니 클러스터에 검증 오류가 없어진다.
- 즉, 이 DestinationRule을 적용하면 클러스터 설정의 문제가 고쳐진다는 것이다.

▶ 이제 문제를 해결해보자!!
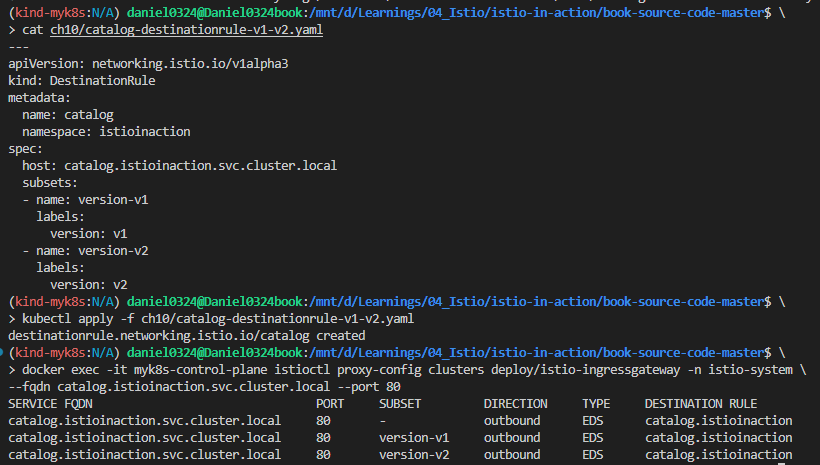
# 문제 해결
cat ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml
kubectl apply -f ch10/catalog-destinationrule-v1-v2.yaml
# 확인
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config clusters deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system \
--fqdn catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local --port 80
SERVICE FQDN PORT SUBSET DIRECTION TYPE DESTINATION RULE
catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 80 - outbound EDS catalog.istioinaction
catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 80 version-v1 outbound EDS catalog.istioinaction
catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 80 version-v2 outbound EDS catalog.istioinaction
CATALOG_POD1=$(kubectl get pod -n istioinaction -l app=catalog -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl x des pod -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD1
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl analyze -n istioinaction
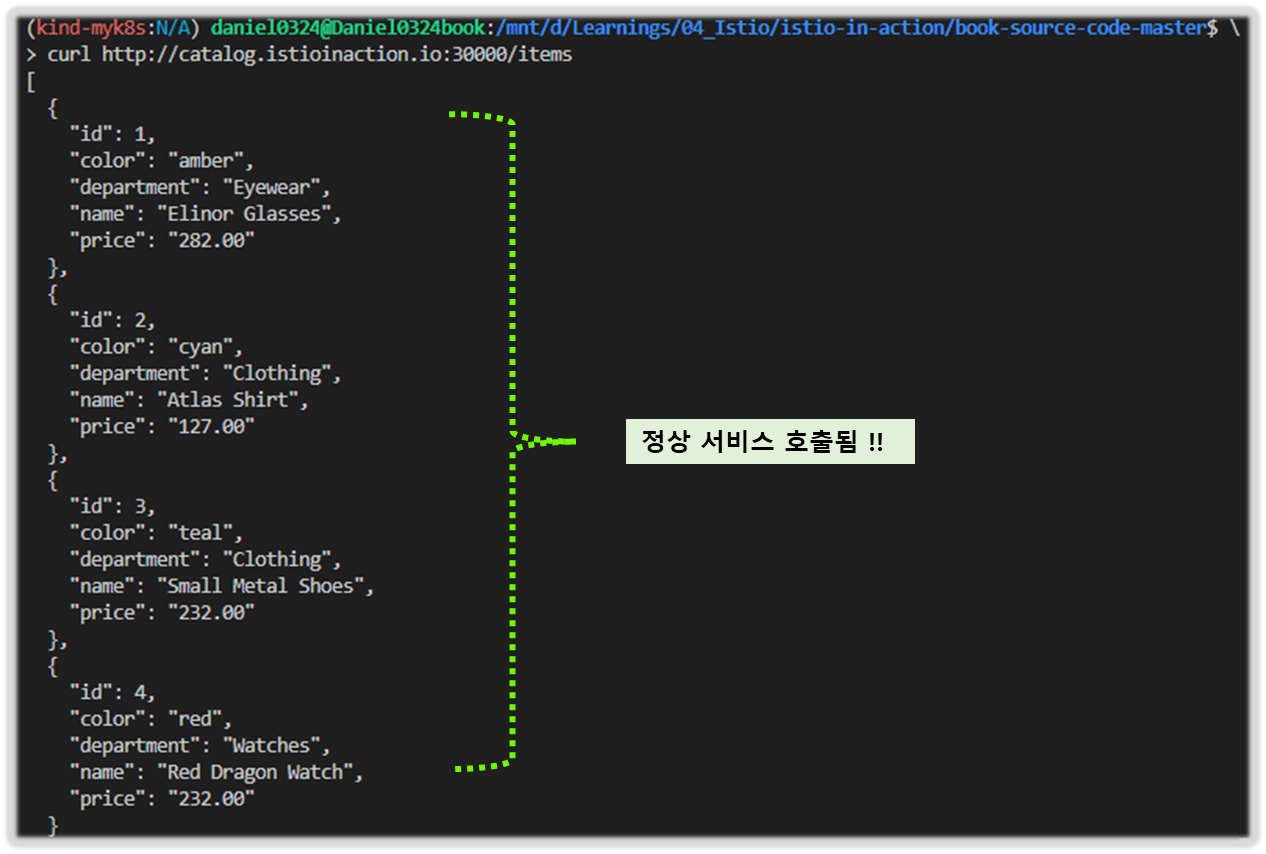
# 호출 확인
curl http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items
curl http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
1) destination Rule 적용
2) 서비스 호출 결과 확인
5. 클러스터는 어떻게 설정되는가? HOW CLUSTERS ARE CONFIGURED
- 엔보이 프록시에는 클러스터 엔드포인트를 발견하기 위한 여러 가지 방법이 있다.
- 사용 중인 방법은 istioctl에서 version-v1 클러스터를 JSON 형식으로 출력해보면 알 수 있다.
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config clusters deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system \
--fqdn catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local --port 80 --subset version-v1 -o json
...
"name": "outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",
"type": "EDS",
"edsClusterConfig": {
"edsConfig": {
"ads": {},
"initialFetchTimeout": "0s",
"resourceApiVersion": "V3"
},
"serviceName": "outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local"
},
...
- 이 출력 내용은 edsClusterConfig 가 엔드포인트를 쿼리하는 데 ADS Aggregated Discovery Service 를 사용하도록 설정됐음을 보여준다.
- 서비스 이름 outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 은 ADS를 쿼리할 때 엔드포인트용 필터로 사용한다.
6. 엔보이 클러스터 엔드포인트 쿼리하기 QUERYING ENVOY CLUSTER ENDPOINTS
- 이제 엔보이 프록시가 서비스 이름으로 ADS를 쿼리하도록 설정된 것을 알았으니, 인그레스 게이트웨이에서 클러스터의 엔드포인트를 istioctl proxy-config endpoints 명령어로 수동으로 쿼리하는데 이 정보를 사용할 수 있다.
# 엔드포인트 정보 확인 : IP 정보
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoints deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system \
--cluster "outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local"
ENDPOINT STATUS OUTLIER CHECK CLUSTER
10.10.0.12:3000 HEALTHY OK outbound|80|version-v1|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
# 해당 IP 쿼리로 실제 워크로드가 있는지 확인
kubectl get pod -n istioinaction --field-selector status.podIP=10.10.0.12 -owide --show-labels
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
catalog-6cf4b97d-l44zk 2/2 Running 0 5h58m 10.10.0.12 myk8s-control-plane <none> <none>- 실제로 있다! 트래픽을 워크로드로 라우팅하도록 서비스 프록시를 설정하는 엔보이 API 리소스 체인 전체를 완성했다.
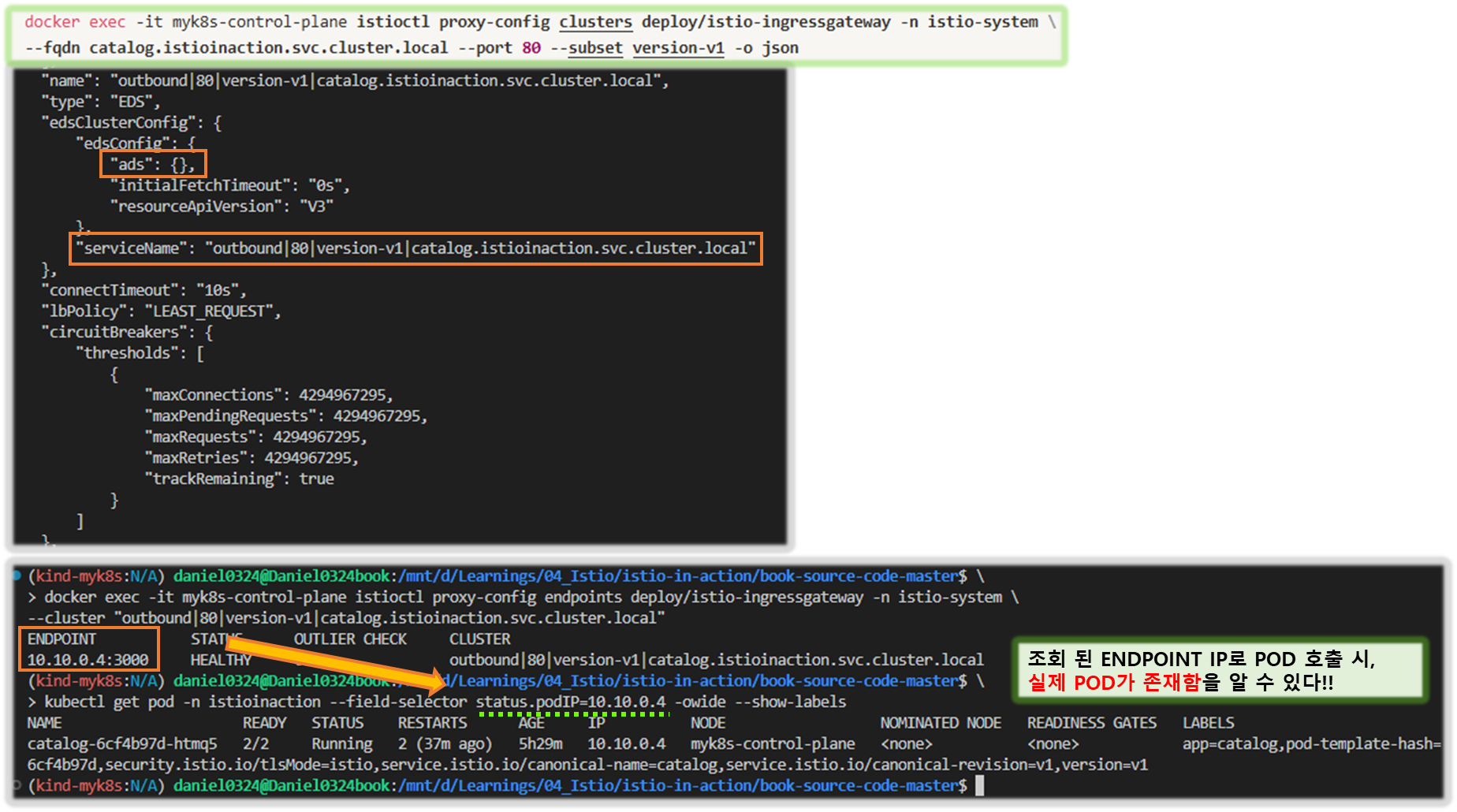
- 지금까지 잘못 설정한 워크로드를 발견하는 것에 대해 이야기했다.
- 다음 절에서는 애플리케이션 문제를 디버깅하는 데 서비스 프록시가 어떻게 도움이 되는지 알아본다.
10.3.3 애플리케이션 문제 트러블슈팅하기 Troubleshooting application issues
- 마이크로서비스 기반 애플리케이션에서 서비스 프록시가 생성하는 로그와 메트릭은 성능 병목을 일으키는 서비스 디스커버리, 빈번하게 실패하는 엔드포인트 식별, 성능 저하 감지 등과 같은 많은 문제를 트러블슈팅하는 데 도움이 된다. 6장에서는 이런 애플리케이션 복원력 문제를 해결하는 방법을 살펴봤다.
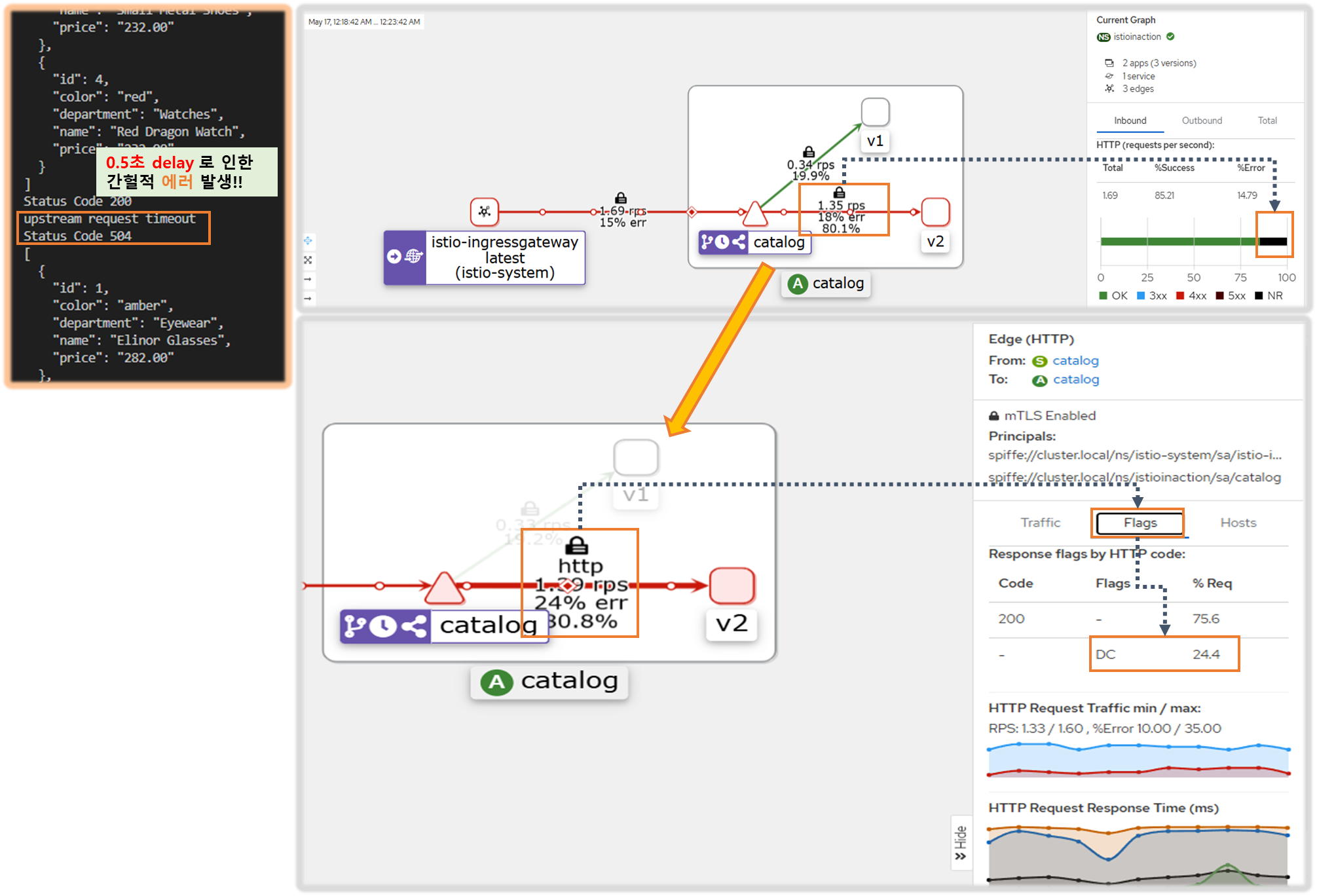
- 이번 절에서는 엔보이 액세스 로그와 메트릭을 사용해 이 문제들 중 일부를 트러블슈팅해본다. 그러나 먼저, 트러블슈팅할 문제가 생기도록 서비스를 업데이트하자.
▶ 간헐적으로 제한 시간을 초과하는 느린 워크로드 준비하기*
SETTING UP AN INTERMITTENTLY SLOW WORKLOAD THAT TIMES OUT
Step1. 설정 전 정상 통신 환경 상태 확인
# 신규 터미널
for in in {1..9999}; do curl http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items -w "\nStatus Code %{http_code}\n"; sleep 1; done
- kiali : catalog - 100% 성공
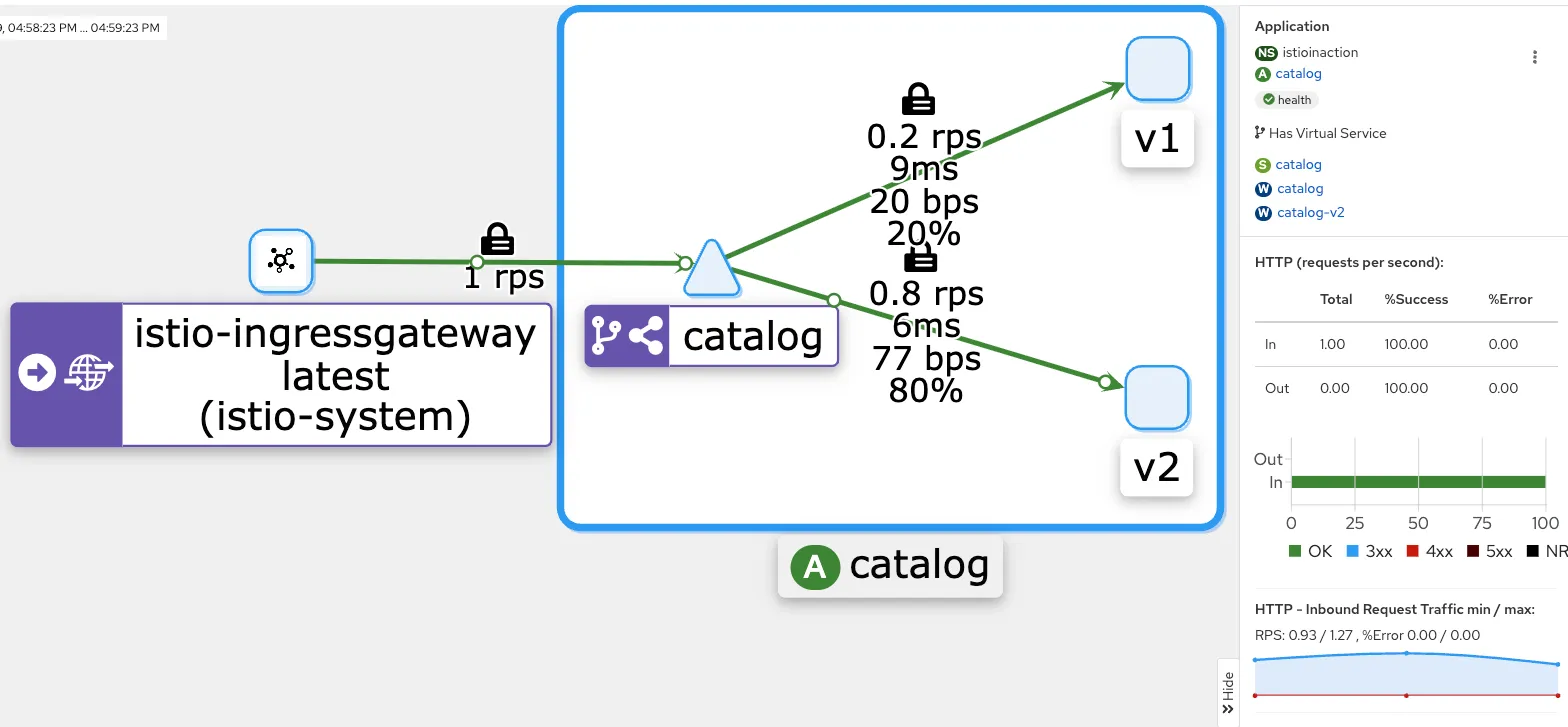
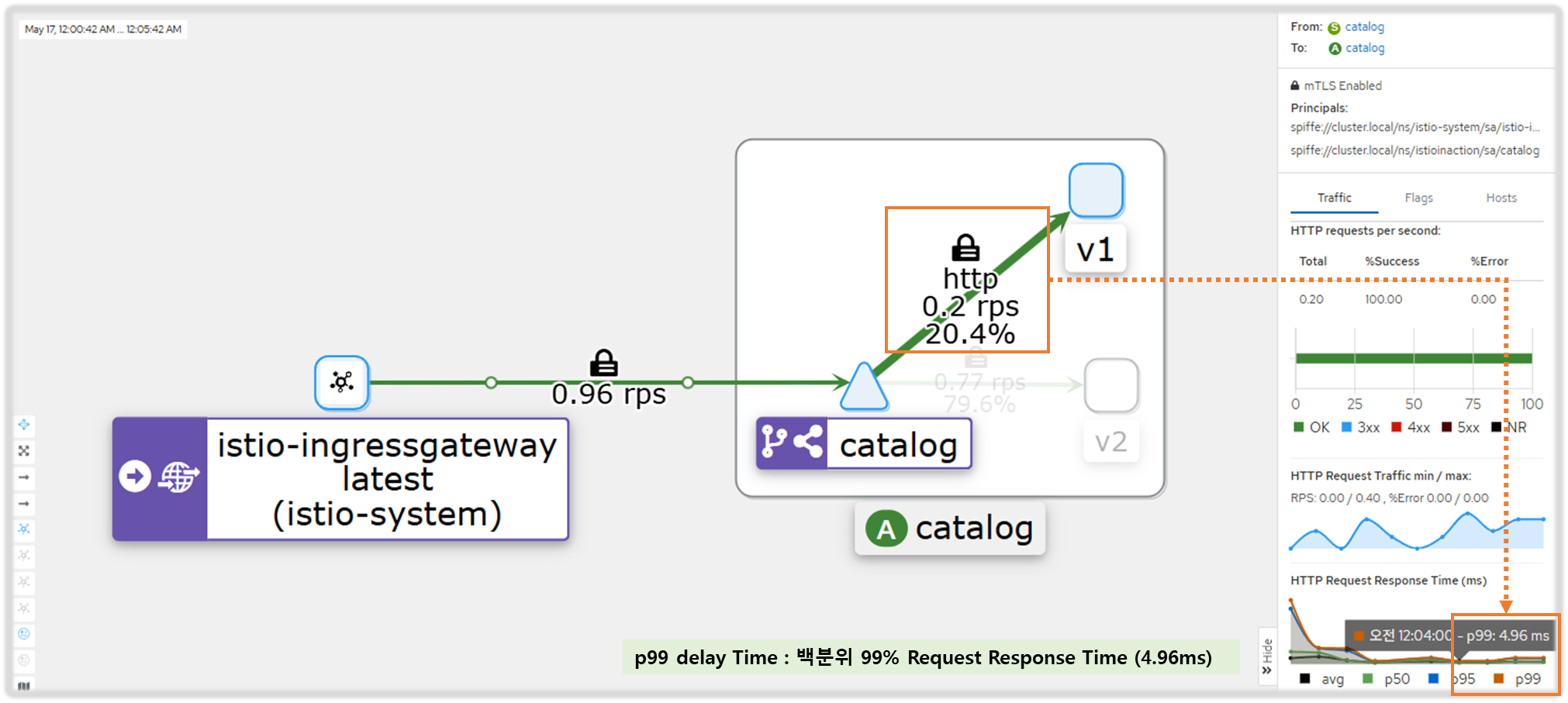
- kiali : catalog 에 v1 링크 클릭 후 오른쪽 탭 메뉴 하단에 HTTP Request Response Time(ms)에 p99 확인 → 4.96ms
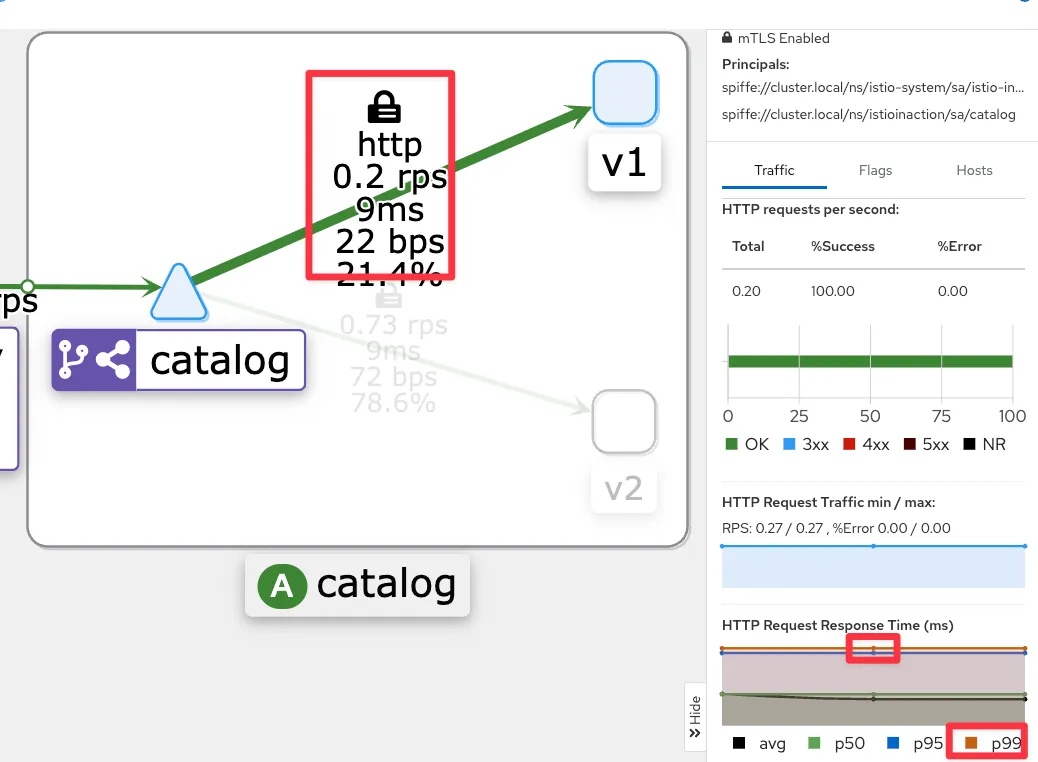
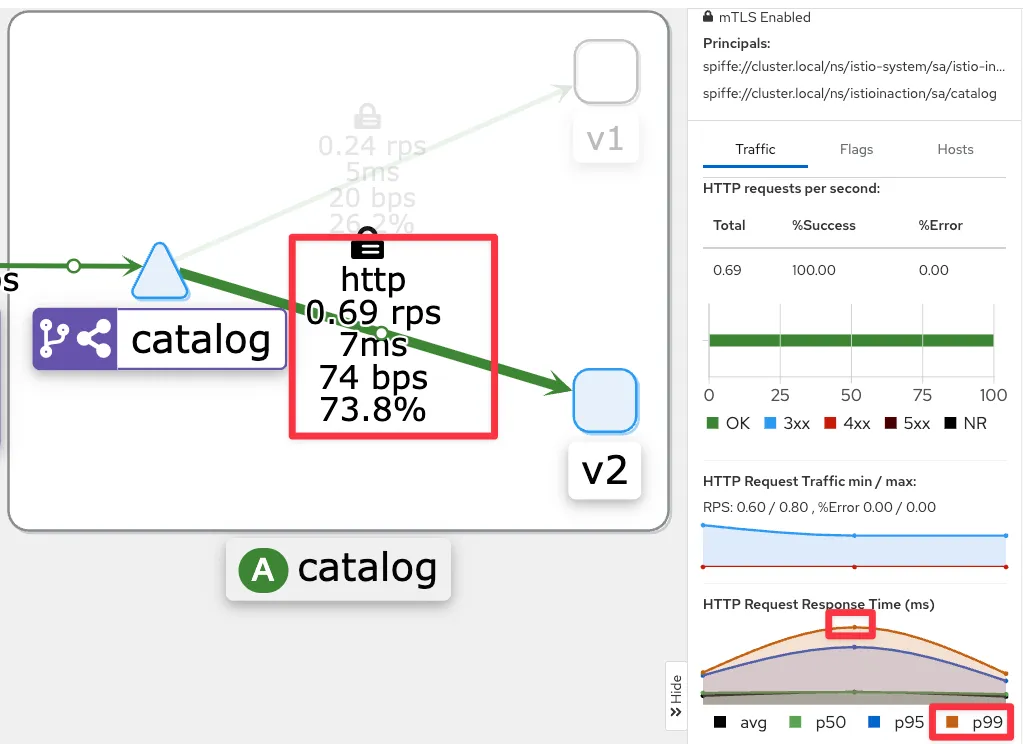
- kiali : catalog 에 v2 링크 클릭 후 오른쪽 탭 메뉴 하단에 HTTP Request Response Time(ms)에 p99 확인 → 4.8ms
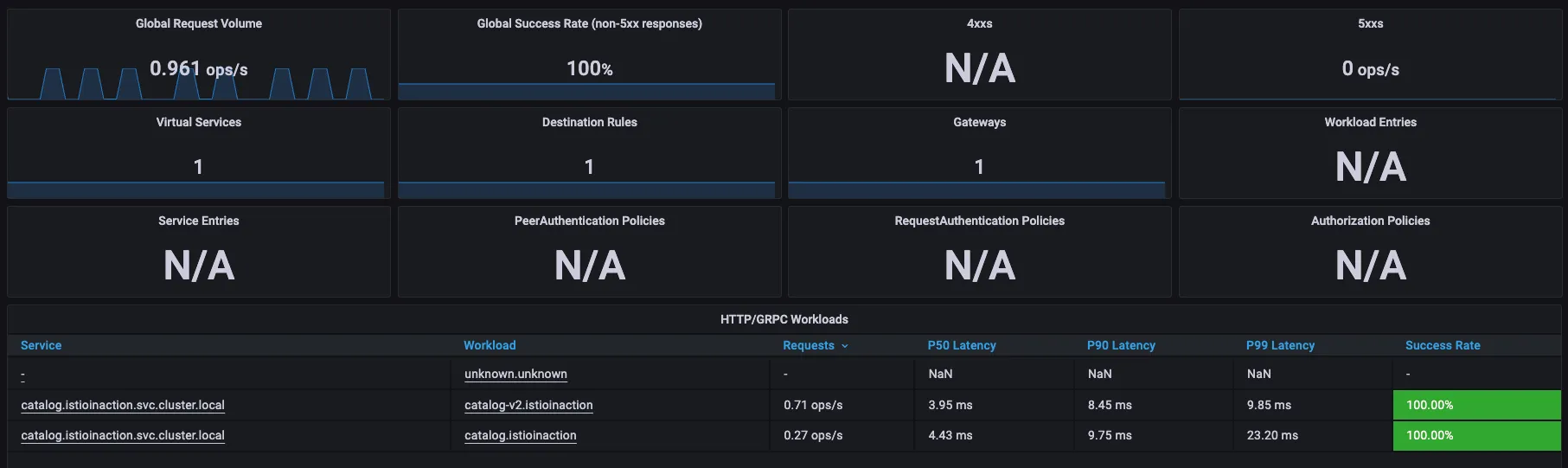
- Grafana - Istio Mesh 대시보드
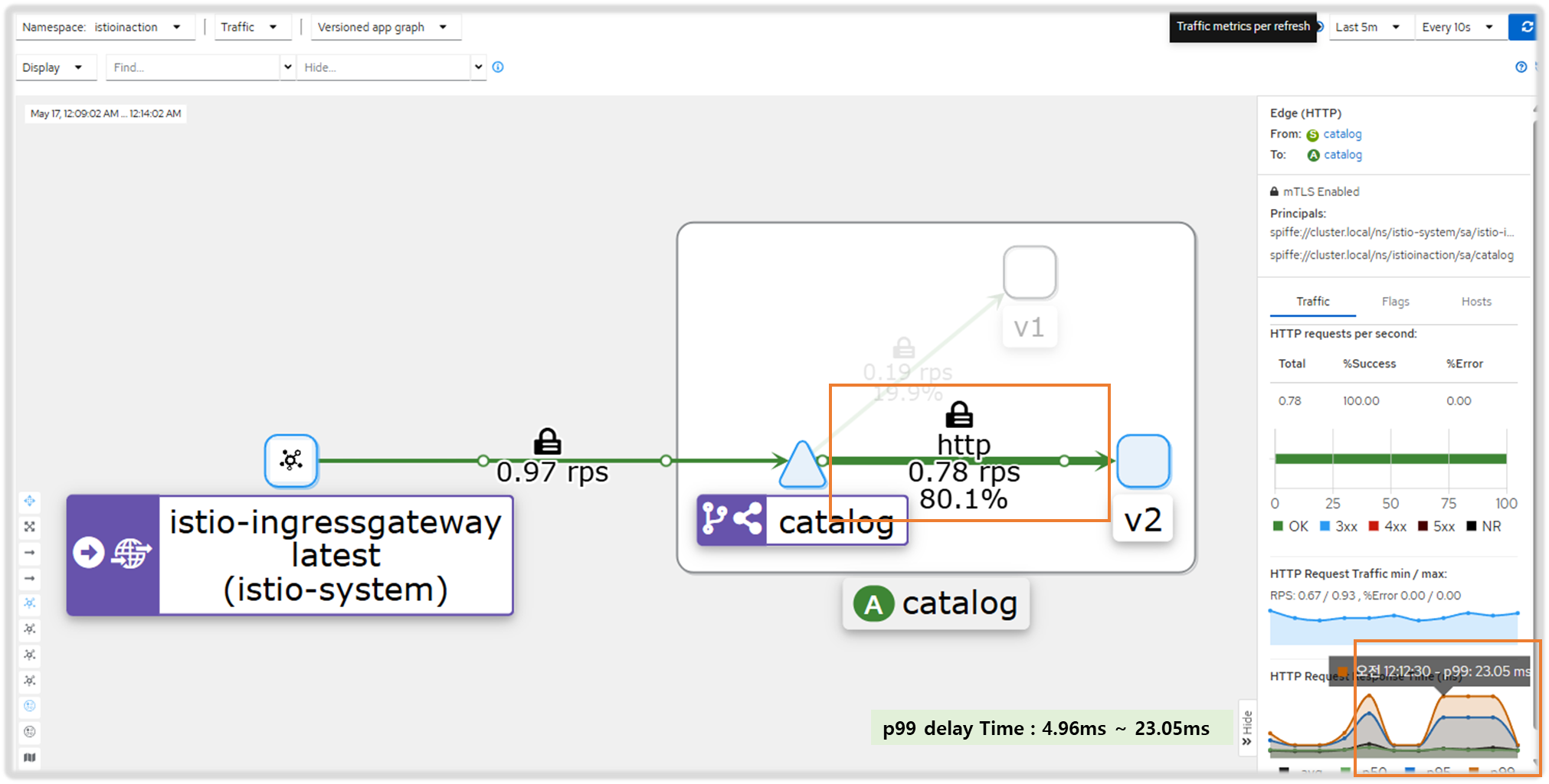
Step2. catalog 워크로드가 간헐적으로 응답을 느리게 반환하도록 설정
# catalog v2 파드 중 첫 번째 파드 이름 변수 지정
CATALOG_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l version=v2 -n istioinaction -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name} | cut -d ' ' -f1)
echo $CATALOG_POD
catalog-v2-56c97f6db-d74kv
# 해당 파드에 latency (지연) 발생하도록 설정
kubectl -n istioinaction exec -c catalog $CATALOG_POD \
-- curl -s -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"active": true, "type": "latency", "volatile": true}' \
localhost:3000/blowup ;
blowups=[object Object]
# 신규 터미널
for in in {1..9999}; do curl http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items -w "\nStatus Code %{http_code}\n"; sleep 1; done
- Grafana - Istio Mesh 대시보드 : v2 에 P90, P99 레이턴스 확인 , v1 과 비교해보자.

- kiali : catalog v2
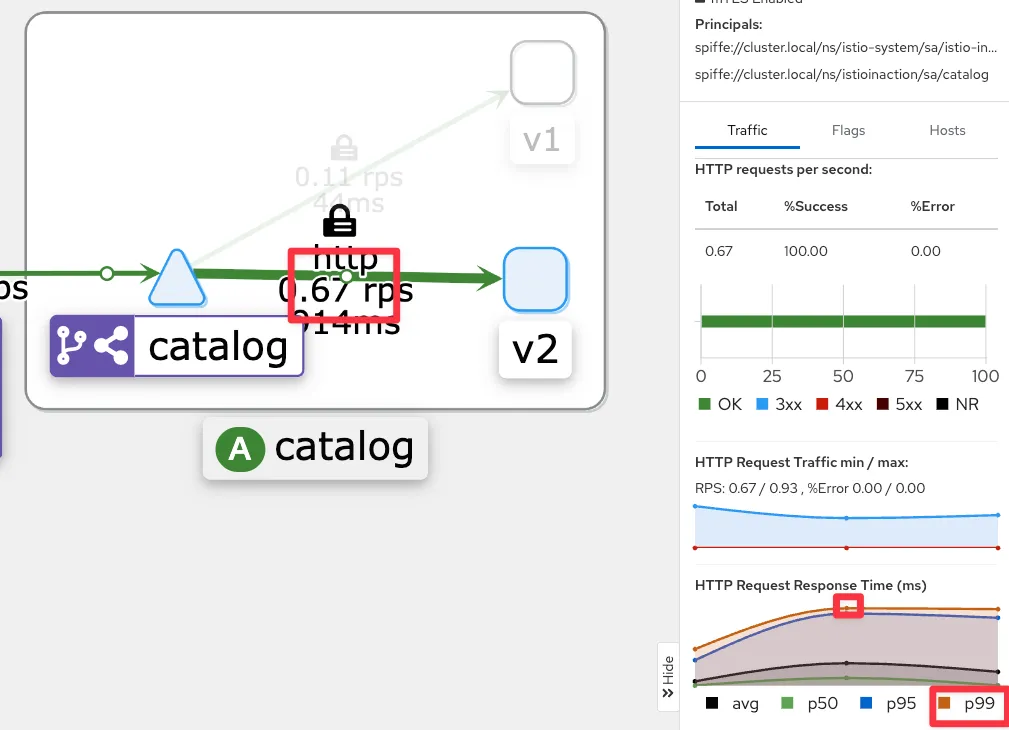
- Istio 에 요청 처리 제한 시간 0.5초가 되도록 VirtualService 설정
#
kubectl get vs -n istioinaction
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
catalog-v1-v2 ["catalog-gateway"] ["catalog.istioinaction.io"] 6h44m
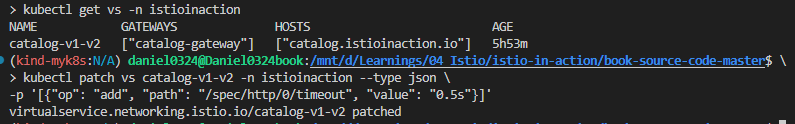
# 타임아웃(0.5s) 적용
kubectl patch vs catalog-v1-v2 -n istioinaction --type json \
-p '[{"op": "add", "path": "/spec/http/0/timeout", "value": "0.5s"}]'
# 적용확인
kubectl get vs catalog-v1-v2 -n istioinaction -o jsonpath='{.spec.http[?(@.timeout=="0.5s")]}' | jq
...
"timeout": "0.5s"
}
# 신규 터미널
for in in {1..9999}; do curl http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items -w "\nStatus Code %{http_code}\n"; sleep 1; done
upstream request timeout
Status Code 504
upstream request timeout
Status Code 504
..
#
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f
[2025-05-09T08:45:41.636Z] "GET /items HTTP/1.1" 504 UT response_timeout - "-" 0 24 501 - "172.18.0.1" "curl/8.7.1" "cb846eff-07ac-902e-9890-7af478c84166" "catalog.istioinaction.io:30000" "10.10.0.13:3000" outbound|80|version-v2|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 10.10.0.7:58078 10.10.0.7:8080 172.18.0.1:61108 - -
[2025-05-09T08:45:43.175Z] "GET /items HTTP/1.1" 200 - via_upstream - "-" 0 502 375 374 "172.18.0.1" "curl/8.7.1" "3f2de0c1-5af2-9a33-a6ac-bca08c1ee271" "catalog.istioinaction.io:30000" "10.10.0.13:3000" outbound|80|version-v2|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local 10.10.0.7:58084 10.10.0.7:8080 172.18.0.1:61118 - -
...
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f | grep 504
...
#
kubectl logs -n istioinaction -l version=v2 -c istio-proxy -f
[2025-05-09T08:42:38.152Z] "GET /items HTTP/1.1" 0 DC downstream_remote_disconnect - "-" 0 0 500 - "172.18.0.1" "curl/8.7.1" "69fef43c-2fea-9e51-b33d-a0375b382d86" "catalog.istioinaction.io:30000" "10.10.0.13:3000" inbound|3000|| 127.0.0.6:36535 10.10.0.13:3000 172.18.0.1:0 outbound_.80_.version-v2_.catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local default
...
☞ 0.5초 delay Patch 적용
- kiali : catalog v2
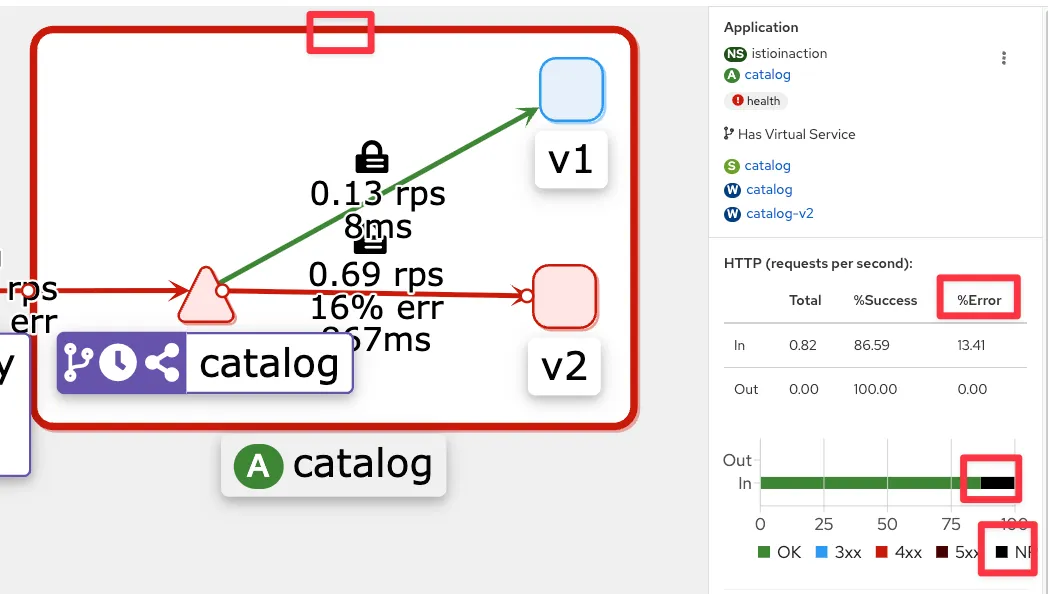
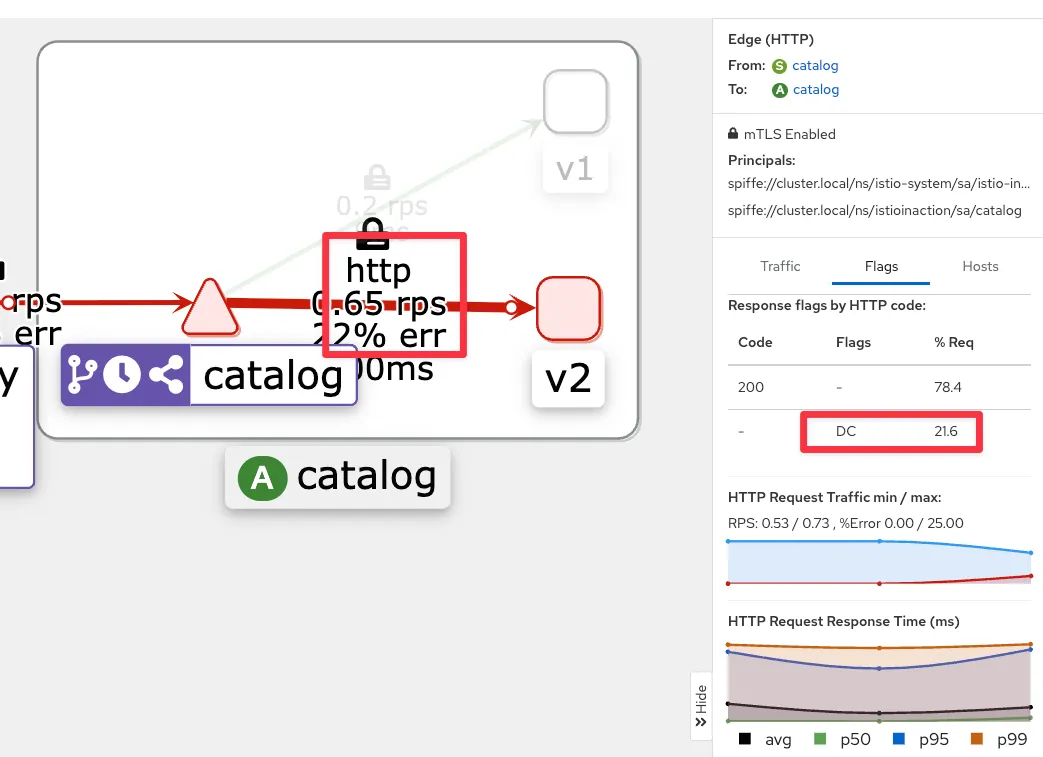
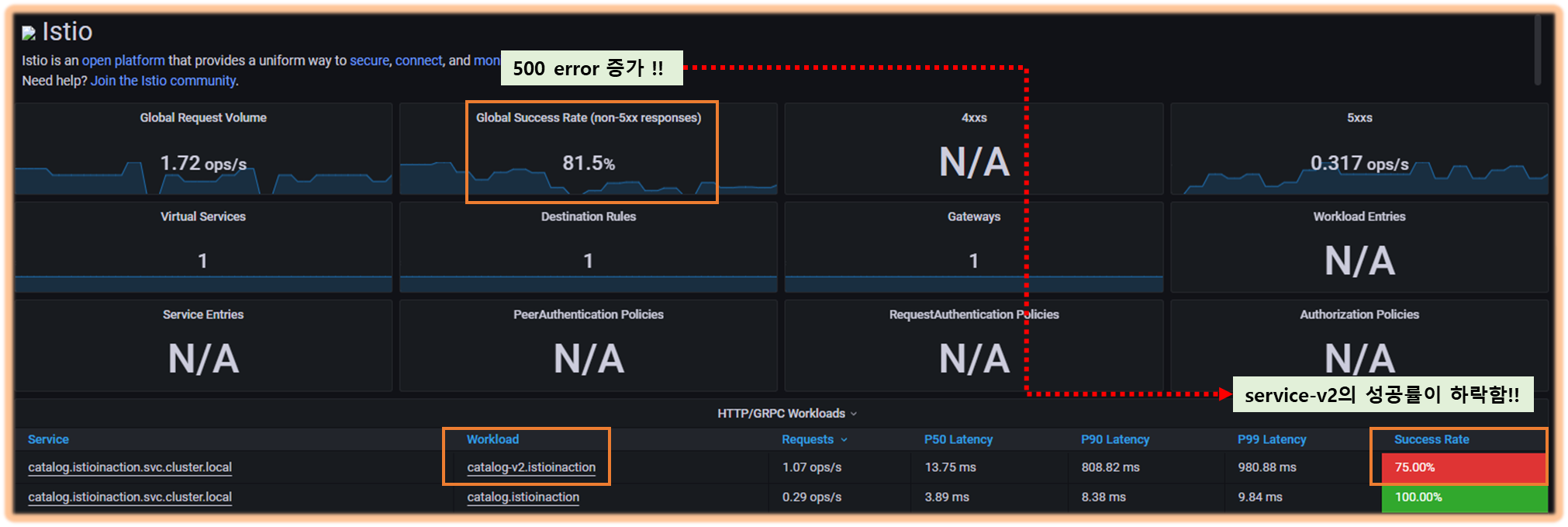
- Grafana - Istio Mesh 대시보드 : 500 응답 증가, v2 에 Success Rate % 확인
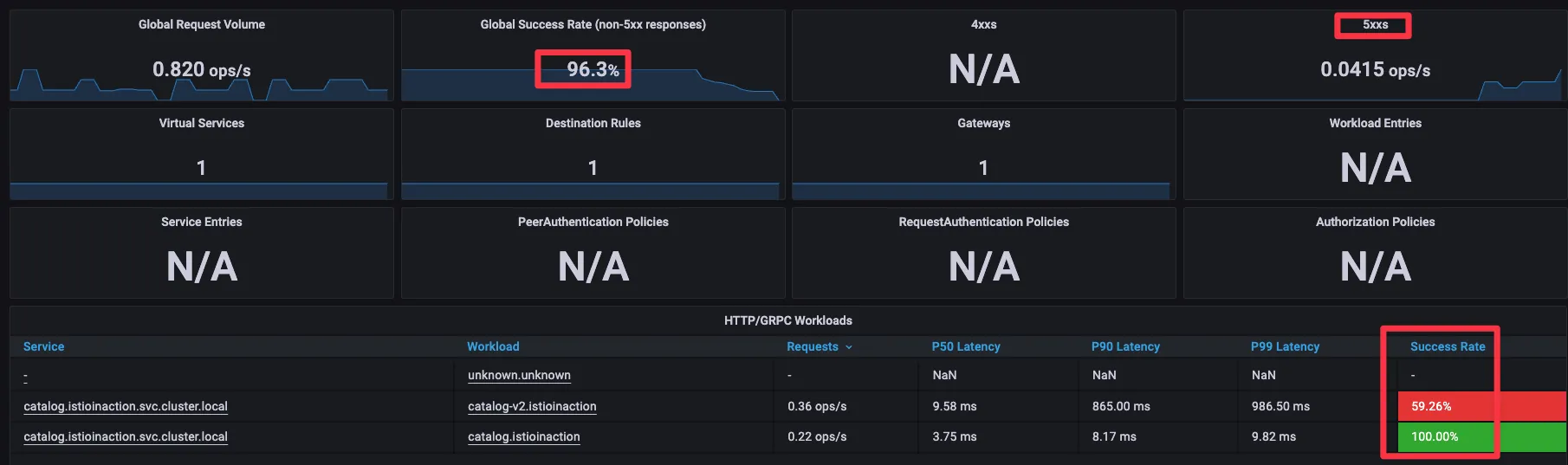
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈 에 보기 ]
▶ 엔보이 액세스 로그 이해하기 + 엔보이 액세스 로그 형식 바꾸기
- 기본적으로 이스티오는 프록시가 로그를 TEXT 형식으로 기록하도록 설정하는데, 간결하지만 읽기는 어렵다.
- JSON 형식을 사용하게 설정 : 이 형식의 이점은 값이 키와 연결돼 의미를 알 수 있다.
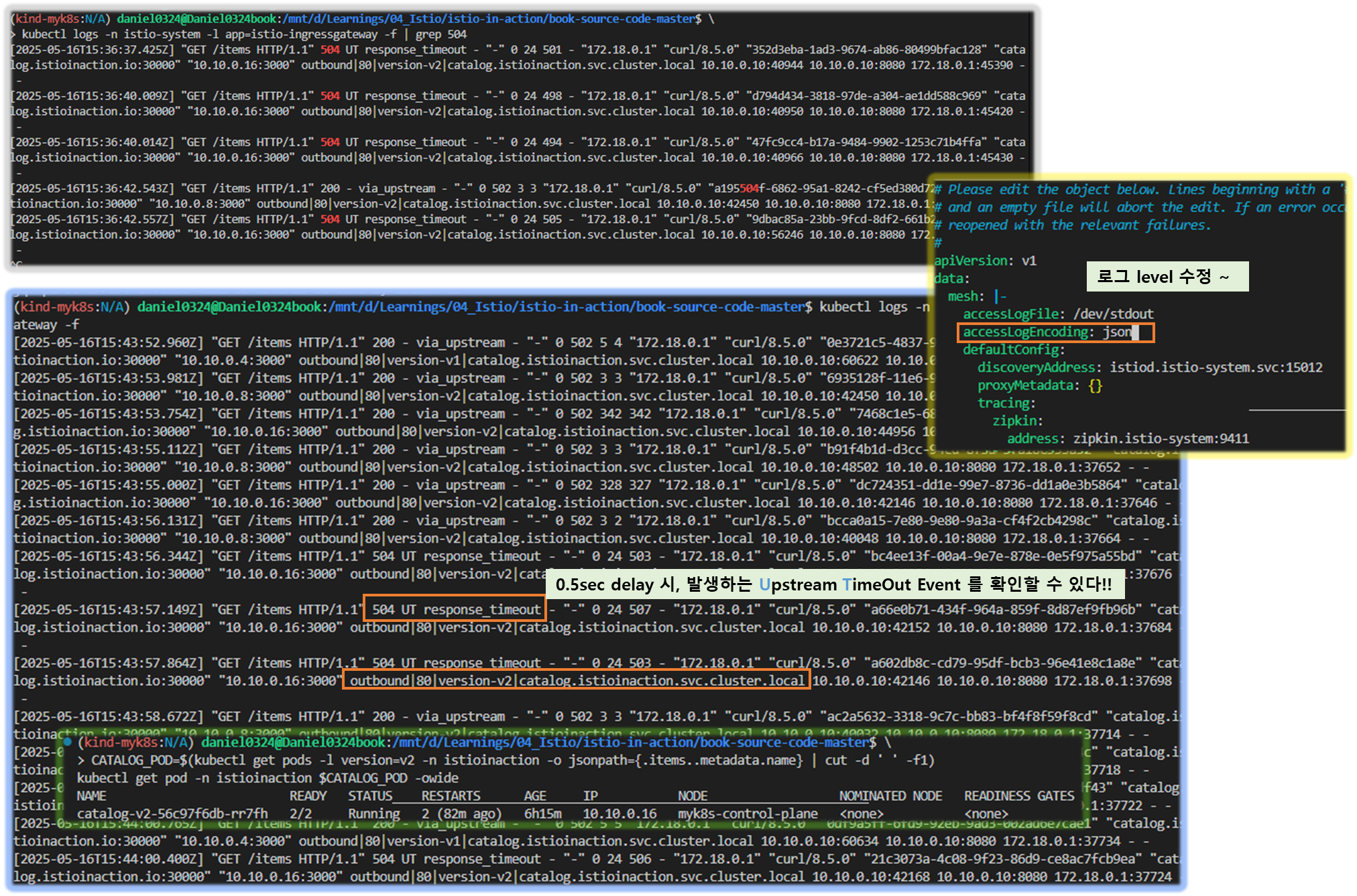
# 형식 설정 전 로그 확인
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f | grep 504
...
# MeshConfig 설정 수정
KUBE_EDITOR="nano" kubectl edit -n istio-system cm istio
...
mesh: |-
accessLogFile: /dev/stdout # 기존 설정되어 있음
accessLogEncoding: JSON # 추가
...
# 형식 설정 후 로그 확인
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f | jq
...
{
"upstream_host": "10.10.0.13:3000", # 요청을 받는 업스트림 호스트
"bytes_received": 0,
"upstream_service_time": null,
"response_code_details": "response_timeout",
"upstream_cluster": "outbound|80|version-v2|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",
"duration": 501, # 500ms 인 제한 시간 초과
"response_code": 504,
"path": "/items",
"protocol": "HTTP/1.1",
"upstream_transport_failure_reason": null,
"connection_termination_details": null,
"method": "GET",
"requested_server_name": null,
"start_time": "2025-05-09T08:56:38.988Z",
"downstream_remote_address": "172.18.0.1:59052",
"upstream_local_address": "10.10.0.7:57154",
"downstream_local_address": "10.10.0.7:8080",
"bytes_sent": 24,
"authority": "catalog.istioinaction.io:30000",
"x_forwarded_for": "172.18.0.1",
"request_id": "062ad02a-ff36-9dcc-8a7d-68eabb01bbb5",
"route_name": null,
"response_flags": "UT", # 엔보이 응답 플래그, UT(Upstream request Timeout)로 중단됨, '업스트림 요청 제한 시간 초과'
"user_agent": "curl/8.7.1"
}
...
# slow 동작되는 파드 IP로 느린 동작 파드 확인!
CATALOG_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l version=v2 -n istioinaction -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name} | cut -d ' ' -f1)
kubectl get pod -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -owide
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES
catalog-v2-56c97f6db-d74kv 2/2 Running 0 7h11m 10.10.0.13 myk8s-control-plane <none> <none>
- 필요 시 엔보이 프록시의 로깅 수준을 높여 더 자세한 로그를 얻을 수 있다.
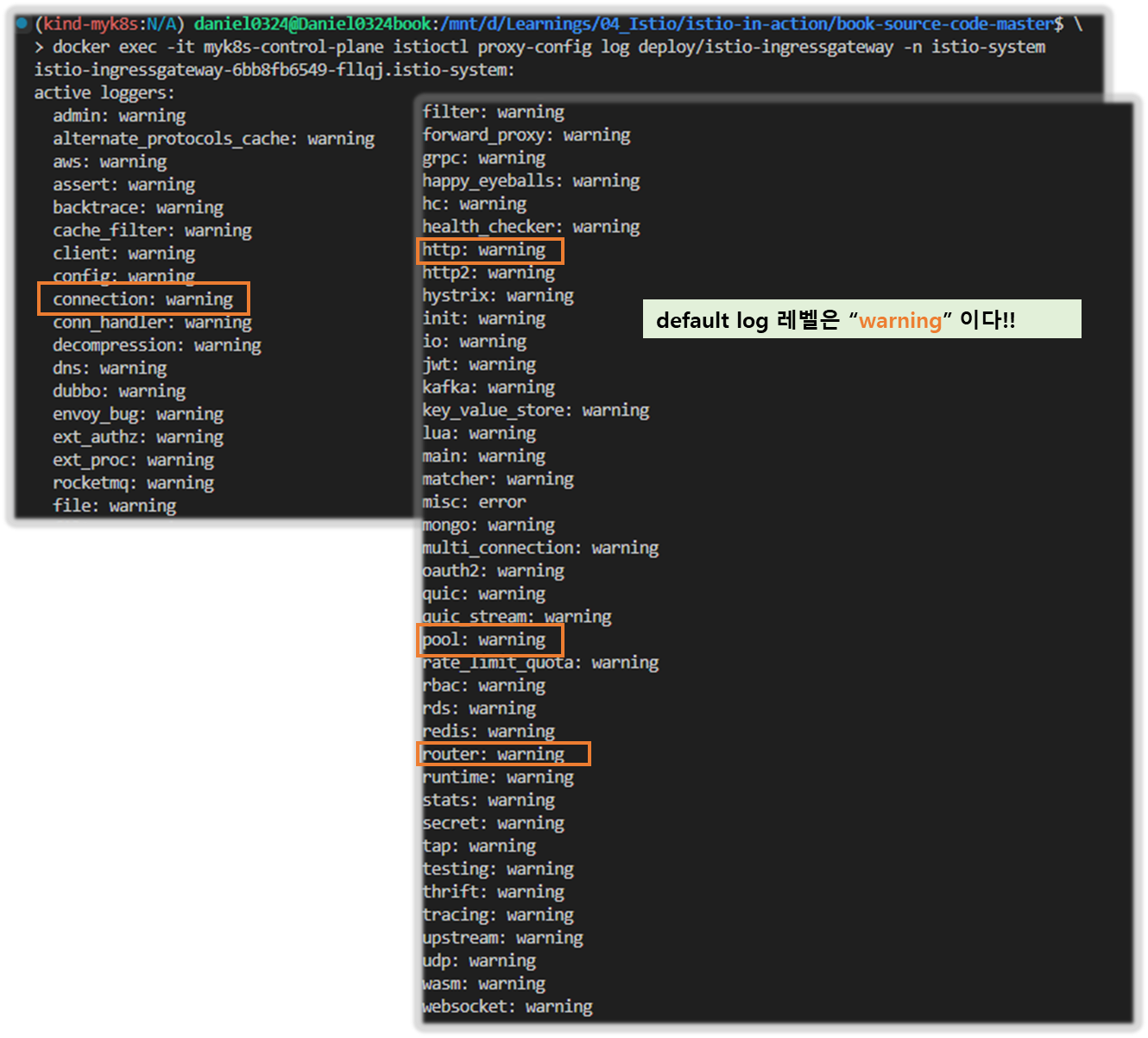
▶엔보이 게이트웨이의 로깅 수준 높이기 INCREASING THE LOGGING LEVEL FOR THE INGRESS GATEWAY
Step1. 현재 로깅 수준 확인
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config log deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system
istio-ingressgateway-6bb8fb6549-hcdnc.istio-system:
active loggers:
admin: warning
alternate_protocols_cache: warning
aws: warning
assert: warning
backtrace: warning
cache_filter: warning
client: warning
config: warning
connection: warning # 커넥션 범위에서는 네트워크 계층과 관련된 정보를 기록.
...
http: warning # HTTP 범위에서는 HTTP 헤더, 경로 등 애플리케이션과 관련된 졍보를 기록.
...
router: warning # 라우팅 범위에서는 요청이 어느 클러스터로 라우팅되는지 같은 세부 사항을 기록.
...
- 사용할 수 있는 로깅 수준에는 none, error, warning, info, debug 가 있다.
- 각 범위에 로깅 수준을 서로 다르게 지정할 수 있는 덕분에 엔보이가 만들어내는 로그에 질식하지 않고 관심 영역의 로깅 수준만 정확하게 높일 수 있다.
- connection : Logs related to layer 4 (transport); TCP connection details
- http : Logs related to layer 7 (application); HTTP details
- router: Logs related to the routing of HTTP requests
- pool : Logs related to how a connection pool acquires or drops a connection’s upstream host
Step2. connection , http , router , pool 로거의 수준을 debug 로 높여보자
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config log deploy/istio-ingressgateway -n istio-system \
--level http:debug,router:debug,connection:debug,pool:debug
# 로그 확인
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f
k logs -n istio-system -l app=istio-ingressgateway -f > istio-igw-log.txt # 편집기로 열어서 보기
...
- 편집기로 열어서 보기
# 504 검색
2025-05-09T09:17:17.762027Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/filter_manager.cc:967 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] Sending local reply with details response_timeout thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.762072Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/conn_manager_impl.cc:1687 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] encoding headers via codec (end_stream=false):
':status', '504'
'content-length', '24'
'content-type', 'text/plain'
'date', 'Fri, 09 May 2025 09:17:17 GMT'
'server', 'istio-envoy'
thread=38
# 커넥션 ID(C18119)로 다시 검색
## [C18119] new stream # 시작
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262341Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/conn_manager_impl.cc:329 [C18119] new stream thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262425Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/conn_manager_impl.cc:1049 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] request headers complete (end_stream=true):
':authority', 'catalog.istioinaction.io:30000'
':path', '/items'
':method', 'GET'
'user-agent', 'curl/8.7.1'
'accept', '*/*'
thread=38
## /items 요청이 cluster로 매칭됨
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262445Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/conn_manager_impl.cc:1032 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] request end stream thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262468Z debug envoy connection external/envoy/source/common/network/connection_impl.h:92 [C18119] current connecting state: false thread=38
025-05-09T09:17:17.262603Z debug envoy router external/envoy/source/common/router/router.cc:470 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] cluster 'outbound|80|version-v2|catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local' match for URL '/items' thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262683Z debug envoy router external/envoy/source/common/router/router.cc:678 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] router decoding headers:
':authority', 'catalog.istioinaction.io:30000'
':path', '/items'
':method', 'GET'
':scheme', 'http'
'user-agent', 'curl/8.7.1'
'accept', '*/*'
'x-forwarded-for', '172.18.0.1'
'x-forwarded-proto', 'http'
'x-envoy-internal', 'true'
'x-request-id', 'a6bc39e7-9215-950f-96ea-4cb5f6b12deb'
'x-envoy-decorator-operation', 'catalog-v1-v2:80/*'
'x-envoy-peer-metadata', 'ChQKDkFQUF9DT05UQUlORVJTEgIaAAoaCgpDTFVTVEVSX0lEEgwaCkt1YmVybmV0ZXMKGwoMSU5TVEFOQ0VfSVBTEgsaCTEwLjEwLjAuNwoZCg1JU1RJT19WRVJTSU9OEggaBjEuMTcuOAqcAwoGTEFCRUxTEpEDKo4DCh0KA2FwcBIWGhRpc3Rpby1pbmdyZXNzZ2F0ZXdheQoTCgVjaGFydBIKGghnYXRld2F5cwoUCghoZXJpdGFnZRIIGgZUaWxsZXIKNgopaW5zdGFsbC5vcGVyYXRvci5pc3Rpby5pby9vd25pbmctcmVzb3VyY2USCRoHdW5rbm93bgoZCgVpc3RpbxIQGg5pbmdyZXNzZ2F0ZXdheQoZCgxpc3Rpby5pby9yZXYSCRoHZGVmYXVsdAowChtvcGVyYXRvci5pc3Rpby5pby9jb21wb25lbnQSERoPSW5ncmVzc0dhdGV3YXlzChIKB3JlbGVhc2USBxoFaXN0aW8KOQofc2VydmljZS5pc3Rpby5pby9jYW5vbmljYWwtbmFtZRIWGhRpc3Rpby1pbmdyZXNzZ2F0ZXdheQovCiNzZXJ2aWNlLmlzdGlvLmlvL2Nhbm9uaWNhbC1yZXZpc2lvbhIIGgZsYXRlc3QKIgoXc2lkZWNhci5pc3Rpby5pby9pbmplY3QSBxoFZmFsc2UKGgoHTUVTSF9JRBIPGg1jbHVzdGVyLmxvY2FsCi8KBE5BTUUSJxolaXN0aW8taW5ncmVzc2dhdGV3YXktNmJiOGZiNjU0OS1oY2RuYwobCglOQU1FU1BBQ0USDhoMaXN0aW8tc3lzdGVtCl0KBU9XTkVSElQaUmt1YmVybmV0ZXM6Ly9hcGlzL2FwcHMvdjEvbmFtZXNwYWNlcy9pc3Rpby1zeXN0ZW0vZGVwbG95bWVudHMvaXN0aW8taW5ncmVzc2dhdGV3YXkKFwoRUExBVEZPUk1fTUVUQURBVEESAioACicKDVdPUktMT0FEX05BTUUSFhoUaXN0aW8taW5ncmVzc2dhdGV3YXk='
'x-envoy-peer-metadata-id', 'router~10.10.0.7~istio-ingressgateway-6bb8fb6549-hcdnc.istio-system~istio-system.svc.cluster.local'
'x-envoy-expected-rq-timeout-ms', '500'
'x-envoy-attempt-count', '1'
thread=38
## upstream timeout 으로 client 에서 끊음 (disconnect)
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262701Z debug envoy pool external/envoy/source/common/conn_pool/conn_pool_base.cc:265 [C17947] using existing fully connected connection thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262710Z debug envoy pool external/envoy/source/common/conn_pool/conn_pool_base.cc:182 [C17947] creating stream thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.262736Z debug envoy router external/envoy/source/common/router/upstream_request.cc:581 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] pool ready thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761697Z debug envoy router external/envoy/source/common/router/router.cc:947 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] upstream timeout thread=38 # 업스트림 서버가 설정된 타임아웃 내에 응답하지 않아 요청이 실패
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761762Z debug envoy router external/envoy/source/common/router/upstream_request.cc:500 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] resetting pool request thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761776Z debug envoy connection external/envoy/source/common/network/connection_impl.cc:139 [C17947] closing data_to_write=0 type=1 thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761779Z debug envoy connection external/envoy/source/common/network/connection_impl.cc:250 [C17947] closing socket: 1 thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761920Z debug envoy connection external/envoy/source/extensions/transport_sockets/tls/ssl_socket.cc:320 [C17947] SSL shutdown: rc=0 thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761982Z debug envoy pool external/envoy/source/common/conn_pool/conn_pool_base.cc:484 [C17947] client disconnected, failure reason: thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.761997Z debug envoy pool external/envoy/source/common/conn_pool/conn_pool_base.cc:454 invoking idle callbacks - is_draining_for_deletion_=false thread=38
## 504 응답
2025-05-09T09:17:17.762027Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/filter_manager.cc:967 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] Sending local reply with details response_timeout thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.762072Z debug envoy http external/envoy/source/common/http/conn_manager_impl.cc:1687 [C18119][S12425904214070917868] encoding headers via codec (end_stream=false):
':status', '504'
'content-length', '24'
'content-type', 'text/plain'
'date', 'Fri, 09 May 2025 09:17:17 GMT'
'server', 'istio-envoy'
thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.762253Z debug envoy pool external/envoy/source/common/conn_pool/conn_pool_base.cc:215 [C17947] destroying stream: 0 remaining thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.763718Z debug envoy connection external/envoy/source/common/network/connection_impl.cc:656 [C18119] remote close thread=38
2025-05-09T09:17:17.763731Z debug envoy connection external/envoy/source/common/network/connection_impl.cc:250 [C18119] closing socket: 0 thread=38
- 두 가지 중요한 발견이 있다.
- 첫 째, 응답이 느린 업스트림의 IP 주소가 액세스 로그에서 가져온 IP 주소와 일치한다는 점이다. 이는 오동작하는 인스턴스가 딱 하나라는 심증을 더욱 굳힌다. that the IP address of the upstream that responds slowly matches the IP address retrieved from the access logs, which further solidifies that only one instance is misbehaving instance
- 둘 째, 로그 [C17947] client disconnected 에 표시된 대로 클라이언트(프록시)는 업스트림 커넥션을 종료했다. that the client (proxy) terminated the connection to the upstream, as indicated by the log [C17947] client disconnected.
- 이는 업스트림 인스턴스가 제한 시간 설정을 초과해 클라이언트(프록시)가 요청을 종료한다는 우리의 예상과 일치한다. This matches our expectation that the client (proxy) is terminating the requests because the upstream instance is exceeding the timeout configuration.
- 엔보이 로거는 프록시 동작을 깊이 꿰뚫는 통찰력을 얻게 해준다.
- 다음 절에서는 서버측에서 네트워크 트래픽을 조사한다.
▶ 10.3.4 ksniff (tcpdump)로 네트워크 트래픽 검사* Inspect network traffic with ksniff
☞ 목표 : 특정 파드에서 tcpdump 후 wireshark 로 분석해보기
0. ksniff 설치 및 패턴 확인 ( P436 ~ 440 )
- ksniff : tcpdump를 사용해 파드의 네트워크 트래픽 포착 및 이를 와이어샤크로 리다이렉트 하는 kubectl 플러그인
- 와이어샤크 : 네트워크 패킷 분석 도구
A. 툴 설치 및 tcpdump 수행
## 1. sniff 설치 ( krew 설치 : https://krew.sigs.k8s.io/docs/user-guide/setup/install )
$ kubectl krew install sniff
## 2. wireshark 설치 후 확인 ( www.wireshark.org/download.html )
$ wireshark -v
...
Wireshark 3.2.5 (v3.2.5-0-ged~~~~ ) ## 버전 정보 확인 (OK!!)
## 3. 로컬호스트 인터페이스에서 네트워크 트래픽 검사하기 ( P431 )
$ SLOW_POD_IP=$(kubectl -n istio-system logs deploy/istio-ingressgateway \
| grep 504 | tail -n 1 | jq -r .upstream_host | cut -d ":" -f1)
$ SLOW_POD=$(kubectl get pods -n istioinaction \
--field-selector status.podIP=$SLOW_POD_IP \
-o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name})
$ echo $SLOW_POD
## Tcpdump 포착 및 와이어샤크로 리다이렉션 !!
$ kubectl sniff -n istioinaction $SLOW_POD i lo
## 4. 부하발생 ( 중요 : 몇 초 후 중지!! )
$ for i in {1..100}; do curl http://http://localhost/items \
-H "Host: catalog.istioinaction.io" \
-w "\nStatus Code %{http_code}\n"; sleep .5s; done
B. Wireshark 분석하기
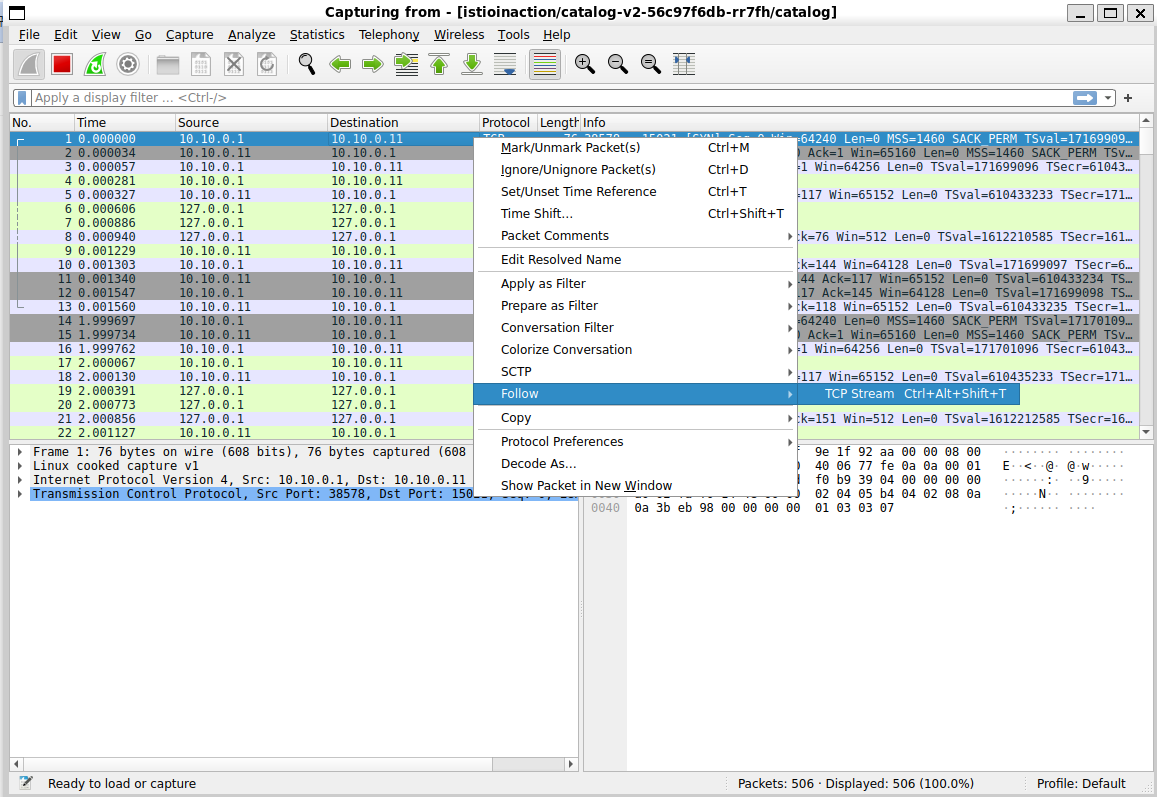
1) dump 첫 번 째 줄에서 우클릭 > 메뉴 아이템 "Follow" 선택 > "TCP Stream" 선택
2) 필터 설정 : http contains "GET /items"
3) TCP Stream 분석 ( 패턴 찾기 )
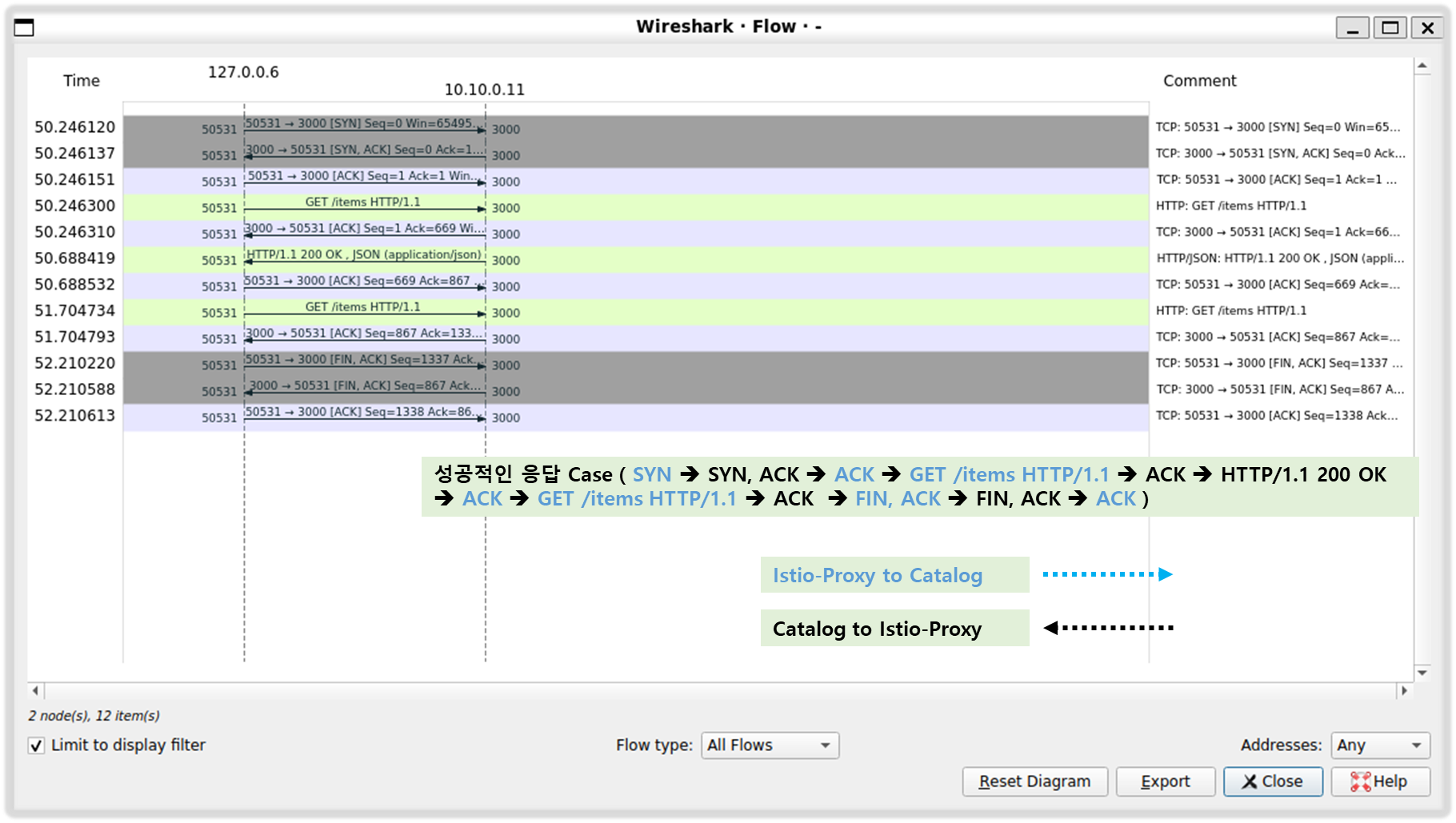
Point #1. 3-handshake 수행결과, TCP 플래그 [SYN], [SYN, ACK], [ACK] 확인
Point #2. 커넥션 설정된 후, 클라이언트의 여러 요청이 동일한 커넥션 재사용 하며, 성공적으로 처리됨 확인
Point #3. 클라이언트에서 다시 요청이 들어와 서버 응답하는 패턴 확인
Point #4. 요청 처리시간이 너무 길어지자, 클라이언트가 FIN 플래그 보내 TCP 세션 종료시킴
서버 측에서 이에 응답하고 커넥션 종료
[ 실행결과 한 눈에 보기 ]
1. 툴 설치
2. wireshark 패킷 조사
[ 정상 케이스 ]
[ 0.5초 이상 delay 시, connection 종료 ]
# kind(k8s) mac M 에서 실행 실패...
kubectl sniff -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -i lo
sudo kubectl sniff -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -i lo
ERRO[0000] failed to start remote sniffing, stopping wireshark error="executing sniffer failed, exit code: '1'"
1. 특정 파드에서 tcpdump 후 wireshark 로 불러오기
# slow 파드 정보 확인
CATALOG_POD=$(kubectl get pods -l version=v2 -n istioinaction -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name} | cut -d ' ' -f1)
kubectl get pod -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -owide
# catalog 서비스 정보 확인
kubectl get svc,ep -n istioinaction
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/catalog ClusterIP 10.200.1.178 <none> 80/TCP 10h
NAME ENDPOINTS AGE
endpoints/catalog 10.10.0.12:3000,10.10.0.13:3000,10.10.0.14:3000 10h
# istio-proxy 에서 기본 정보 확인
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo whoami
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- tcpdump -h
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- ip -c addr
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- ip add show dev eth0
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- ip add show dev lo
# istio-proxy 에 eth0 에서 패킷 덤프
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i eth0 tcp port 3000 -nnq
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i eth0 tcp port 3000 -nn
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i eth0 tcp port 3000
# istio-proxy 에 lo 에서 패킷 덤프
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i lo -nnq
# istio-proxy 에 tcp port 3000 에서 패킷 덤프
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i any tcp port 3000 -nnq
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i any tcp port 3000 -nn
#
kubectl describe pod -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD
...
Mounts:
/etc/istio/pod from istio-podinfo (rw)
/etc/istio/proxy from istio-envoy (rw)
/var/lib/istio/data from istio-data (rw)
/var/run/secrets/credential-uds from credential-socket (rw)
/var/run/secrets/istio from istiod-ca-cert (rw)
/var/run/secrets/tokens from istio-token (rw)
/var/run/secrets/workload-spiffe-credentials from workload-certs (rw)
/var/run/secrets/workload-spiffe-uds from workload-socket (rw)
...
# istio-proxy 에 tcp port 3000 에서 패킷 덤프에 출력 결과를 파일로 저장
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- sudo tcpdump -i any tcp port 3000 -w /var/lib/istio/data/dump.pcap
kubectl exec -it -n istioinaction $CATALOG_POD -c istio-proxy -- ls -l /var/lib/istio/data/
# 출력 결과 파일을 로컬로 다운로드
kubectl cp -n istioinaction -c istio-proxy $CATALOG_POD:var/lib/istio/data/dump.pcap ./dump.pcap
# 로컬로 다운 받은 파일을 wireshark 로 불러오기
wireshark dump.pcap
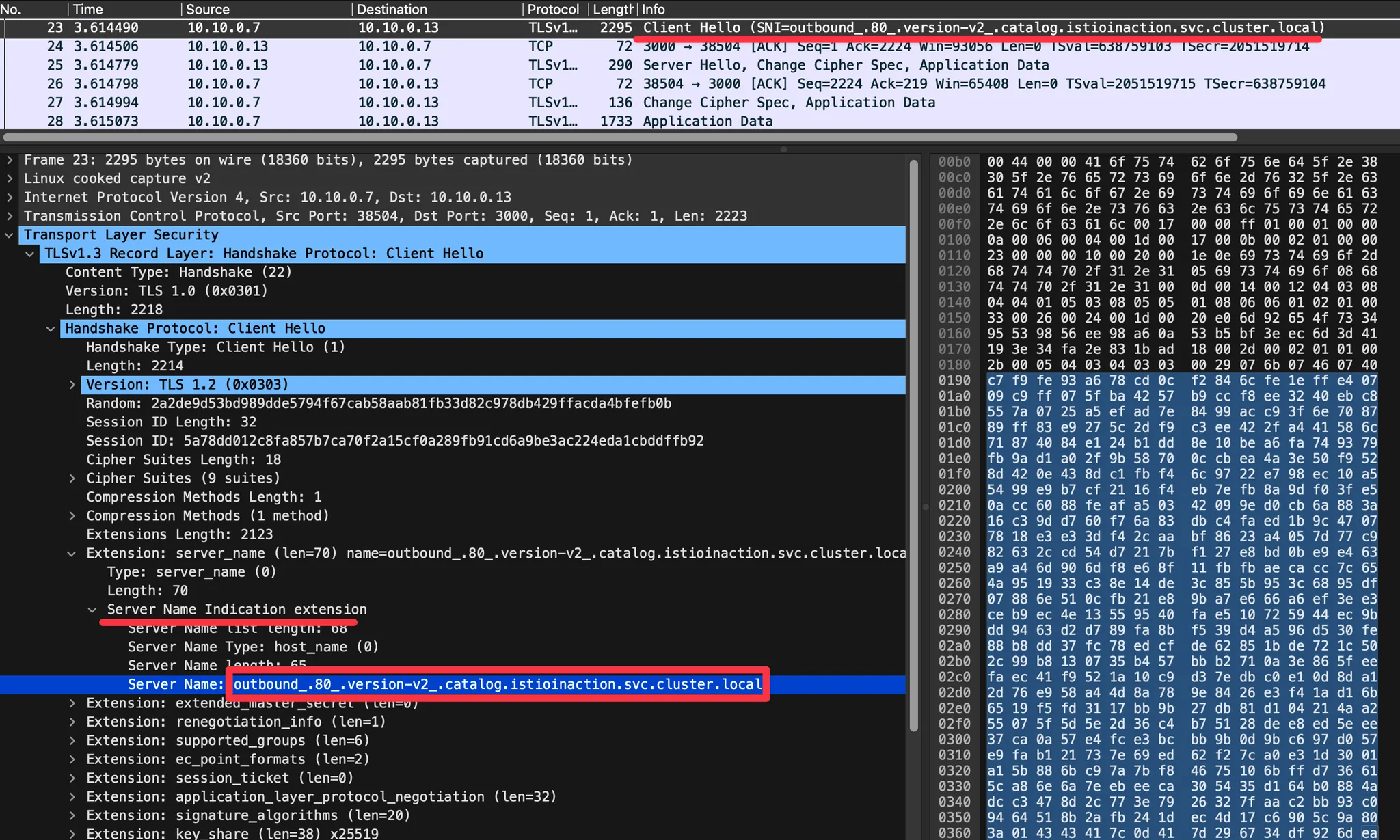
2. Wireshark 에서 TLS 암호 통신 확인 : istio-ingressgateway → [ (캡처 지점) istio-proxy ⇒ catalog application ]
- Client Hello (SNI 확인) : EDS 의 클러스터 이름으로 접속!
outbound_.80_.version-v2_.catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
- SNI에 값 형태를 추정(?) 해보면, https 통신 시 EDS 기준 요청에 대한 통제를 SNI에서 값을 기준하기 위해서, 좀 더 상세한 출력으로 보임
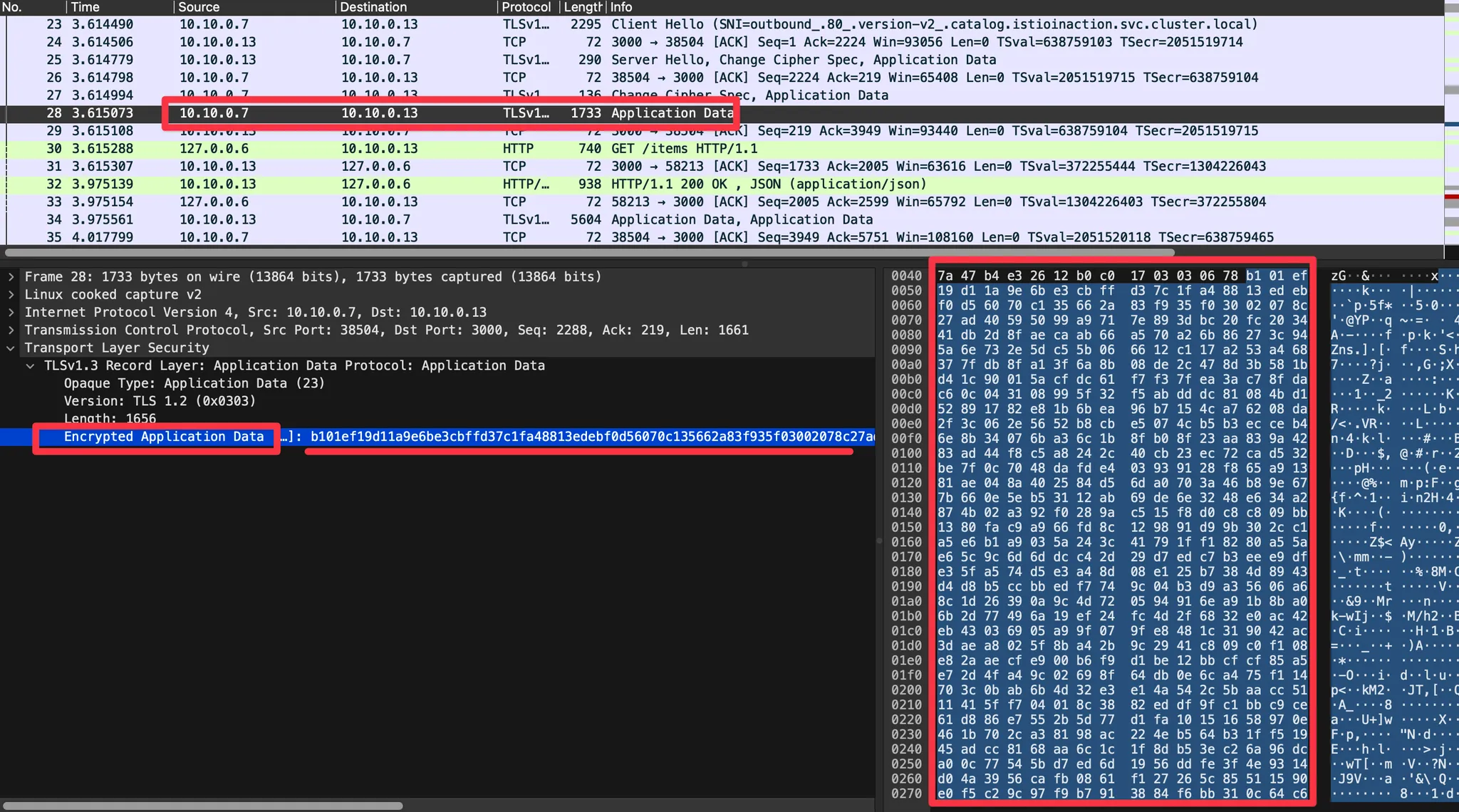
- 암호화된 내용 확인 : Encrypted Application Data 에 값 확인
3. Wireshark 에서 평문 통신 확인 : istio-ingressgateway → [ istio-proxy (캡처 지점) ⇒ catalog application ]
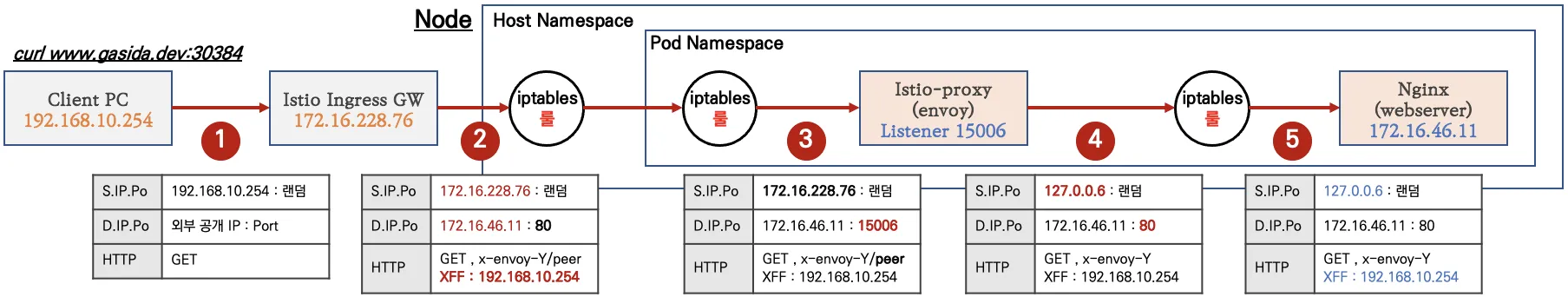
- istio-proxy 가 HTTPS를 복호화해서 평문으로 애플리케이션으로 요청 : x-envoy, x-b3 등 헤더 추가 확인
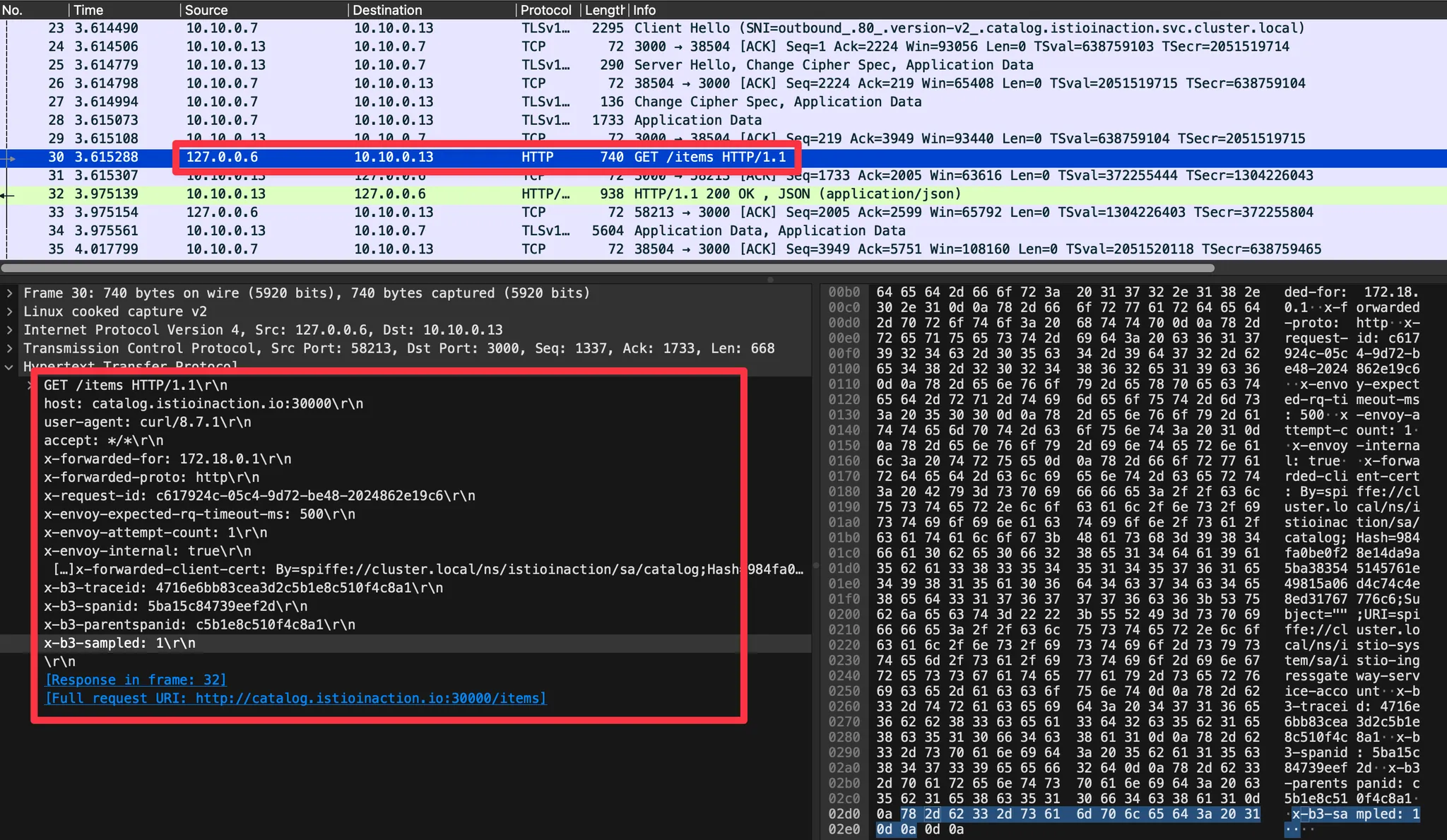
- GET /items 패킷에서 우클릭 후 Follow → TCP Stream 클릭해서 해당 스트림(TCP) 필터링
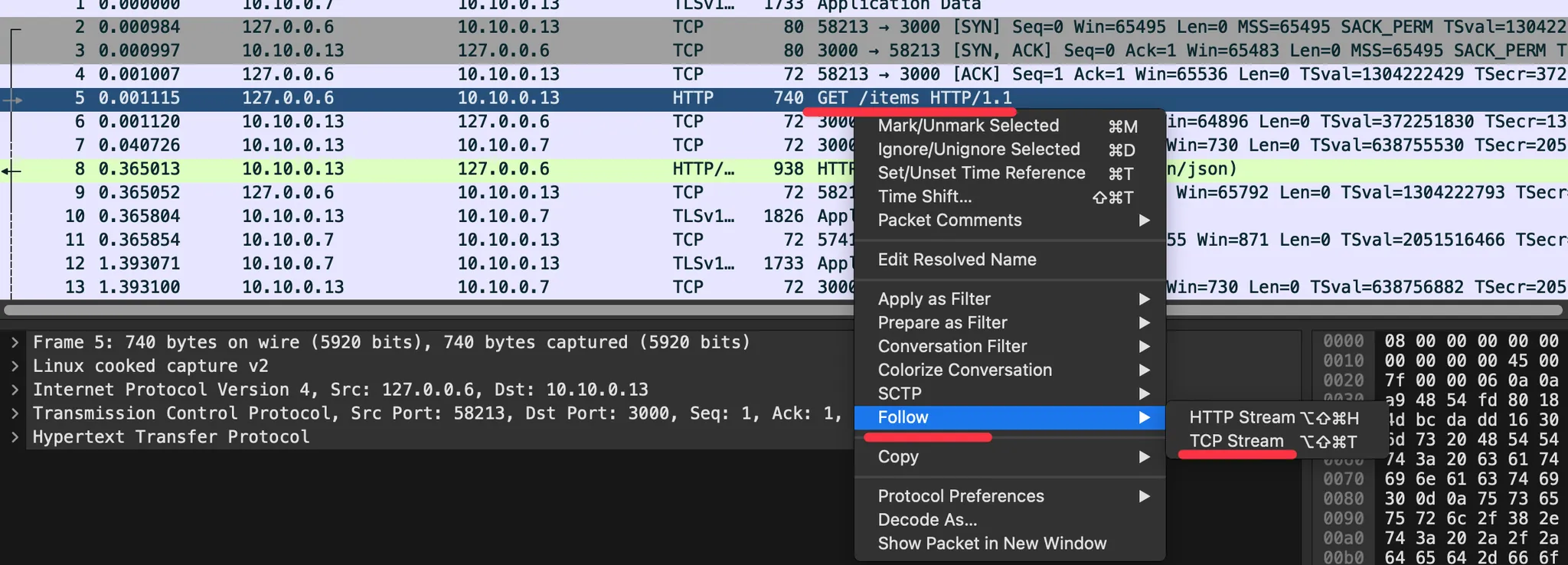
- Statistics → Flow Graph 확인 : 정상적으로 GET 요청과 200 응답 확인
☞ 필터 (tcp.stream == 1 and http) 사용 ← 숫자 1은 각자 스트림 필터링 값 입력
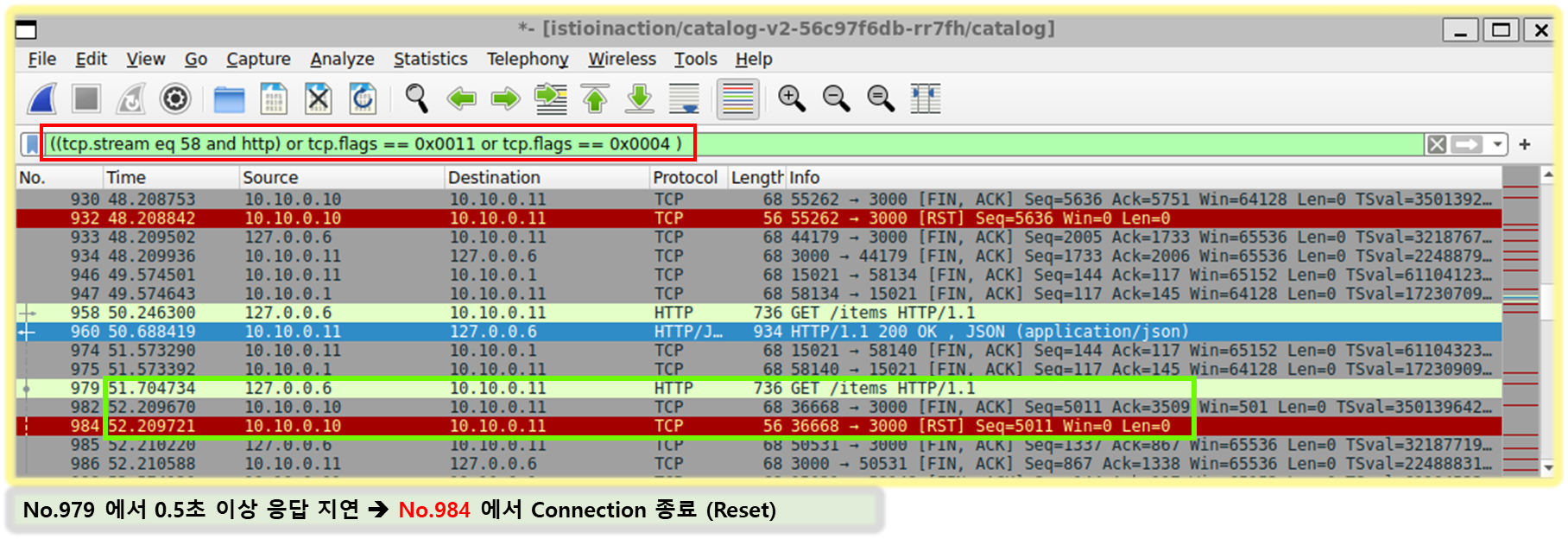
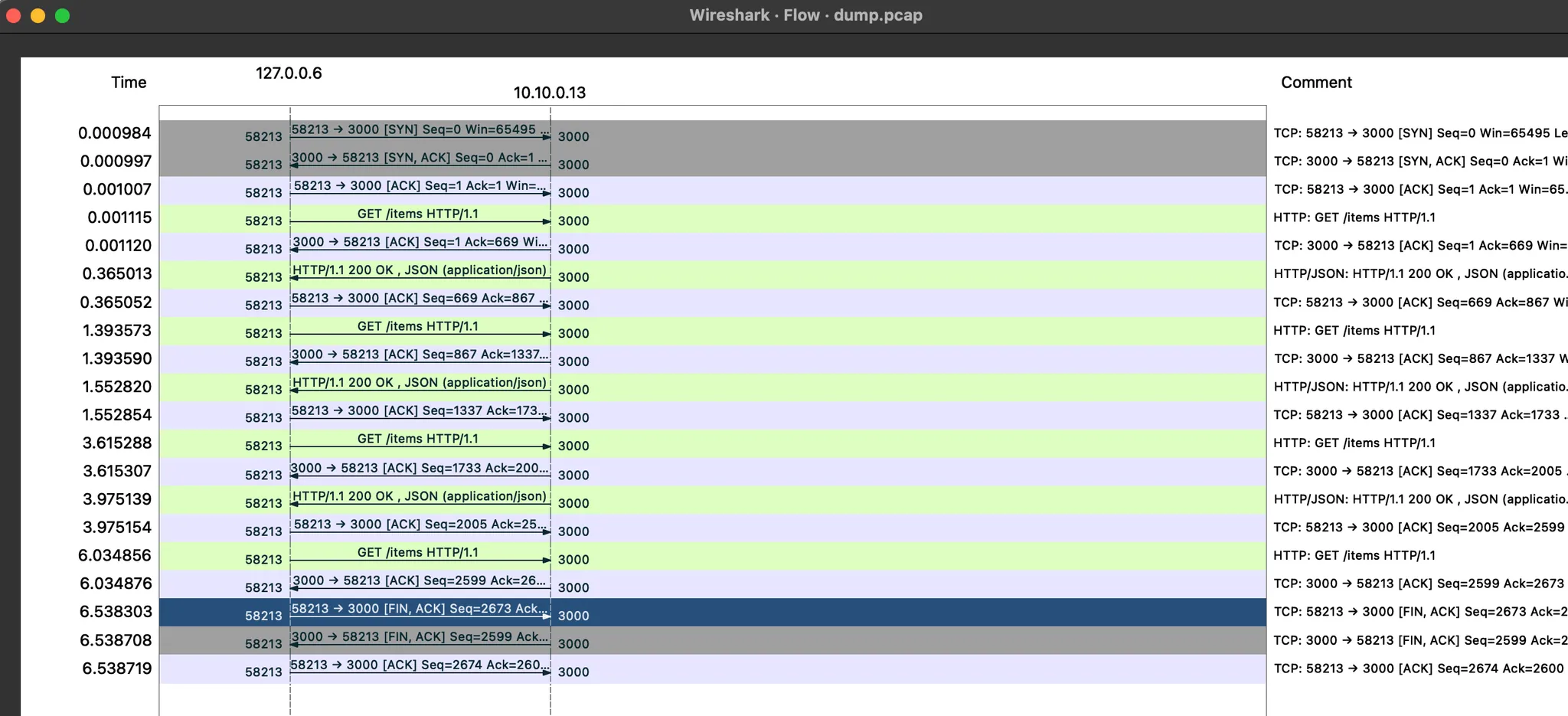
4. catalog v2 가 늦게 응답을 해서 istio-proxy 가 timeout 으로 먼저 종료 확인
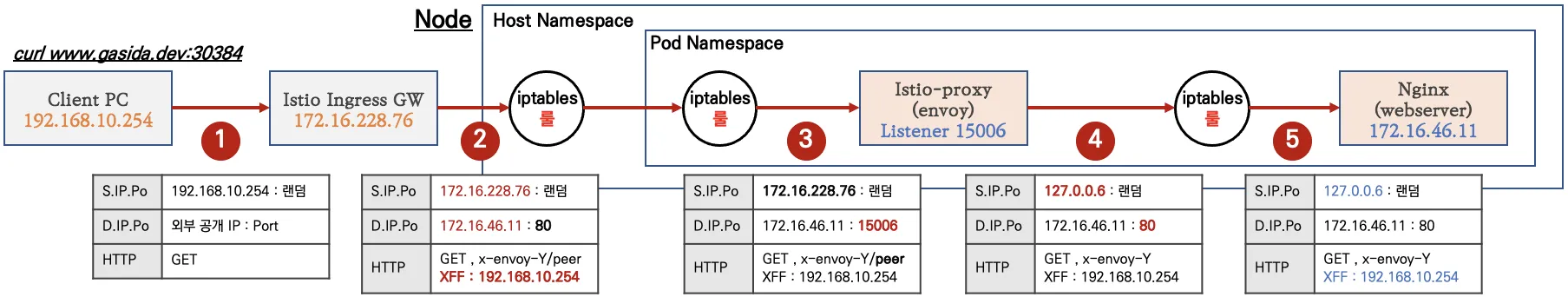
☞ 필터 ((tcp.stream == 1 and http) or tcp.flags == 0x0011 or tcp.flags == 0x0004) : TCP RST, FIN/ACK 플래그 필터링 추가
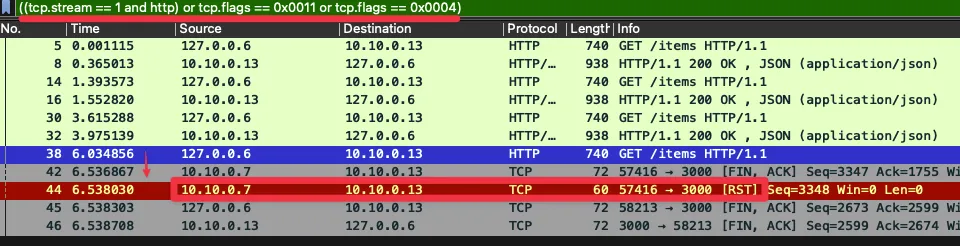
- No. 38번에서 요청 후 0.5초 이상 응답이 없으니 (42번)44번에 istio-ingressgateway istio-proxy 가 TCP RST 로 연결 종료
- ⇒ 즉, 현재 구성 상 istio-ingressgw → catalog 이므로, istio-ingressgw 가 TCP Timeout 후 종료 처리함
- 이후 45번은 catalog v2 istio-proxy 가 FIN/ACK를 applcation 에게 전달 이후 연결 종료
☞ TCP control flags TCP 제어 플래그는 커넥션의 특정 상태를 나타낸다. 여기서 볼 수 있는 플래그는 다음과 같다.
- Synchronization (SYN)은 커넥션을 새로 수립하는 데 사용한다.
- Acknowledgment (ACK)는 패킷 수신이 성공했음을 확인하는 데 사용한다.
- Finish (FIN)는 커넥션 종료를 요청하는 데 사용한다.
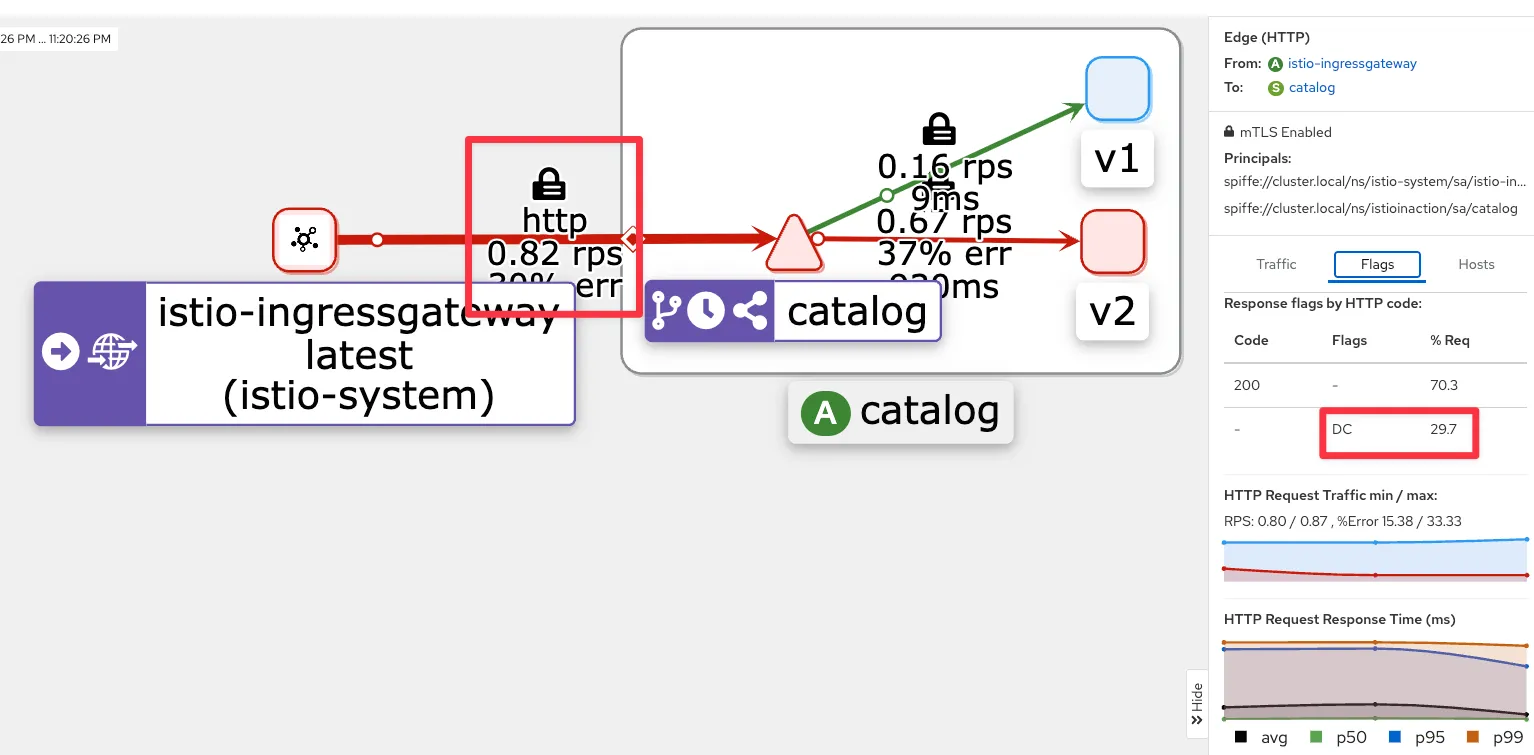
[ Kiali 확인 ]
[ Jaeger 확인 ]
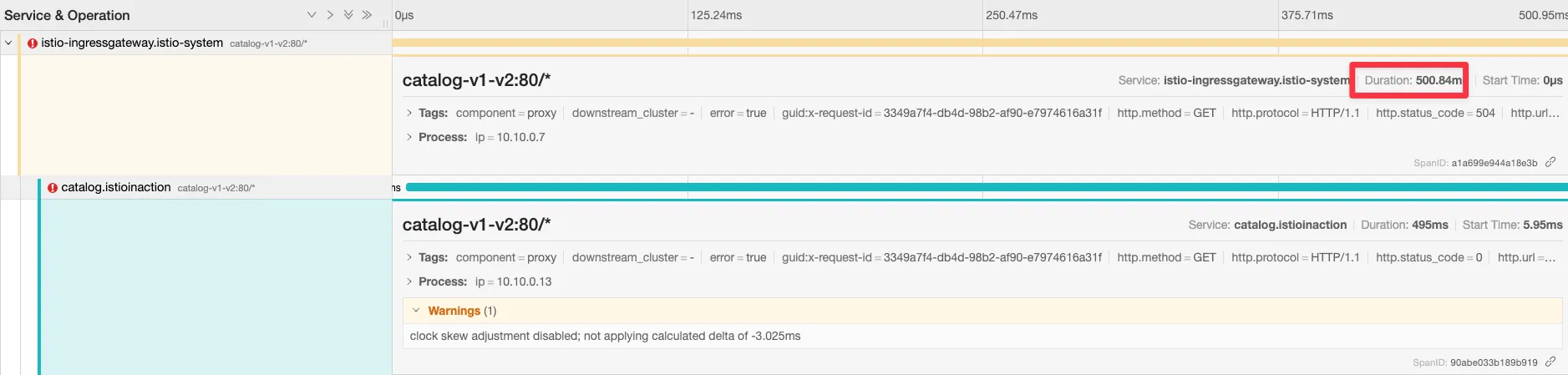
- 네트워크 트래픽을 검사하면 앞 서 관찰한 두 가지를 모두 확인할 수 있다.
- 클라이언트가 커넥션 종료를 시작했고, 서비는 요청 응답이 느렸다.
- 다음 절에서는 이 문제가 드문 문제인지, 즉시 주의를 기울여야 하는 빈번한 문제인지 파악하기 위해 서버를 성공률을 조사한다.
10.4 엔보이 텔레메트리로 자신의 애플리케이션 이해하기
10.4.1 그라파나에서 실패한 요청 비율 찾기 Finding the rate of failing requests in Grafana
- Grafana - Istio Service 대시보드 ⇒ Service(catalog.istioinaction..) , Reporter(source) 선택
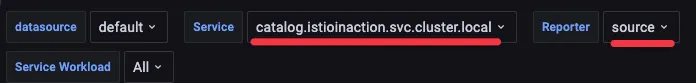
- 클라이언트 성공률은 요청 중 70% 정도(아래 스샷은 79%)로 30% 정도 실패. ⇒ Client 응답에 5xx가 30% 정도 있음 상태 코드 504 (’Gateway timeout’)로 표기되어 클라이언트 측 실패율에 반영.
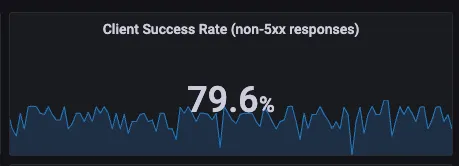
- 서버 성공률은 100%, 즉 서버 문제는 아님 ⇒ Server 응답에는 5xx 없음.
- 엔보이 프록시가 다운스트림 종료 요청에 대한 응답 코드를 0으로 표시하며, 이는 5xx 응답이 아니라서 실패율에 포함되지 않는다.
[인그레스 게이트웨이 : 응답 플래그 UT, 상태 코드 504] ⇒ (요청 타임아웃) ⇒ [catalog v2 : 응답 플래그 DC, 상태 코드 0]
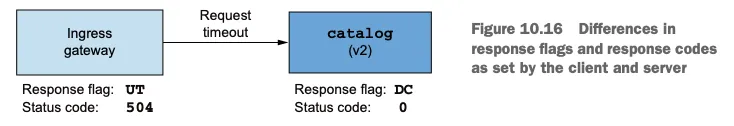
- 정리하면, 올바른 값은 클라이언트가 보고하는 성공률이라는 것을 알 수 있다.
- 실패율이 20~30%이면 즉시 주의를 기울여야 한다!
- 그러나 현재 그라파나 대시보드는 catalog 서비스에 속한 모든 워크로드(v1,v2)의 성공률을 보여준다.
- 문제가 있는 단일 인스턴스를 식별하려면 좀 더 상세한 출력이 필요하다.
10.4.2 프로메테우스를 사용해 영향받는 파드 쿼리하기 Querying the affected Pods using Prometheus
- 그라파나 대시보드의 정보가 부족하면 프로메테우스에 직접 쿼리할 수 있다.
- 예를 들어 파드 별 실패율을 쿼리해보자. 다음 기준을 충족하는 메트릭을 쿼리해보자.
- destination 이 보고한 요청
- destination 서비스가 catalog 인 요청
- 응답 플래그가 DC(다운스트림 커넥션 종료)인 요청 ⇒ 서버 입장에서는 응답을 하려는데, 클라이언트가 먼저 끊어 버린 것!
sort_desc( # 가장 높은 값부터 내림차순 정렬
sum( # irate 값들을 집계
irate( # 요청 수 초당 증가율
istio_requests_total {
reporter="destination", # 서버(destination) 측에서 보고한 메트릭만 필터링
destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local", # catalog 가 서버(destination)측인 메트릭만 필터링
response_flags="DC" # DC (다운스트림 커넥션 종료)로 끝난 메트릭만 필터링
}[5m]
)
)by(response_code, pod, version) # 응답 코드(response_code), 대상 pod, 버전(version) 별로 분리 => sum.. 합산
)# 쿼리1
istio_requests_total
istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local"}
istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",response_flags="DC"}
# 쿼리2
istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",response_flags="DC"}[5m]
irate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",response_flags="DC"}[5m])
sum(irate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",response_flags="DC"}[5m]))
# 쿼리3
sum(irate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",response_flags="DC"}[5m])) by(response_code, pod, version)
sort_desc(sum(irate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local",response_flags="DC"}[5m]))by(response_code, pod, version))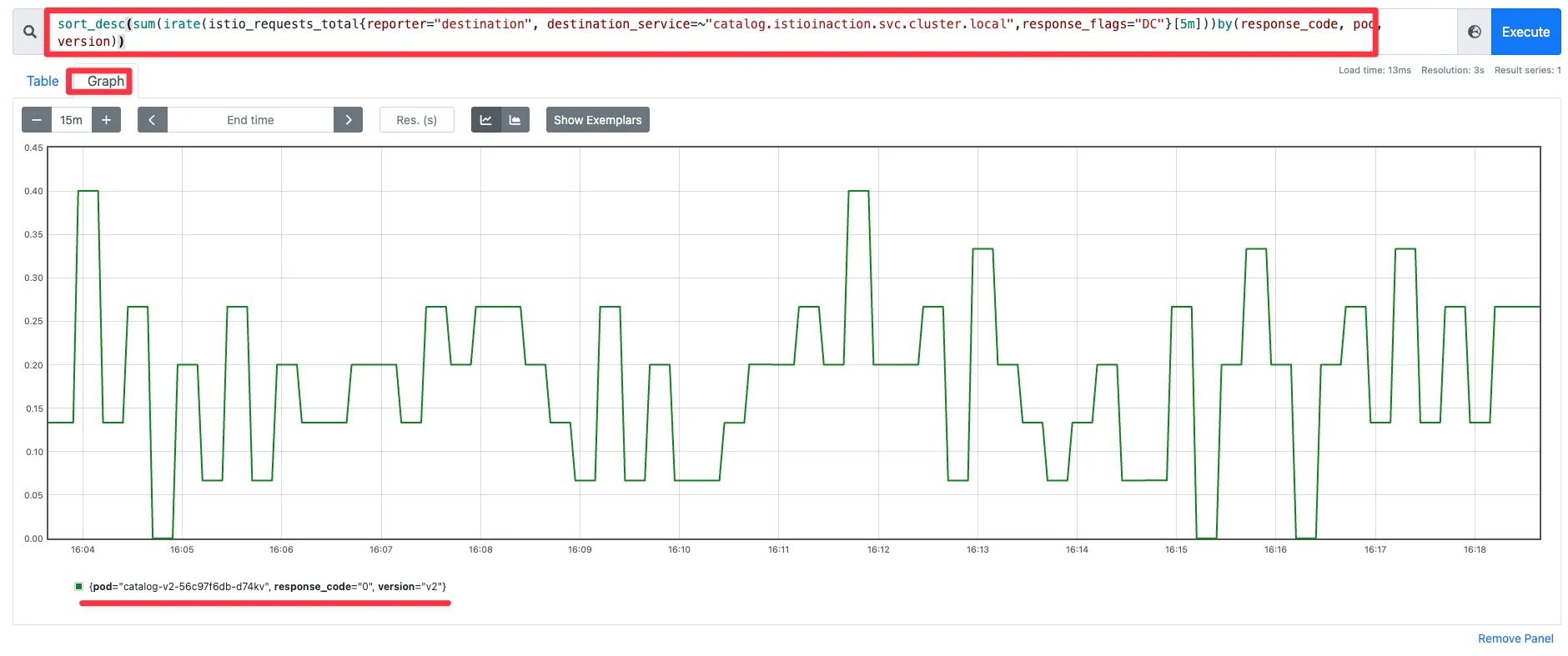
☞ 해당 그래프는 오직 워크로드 하나만 실패를 보고 하고 있음을 보여준다.
▶ 퀴리를 조금 수정해서 확인 : 여러 개 파드 중 catalog v2 만 응답 코드 0 기록 확인
sort_desc(sum(irate(istio_requests_total{reporter="destination", destination_service=~"catalog.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local"}[5m]))by(response_code, pod, version))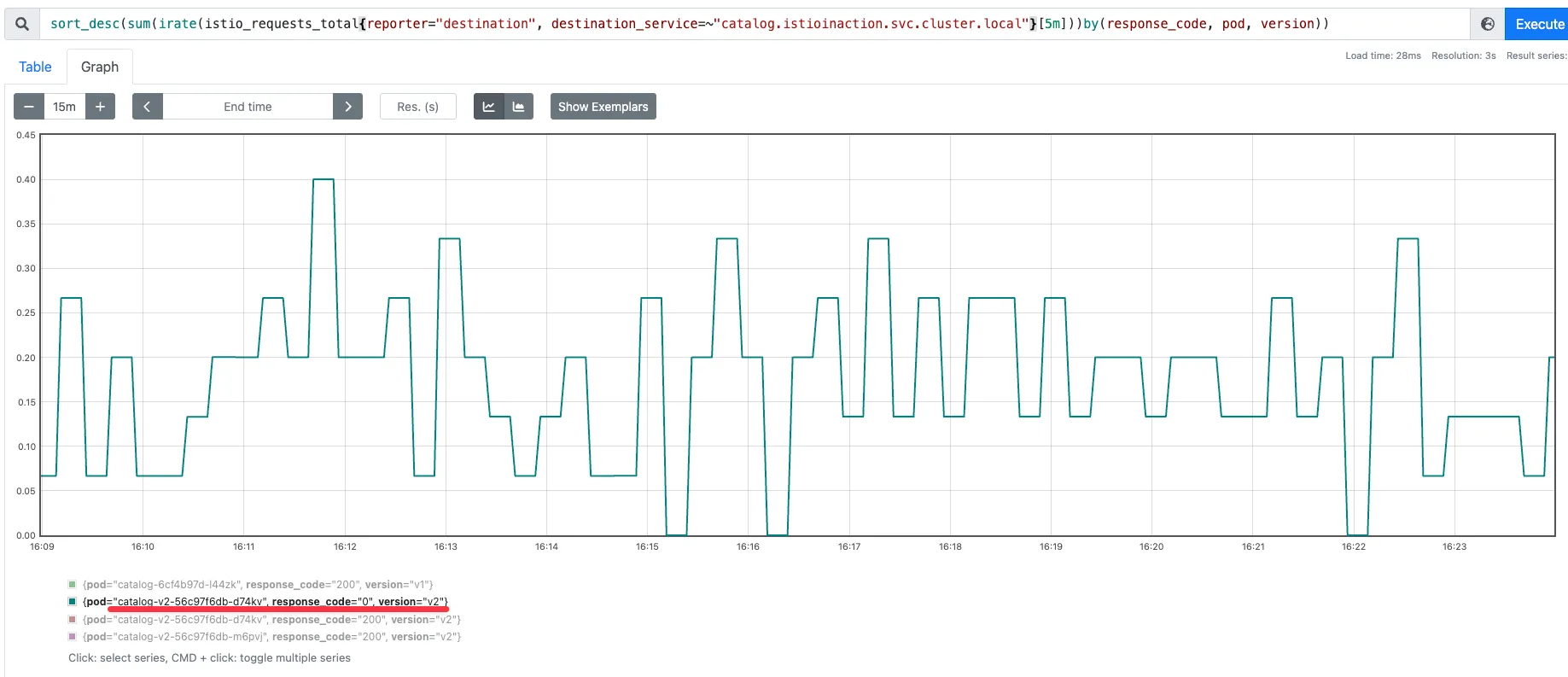
- 이스티오 표준 메트릭에 필요한 정보가 없으며, 7장의 7.4절에서 소개한 방법처럼 커스텀 메트릭을 추가할 수 있다.
- 또한 프로메테우스 클라이언트 라이브러리를 사용해 애플리케이션에 모니터링을 원하는 대로 설정할 수도 있다.
- 이것으로 데이터 플레인을 트러블슈팅하는 데 흔히 사용하는 도구 탐색을 마치겠다.
- 다양한 데이터 플레인 문제가 이전에는 블랙박스철머 보였을 수 있다.
- 하지만 지금부터 이런 문제를 마주했을 때 자신감을 갖고 명확한 출발점을 찾을 수 있어야 한다.
- 이스터이 작동 방식을 깊이 이해하고 적절한 도구가 있다면, 데이터 플레인 문제 디버깅이 휠씬 쉬워진다. (단, 결코 쉬운 일은 아니다)
- 다음 장에서는 컨트롤 플레인에서 일어나는 문제를 해결하는 방법을 알아본다.
- 서비스 메시 내 워크로드 개수가 늘어나면 컨트롤 플레인이 따라서 확장될 수 있도록 함으로써, 컨트롤 플레인 성능을 개선하는 방법을 알아본다.
▶ Summary
- istioctl 명령어를 사용해 서비스 메시와 서비스 프록시에 대한 통찰력을 얻는다.
- proxy-status 는 데이터 플레인 동기화 상태의 개요를 보여준다.
- analyze는 서비스 메시 설정을 분석한다.
- describe는 요약을 가져오고 서비스 프록시 설정을 검증한다.
- proxy-config는 서비스 프록시 설정을 쿼리하고 수정한다.
- istioctl analyze 명령을 사용해 클러스터에 적용하기 전에 설정을 검증할 수 있다.
- 키알리와 그 검증 기능을 사용해 일반적인 설정 실수를 잡아낼 수 있다.
- 장애 상황을 살펴보려면 프로메테우스와 수집한 메트릭을 사용하자.
- ksniff(tcpdump)를 사용해 영향을 받는 파드의 네트워크 트래픽을 캡처할 수 있다.
- istioctl proxy-config log 명령어를 사용해 엔보이 프록시의 로깅 수준을 높일 수 있다.
부록 D. 이스티오 구성 요소 트러블 슈팅하기
Internal Architecture by Port : Istiod(컨트롤플레인) + Istio Proxy(데이터플레인) 도식화 - Blog
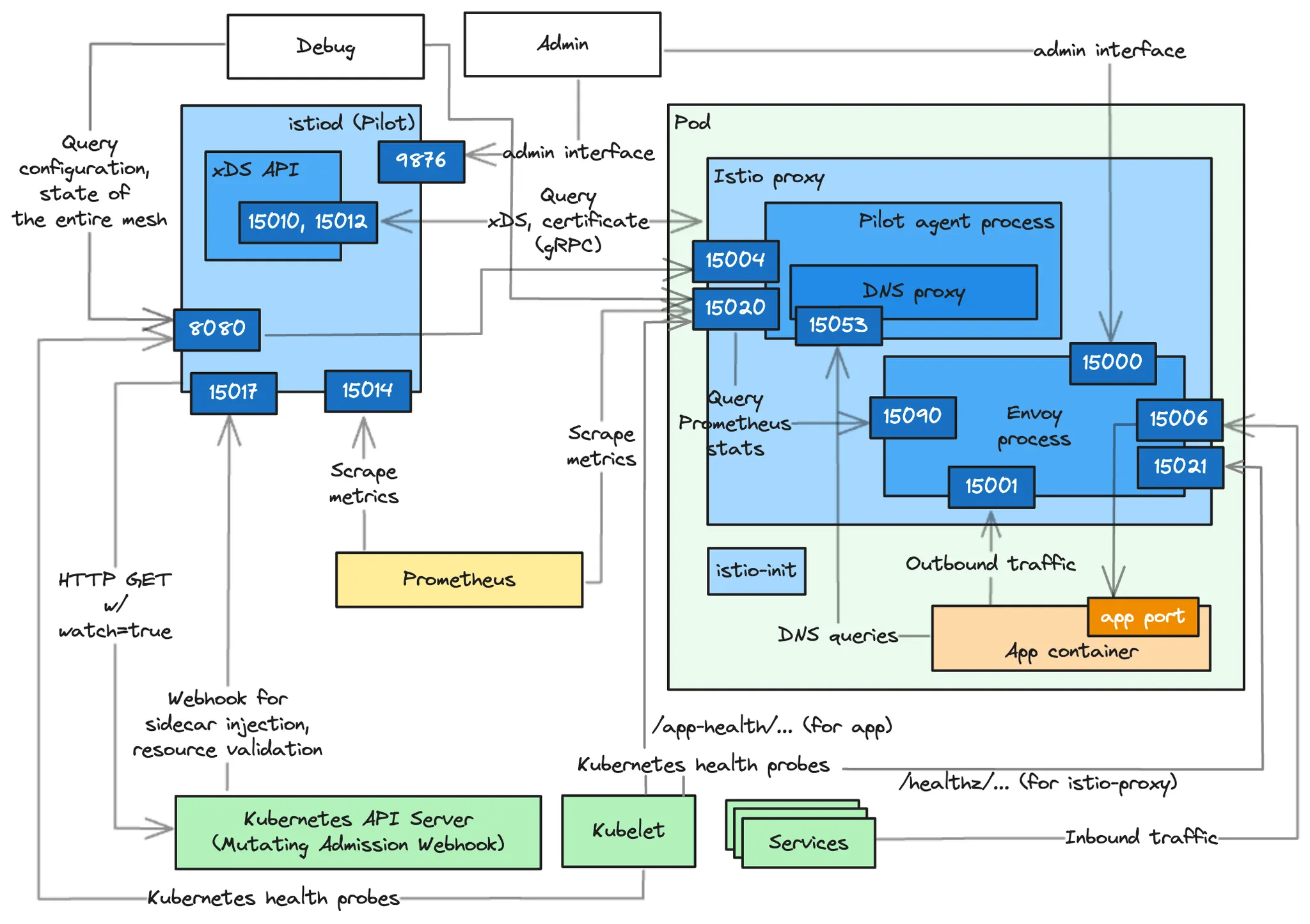
D.1 이스티오 에이전트(DataPlane 위치에서 확인)가 노출하는 정보
- Information exposed by the Istio agent (실습~)
Step1. 실습 환경 초기화 ( * 서비스 호출 curl 테스트는 반드시 hosts 파일 등록 선행 필요 !! )
# 기존 리소스 삭제
kubectl delete -n istioinaction deploy,svc,gw,vs,dr,envoyfilter --all
# 샘플 애플리케이션 배포
kubectl apply -f services/catalog/kubernetes/catalog.yaml -n istioinaction
kubectl apply -f services/webapp/kubernetes/webapp.yaml -n istioinaction
kubectl apply -f services/webapp/istio/webapp-catalog-gw-vs.yaml -n istioinaction
# 확인
kubectl get gw,vs -n istioinaction
curl -s http://webapp.istioinaction.io:30000/api/catalog | jq
# 신규 터미널 : 반복 접속
while true; do curl -s http://webapp.istioinaction.io:30000/api/catalog ; date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ; sleep 1; echo; done- 이스티오 사이드카는 많은 기능을 제공한다.
- 헬스체크 Health checking
- 프록시로서의 엔보이는 트래픽을 처리할 수 있는 즉시 준비 상태다.
- 그러나 서비스 메시의 관점에서 보면 이 정도로는 충분하지 않다.
- 프록시가 트래픽을 처리하기 전에 설정을 받았는지, ID를 할당받았는지 등의 더 많은 확인이 필요하다.
- 메트릭 수집 및 노출 Metrics collection and exposure
- 서비스 내에서 메트릭을 생성하는 세 가지 구성 요소는 애플리케이션, 에이전트, 엔보이 프록시다.
- 에이전트는 다른 구성 요소의 메트릭을 집계해 노출한다.
- DNS resolution 해석, 인바운드 및 아웃바운드 트래픽 라우팅 등
- 헬스체크 Health checking
Step2. 서비스 노출 포트 확인
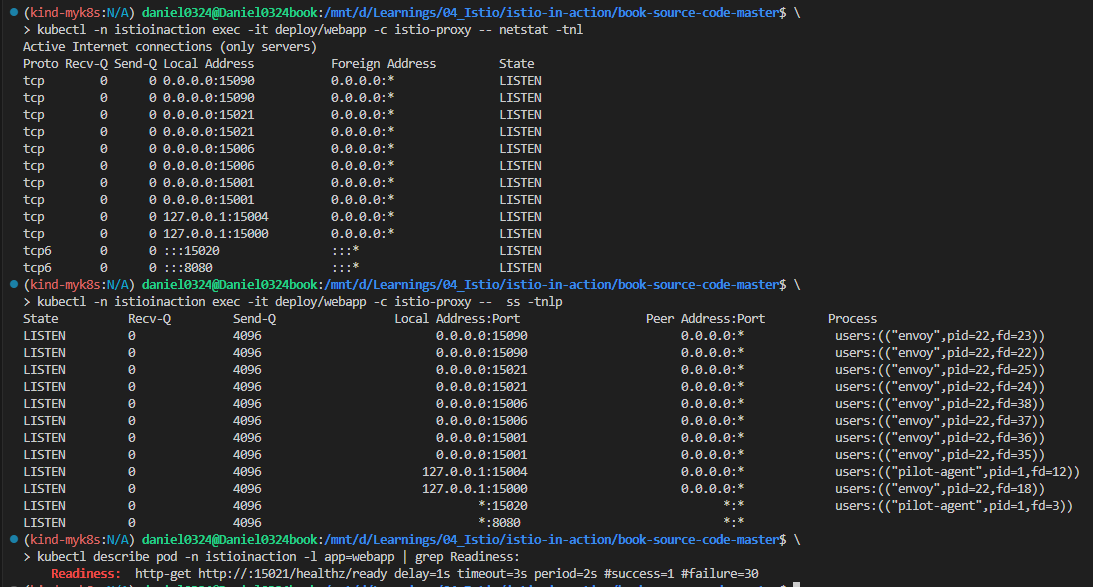
kubectl -n istioinaction exec -it deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- netstat -tnl
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:15000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:15004 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15021 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15021 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15001 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15001 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15006 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15006 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15090 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:15090 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::15020 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN
# 포트별 프로세스 확인 : 파일럿에이전트, 엔보이
kubectl -n istioinaction exec -it deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- ss -tnlp
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:15000 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=18))
LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:15004 0.0.0.0:* users:(("pilot-agent",pid=1,fd=11))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15021 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=25))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15021 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=24))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15001 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=36))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15001 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=35))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15006 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=38))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15006 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=37))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15090 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=23))
LISTEN 0 4096 0.0.0.0:15090 0.0.0.0:* users:(("envoy",pid=21,fd=22))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:15020 *:* users:(("pilot-agent",pid=1,fd=7))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:8080 *:*
# istio-proxy 컨테이너에 Readiness Probe 정보 확인 : 15021 헬스체크 포트
kubectl describe pod -n istioinaction -l app=webapp | grep Readiness:
Readiness: http-get http://:15021/healthz/ready delay=1s timeout=3s period=2s #success=1 #failure=30
▶ 에이전트 및 엔보이 프록시의 포트와 각 포트의 기능
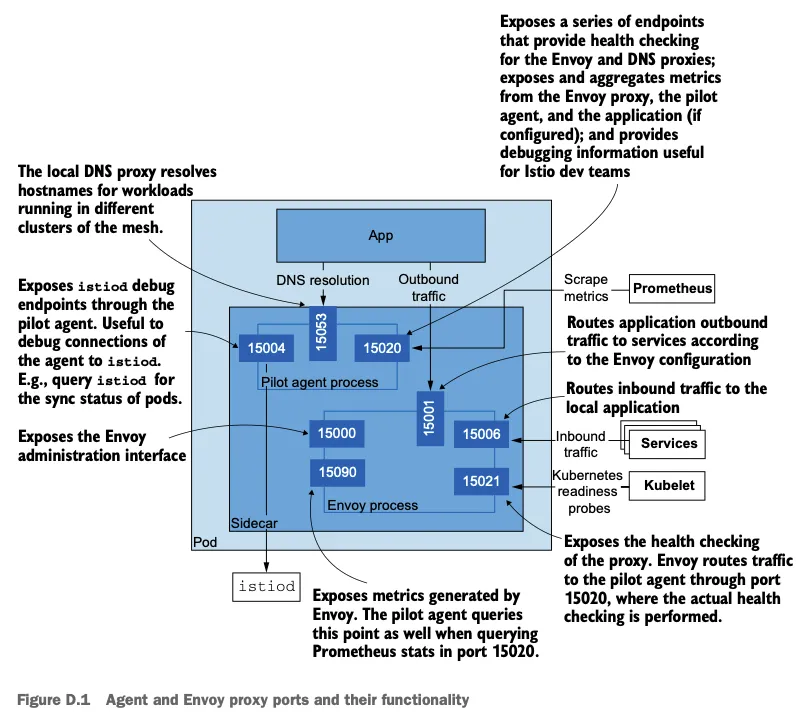
- 서비스용 포트 Ports facing other services
- 15020 : (파일럿 에이전트 프로세스) 여러 기능 제공!
- 메트릭을 집계하고 노출하며, 이때 메트릭에는 엔보이 프록시의 15090 포트에 쿼리한 메트릭, 애플리케이션 메트릭(설정한 경우), 자체 메트릭이 있다.
- 엔보이 및 DNS 프록시를 헬스 체크. 이 엔드포인트에서 애플리케이션도 헬스 체크하도록 프록시를 설정할 수 있지만, 보통은 가상머신과 같이 쿠버네티스가 아닌 워크로드에만 사용한다.
- 이스티오 개발 팀에 유용한 파일럿 에이전트 디버깅용 엔드포인트로, 메모리 정보, CPU 프로파일링 등과 같은 정보를 노출한다.
- 15021 : (엔보이 프로세스) 사이드카 주입된 파드는 이 포트에서 트래픽을 받을 준비가 됐는지 확인하도록 설정된다. Pods with the sidecar injected are configured to check their readiness to receive traffic on this port.
- 앞서 설명한 것처럼 엔보이 프록시는 헬스 체크를 15020 포트의 파일럿 에이전트로 라우팅하며, 실제 헬스 체크는 여기서 일어난다. the Envoy proxy routes the health checks to the Pilot agent on port 15020, where the actual healthchecking occurs.
- 15053 : (파일럿 에이전트 프로세스) 쿠버네티스 DNS 해석이 충분하지 않은 에지 케이스를 해결하기 위해 istiod가 구성한 로컬 DNS 프록시 Local DNS proxy configured by istiod to resolve edge cases where Kubernetes DNS resolution doesn’t suffice.
- 15001 : (엔보이 프로세스) 애플리케이션에서 나가는 트래픽은 Iptable 규칙에 의해 일단 이 포트로 리다이렉트되며, 이후 프록시가 트래픽을 서비스로 라우팅한다.
- 15006 : (엔보이 프로세스) 애플리케이션으로 들어오는 트래픽은 Iptable 규칙에 의해 일단 이 포트로 리다이렉트되며, 여기서 로컬 애플리케이션 라우팅된다.
- 15020 : (파일럿 에이전트 프로세스) 여러 기능 제공!
- 에이전트 디버깅 및 내부 상태 조사에 유용한 포트 useful for debugging and introspecting the agent
- 15000 : (엔보이 프로세스) 엔보이 프록시 관리 인터페이스
- 15090 : (엔보이 프로세스) 엔보이 프록시 메트릭을 노출 (xDS 통계, 커넥션 통계, HTTP 통계, 이상값 outlier 통계, 헬스 체크 통계, 서킷 브레이커 통계 등)
- 15004 : (파일럿 에이전트 프로세스) 에이전트를 통해 이스티오 파일럿 디버그 엔드포인트를 노출. 파일럿과의 연결 문제를 디버깅에 유용.
- 15020 : (파일럿 에이전트 프로세스) 파일럿 에이전트 디버기용 엔드포인트들을 노출.
D.1.1 이스티오 에이전트를 조사하고 트러블슈팅하기 위한 엔드포인트들
- Endpoints to introspect and troubleshoot the Istio agent
- 15020 포트의 엔드포인트들
- /healthz/ready : 엔보이 및 DNS 프록시에서 일련의 검사를 수행한다.
- 이느 워크로드가 클라이언트 요청을 처리할 준비가 됐는지 확인하기 위한 것이다.
- /stats/prometheus : 엔보이 프록시와 애플리케이션의 메트릭을 자체 메트릭과 병합하고 긁어갈 수 있도록 노출한다.
- /quitquitquit : 파일럿 에이전트의 프로세스를 종료시킨다.
- /app-health/ : 이스티오 프록시 사이드카의 환경 변수 ISTIO_KUBE_APP_PROBERS로 정의한 애플리케이션 프로브를 실행한다.
- 애플리케이션이 쿠버네티스 프로브를 정의하면 istiod mutating 웹훅이 정보를 추출해 이 환경 변수로 프로브를 설정한다 - Docs
- 그러므로 에이전트는 이 경로로의 퀴리를 애플리케이션으로 리다이렉트한다.
- /healthz/ready : 엔보이 및 DNS 프록시에서 일련의 검사를 수행한다.
#
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: liveness-http
namespace: istioinaction
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: liveness-http
version: v1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: liveness-http
version: v1
spec:
containers:
- name: liveness-http
image: docker.io/istio/health:example
ports:
- containerPort: 8001
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /foo
port: 8001
initialDelaySeconds: 5
periodSeconds: 5
EOF
#
kubectl get pod -n istioinaction -l app=liveness-http
kubectl describe pod -n istioinaction -l app=liveness-http
...
Containers:
liveness-http:
Container ID: containerd://edaf01bff5d553e03290b3d44f60bb26958319e615a27a9b38309aad9b2df477
Image: docker.io/istio/health:example
Image ID: docker.io/istio/health@sha256:d8a2ff91d87f800b4661bec5aaadf73d33de296d618081fa36a0d1cbfb45d3d5
Port: 8001/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Sat, 10 May 2025 16:58:35 +0900
Ready: True
Restart Count: 0
Liveness: http-get http://:15020/app-health/liveness-http/livez delay=5s timeout=1s period=5s #success=1 #failure=3
...
istio-proxy:
Container ID: containerd://d4b0955372bdb7b3e1490eb3f290c6c6f5a9f2691eabea4cebafaafa8be85fc9
Image: docker.io/istio/proxyv2:1.17.8
Image ID: docker.io/istio/proxyv2@sha256:d33fd90e25c59f4f7378d1b9dd0eebbb756e03520ab09cf303a43b51b5cb01b8
Port: 15090/TCP
...
Readiness: http-get http://:15021/healthz/ready delay=1s timeout=3s period=2s #success=1 #failure=30
Environment:
...
ISTIO_META_POD_PORTS: [
{"containerPort":8001,"protocol":"TCP"}
]
ISTIO_META_APP_CONTAINERS: liveness-http
ISTIO_META_CLUSTER_ID: Kubernetes
ISTIO_META_NODE_NAME: (v1:spec.nodeName)
ISTIO_META_INTERCEPTION_MODE: REDIRECT
ISTIO_META_WORKLOAD_NAME: liveness-http
ISTIO_META_OWNER: kubernetes://apis/apps/v1/namespaces/istioinaction/deployments/liveness-http
ISTIO_META_MESH_ID: cluster.local
TRUST_DOMAIN: cluster.local
ISTIO_KUBE_APP_PROBERS: {"/app-health/liveness-http/livez":{"httpGet":{"path":"/foo","port":8001,"scheme":"HTTP"},"timeoutSeconds":1}}
kubectl get pod -n istioinaction -l app=liveness-http -o json | jq '.items[0].spec.containers[0].livenessProbe.httpGet'
{
"path": "/app-health/liveness-http/livez",
"port": 15020,
"scheme": "HTTP"
}
# 헬스체크 확인
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/liveness-http -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15020/app-health/liveness-http/livez -v
# 실습 확인 후 삭제
kubectl delete deploy liveness-http -n istioinaction
- /debug/ndsz : istiod가 NDS Name Discovery Service API로 DNS 프록시에 설정한 호스트네임들을 나열한다.
- Lists the hostnames for which DNS proxy is configured by istiod using the Name Discovery Service (NDS) API.
- /debug/pprof/* : 성능 문제, 메모리 누수 등을 디버깅하는 데 도움이 되는 Go 언어 프로파일링 엔드포인트. - Docs
- 기본 경로 localhost:15020/debug/pprof 에 쿼리해 디버그 엔드포인트의 전체 목록을 확인할 수 있다.
- 출력은 HTML이며 브라우저에서 보는 것이 가장 좋다 (로컬호스트 포트 포워딩).
- 프로파일링 엔드포인트는 이스티오 개발자와 관련 있으며 이스티오 사용자는 신경 쓸 필요가 없다.
- 접근 확인
#
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15020/healthz/ready -v
# webapp 워크로드의 병합된 통계 확인 : istio_agent로 시작하는 메트릭(에이전트에서 온 것) + envoy로 시작하는 메트릭(프록시에서 온 것)
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15020/stats/prometheus
## 응답에서는 istio_agent로 시작하는 메트릭(에이전트에서 온 것)과 envoy로 시작하는 메트릭(프록시에서 온 것)을 볼 수 있는데,
## 이는 이 둘이 병합됐음을 보여준다.
#
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15020/quitquitquit
#
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15020/debug/ndsz
#
kubectl port-forward deploy/webapp -n istioinaction 15020:15020
open http://localhost:15020/debug/pprof # 혹은 웹 브라우저에서 열기
D.1.2 이스티오 에이전트를 통해 이스티오 파일럿 디버그 엔드포인트들 쿼리하기
- 에이전트는 기본적으로 15004 포트에서 몇 가지 istiod 디버그 엔드포인트들을 노출한다.
- 이 엔드포인트들에 한 요청은 xDS 이벤트 형태로 안전하게 istiod로 전달되는데, 이는 에이전트에서 컨트롤 플레인으로의 연결 상태를 확인 할 수 있는 좋은 방법이다.
- 예를 들어 노출된 엔드포인트들 중 하나로 워크로드의 동기화 상태를 쿼리할 수 있다.
- 이를 보려면, 프록시 중 하나의 셸 커넥션을 가져와서 파일럿 에이전트의 15004 포트에 /debug/sync 엔드포인트로 요청해보자.
#
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15004/debug/syncz -v
kubectl exec -n istioinaction deploy/webapp -c istio-proxy -- curl -s localhost:15004/debug/syncz | jq
...
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.service.status.v3.ClientConfig",
"node": {
"id": "catalog-6cf4b97d-fbftr.istioinaction", # 워크로드 ID
"metadata": {
"CLUSTER_ID": "Kubernetes"
}
},
"genericXdsConfigs": [
{
"typeUrl": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.listener.v3.Listener",
"configStatus": "SYNCED" # xDS API는 최신 상태로 동기화됬다
},
{
"typeUrl": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.route.v3.RouteConfiguration",
"configStatus": "SYNCED" # xDS API는 최신 상태로 동기화됬다
},
{
"typeUrl": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.endpoint.v3.ClusterLoadAssignment",
"configStatus": "SYNCED" # xDS API는 최신 상태로 동기화됬다
},
{
"typeUrl": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.cluster.v3.Cluster",
"configStatus": "SYNCED" # xDS API는 최신 상태로 동기화됬다
},
...
# 하위 명령 출력 내용과 동일
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl x internal-debug -h
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl x internal-debug syncz
- 노출된 정보는 이스티오 파일럿 디버그 엔드포인트들이 노출하는 정보의 부분집합이다.
- 또한 istioctl에 새로 추가된 istioctl x internal-debug 명령어가 동일한 엔드포인트를 노출한다.
- 이들이 노출하는 이런 포트와 서비스에 대한 지식은 트러블슈팅을 더 쉽게 만든다.
- 따라서 최신 엔보이 설정을 쿼리할 수도 있고, DNS 해석을 직접 시험해볼 수도 있으며, 구성 요소의 동작을 알아보고자 메트릭을 퀴리할 수도 있다.
- 다음으로 이스티오 파일럿이 노출하는 것들을 살펴보자.
D.2 이스티오 파일럿(ControlPlane 영역에서 확인)이 노출하는 정보
- Information exposed by the Istio Pilot
- 파일럿은 서비스 메시를 검사하고 디버깅하기 위한 정보들도 노출한다.
- 이 정보는 서비스 메시 운영자는 물론이고 외부 서비스들에도 유용하다.
- 이스티오 파일럿이 열어둔 포트를 확인
#
kubectl -n istio-system exec -it deploy/istiod -- netstat -tnl
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:9876 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::15017 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::15014 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::15012 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::15010 :::* LISTEN
tcp6 0 0 :::8080 :::* LISTEN
# pilot-discovery 프로세스 확인
kubectl -n istio-system exec -it deploy/istiod -- ss -tnlp
State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port Process
LISTEN 0 4096 127.0.0.1:9876 0.0.0.0:* users:(("pilot-discovery",pid=1,fd=8))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:15017 *:* users:(("pilot-discovery",pid=1,fd=12))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:15014 *:* users:(("pilot-discovery",pid=1,fd=9))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:15012 *:* users:(("pilot-discovery",pid=1,fd=10))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:15010 *:* users:(("pilot-discovery",pid=1,fd=11))
LISTEN 0 4096 *:8080 *:* users:(("pilot-discovery",pid=1,fd=3))
#
kubectl describe pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod
...
Containers:
discovery:
Container ID: containerd://f13d7ad8a32cc0cecf47392ef426ea4687ce12d1abf64b5a6d2a60c2f8934e04
Image: docker.io/istio/pilot:1.17.8
Image ID: docker.io/istio/pilot@sha256:cb9e7b1b1c7b8dcea37d5173b87c40f38a5ae7b44799adfdcf8574c57a52ad2c
Ports: 8080/TCP, 15010/TCP, 15017/TCP
Host Ports: 0/TCP, 0/TCP, 0/TCP
Args:
discovery
--monitoringAddr=:15014
--log_output_level=default:info
--domain
cluster.local
--keepaliveMaxServerConnectionAge
30m
...
Readiness: http-get http://:8080/ready delay=1s timeout=5s period=3s #success=1 #failure=3
Environment:
REVISION: default
JWT_POLICY: third-party-jwt
PILOT_CERT_PROVIDER: istiod
POD_NAME: istiod-8d74787f-ltkhs (v1:metadata.name)
POD_NAMESPACE: istio-system (v1:metadata.namespace)
SERVICE_ACCOUNT: (v1:spec.serviceAccountName)
KUBECONFIG: /var/run/secrets/remote/config
PILOT_TRACE_SAMPLING: 100
PILOT_ENABLE_PROTOCOL_SNIFFING_FOR_OUTBOUND: true
PILOT_ENABLE_PROTOCOL_SNIFFING_FOR_INBOUND: true
ISTIOD_ADDR: istiod.istio-system.svc:15012
PILOT_ENABLE_ANALYSIS: false
CLUSTER_ID: Kubernetes
...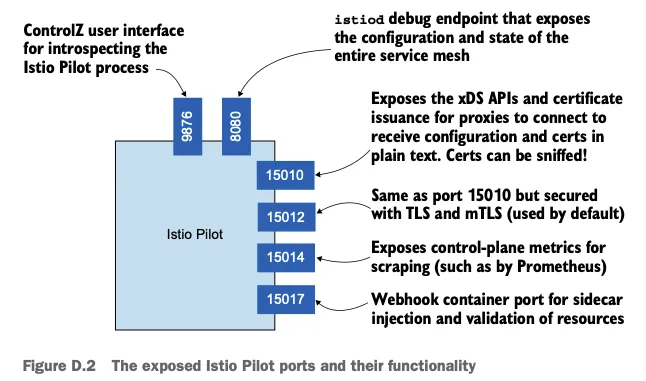
- 서비스용 포트
- 15010 : xDS API 및 인증서 발급을 평문으로 노출한다. 트래픽을 스니핑할 수 있으므로 이 포트는 사용하지 않는 것이 좋다.
- 15012 : 15010 포트와 노출하는 정보는 같지만 보안을 적용한다. 이 포트는 TLS를 사용해 ID를 발급하여, 후속 요청은 상호 인증된다.
- 15014 : 11장에서 다룬 것과 같은 컨트롤 플레인 메트릭을 노출한다.
- 15017 : 쿠버네티스 API 서버가 호출하는 웹훅 서버를 노출한다.
- 쿠버네티스 API 서버는 새로 만들어진 파드에 사이드카를 주입하고, Gateway나 VirtualServie 같은 이스티오 리소스를 검증하기 위해 호출한다.
- 디버깅 및 검사 포트
- 8080 : 이스티오 파일럿 디버그 엔드포인트를 노출한다.
- 9876 : istiod 프로세스에 대한 검사 정보를 노출한다.
D.2.1 이스티오 파일럿 디버그 엔드포인트 The Istio Pilot debug endpoints
- 이스티오 파일럿 디버그 엔드포인트는 파일럿이 알고 있는 전체 서비스 메시의 설정과 상태를 노출한다.
- 엔드포인트는 다음과 같은 질문들에 답한다.
- 프록시는 동기화됐는가? Are the proxies synchronized?
- 프록시에 대한 마지막 푸시는 언제 수행됐는가? When was the last push to a proxy performed?
- xDS API의 상태는 어떤가? What’s the state of the xDS APIs?
- 디버그 엔드포인트로 접근해보자
#
kubectl -n istio-system port-forward deploy/istiod 8080
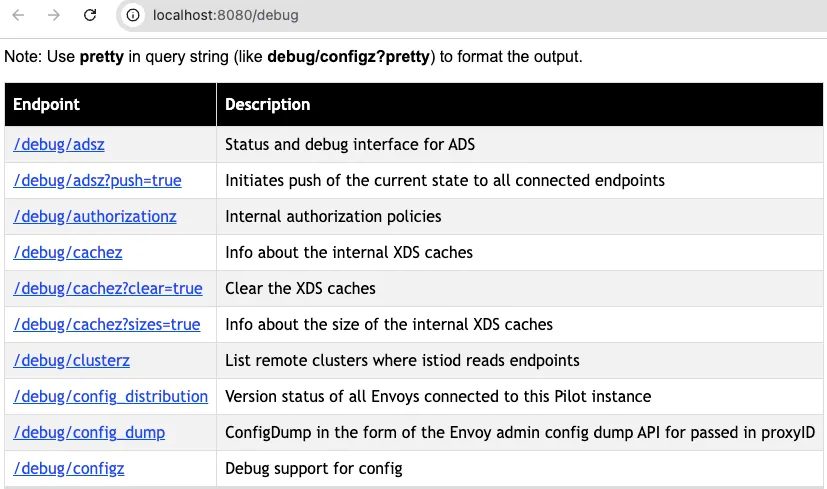
open http://localhost:8080/debug
# 파일럿이 알고 있는 서비스 메시 상태
## 클러스터, 루트, 리스너 설정
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/adsz | jq
## 이 파일럿이 관리하는 모든 프록시에 대한 푸시를 트리거한다.
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/adsz?push=true
Pushed to 4 servers
## /debug/edsz=proxyID=<pod>.<namespace> : 프록시가 알고 있는 엔드포인트들
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/edsz=proxyID=webapp.istioninaction
## /debug/authorizationz : 네임스페이스에 적용되는 인가 정책 목록
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/authorizationz | jq
# 파일럿이 알고 있는 데이터 플레인 설정을 나타내는 엔드포인트
## 이 파일럿 인스턴스에 연결된 모든 엔보이의 버전 상태 : 현재 비활성화되어 있음
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/config_distribution
Pilot Version tracking is disabled. It may be enabled by setting the PILOT_ENABLE_CONFIG_DISTRIBUTION_TRACKING environment variable to true
## 이스티오 파일럿의 현재 알려진 상태에 따라 엔보이 설정을 생성한다.
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/config_dump?=proxyID=webapp.istioninaction
## 이 파일럿이 관리하는 프록시들을 표시한다.
curl -s http://localhost:8080/debug/syncz | jq
...
{
"cluster_id": "Kubernetes",
"proxy": "webapp-7685bcb84-lwsvj.istioinaction",
"istio_version": "1.17.8",
"cluster_sent": "ff5e6b2c-e857-4e12-b17e-46ad968567f4",
"cluster_acked": "ff5e6b2c-e857-4e12-b17e-46ad968567f4",
"listener_sent": "7280c908-010d-4788-807f-7138e74fe72e",
"listener_acked": "7280c908-010d-4788-807f-7138e74fe72e",
"route_sent": "2a1916c3-9c05-4ce5-8cfa-d777105b9205",
"route_acked": "2a1916c3-9c05-4ce5-8cfa-d777105b9205",
"endpoint_sent": "dffacd32-2674-4e39-8e76-17016ff32514",
"endpoint_acked": "dffacd32-2674-4e39-8e76-17016ff32514"
},
...
☞ 디버그 엔드포인트가 노출될 경우 오용될 수 있는 민감 정보가 포함돼 있다. 운영 환경에서는 이스티오를 설치할 때 환경 변수 ENABLE_DEBUG_ON_HTTP 를 false 로 설정해 디버그 엔드포인트를 비활성화를 권장한다. 이렇게 하면 해당 엔드포인트에 의존하는 도구가 제 역할을 할 수 없지만, 향후 릴리스에서는 이러한 엔드포인트가 xDS를 통해 안전하게 노출될 것이다.
Doing so will break the functionality of tools dependent on those endpoints; however, in future releases, these endpoints will be exposed securely over xDS.
- 파일럿이 알고 있는 서비스 메시 상태를 나타내는 엔드포인트
- /debug/adsz : 클러스터, 루트, 리스너 설정
- /debug/adsz?push=true : 이 파일럿이 관리하는 모든 프록시에 대한 푸시를 트리거한다.
- /debug/edsz=*proxyID*=*<pod>.<namespace>* : 프록시가 알고 있는 엔드포인트들
- /debug/authorizationz : 네임스페이스에 적용되는 인가 정책 목록
- 파일럿이 알고 있는 데이터 플레인 설정을 나타내는 엔드포인트
- /debug/config_distribution : 이 파일럿 인스턴스에 연결된 모든 엔보이의 버전 상태
- /debug/config_dump?proxyID=<pod>.<namespace> : 이스티오 파일럿의 현재 알려진 상태에 따라 엔보이 설정을 생성한다.
- /debug/syncz : 이 파일럿이 관리하는 프록시들을 표시한다.
- 또한 프록시로 보낸 최신 논스 nonce 와 응답받은 최신 논스도 보여준다. 이 둘이 동일하면 프록시의 설정이 최신인 것이다.
- 서비스 메시 운영자는 보통 키알리, istioctl 등 다른 도구를 통해 엔드포인트를 간접적으로 사용할 것이다.
- 예를 들어 istioctl proxy-status 명령어는 프록시가 동기화됐는지 확인하기 위해 /debug/syncz 엔드포인트를 사용한다.
- 그러나 이런 도구가 제공하는 정보로 충분하지 않을 때는 직접 디버그 엔드포인트를 사용해 더 깊이 파고들 수 있다.
D.2.2 ControlZ 인터페이스
- 이스티오 파일럿에는 파일럿 프로세스의 현재 상태와 몇 가지 사소한 설정 가능성을 확인 할 수 있는 관리자 인터페이스가 함께 제공된다.
- 이 인터페이스는 아래 표 D.1 에서 다룬 것 처럼 파일럿 인스턴스와 관련된 정보를 빠르게 조회할 수 있다.
| 페이지 | 설명 |
| 로깅 범위 Logging Scopes | 이 프로세스에 대한 로깅은 범위별로 구성돼 있어 범위별로 로깅 단계를 별도로 설정할 수 있다. |
| 메모리 사용량 Memory Usage | 이 정보는 Go 런타임에서 수집되며 이 프로세스의 메모리 소비량을 나타낸다. |
| 환경 변수 Environment Variables | 이 프로세스에 정의된 환경 변수 집합이다. |
| 프로세스 정보 Process Information | 이 프로세스에 대한 정보다. |
| 명령줄 인수 Command-Line Arguments | 이 프로세스를 시작할 때 사용한 명령줄 인수 집합이다. |
| 버전 정보 Version Info | 바이너리(예: 이스티오 파일럿 1.7.3)와 Go 런타임(go 1.14.7)에 대한 정보다. |
| 메트릭 Metrics | 파일럿에서 노출하는 메트릭을 가져오는 방법 중 하나다. |
| 시그널 Signals | 실행 중인 프로세스에 SUGUSR1 시그널을 보낼수 있다. |
- 접속 확인
#
kubectl -n istio-system port-forward deploy/istiod 9876
open http://localhost:9876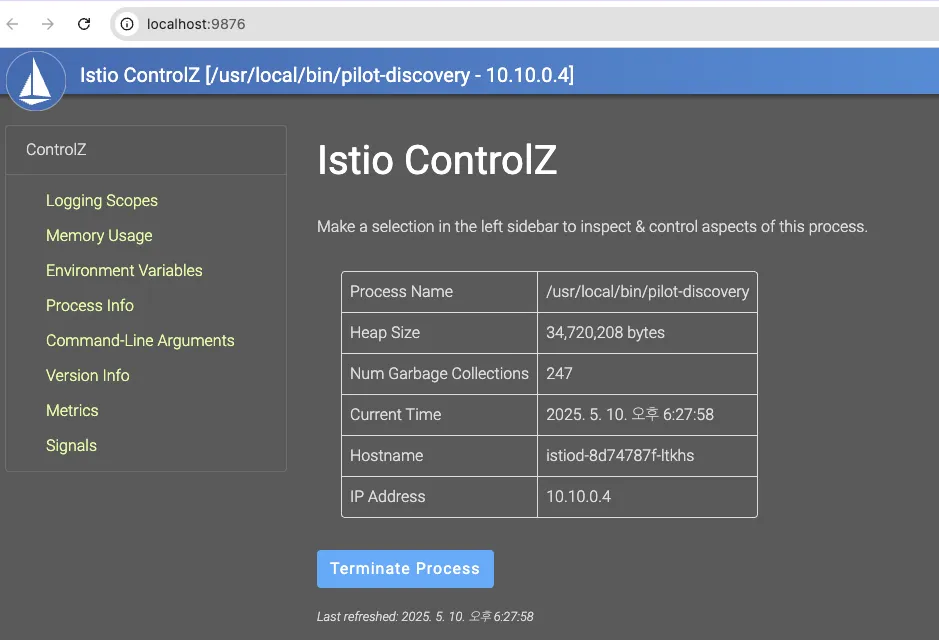
11장. 튜닝
☞ This chapter covers Performance-tuning the control plane
- 컨트롤 플레인 성능에 영향을 미치는 요소 이해하기 Understanding the factors of control-plane performance
- 성능 모니터링 방법 알아보기 How to monitor performance
- 주요 성능 메트릭 알아보기 What are the key performance metrics
- 성능 최적화 방법 이해하기 Understanding how to optimize performance
▶ 들어가며 : 컨트롤 플레인 성능 최적화
- 데이터 플레인 문제 해결을 다룬 앞 장에서는 프록시 설정 및 동작 문제를 진단하는 데 사용할 수 있는 디버깅 도구를 자세히 살펴봤다.
- 서비스 프록시 설정을 이해하면 예상과 다를 때 문제를 해결하는 것이 간단해진다.
- 이번 장에서는 컨트롤 플레인 성능 최적화에 초점을 맞춘다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 어떻게 서비스 프록시를 설정하는지, 이 과정을 느리게 만드는 요인이 무엇인지, 이 과정을 어떻게 모니터링하는지, 성능을 향상시키기 위해 조정할 수 있는 변수는 무엇인지 등을 알아본다.
[ 11장 환경 설치 ]
▶ [실습 환경 구성] k8s(1.23.17) 배포 : NodePort(30000 HTTP, 30005 HTTPS)
#
git clone https://github.com/AcornPublishing/istio-in-action
cd istio-in-action/book-source-code-master
pwd # 각자 자신의 pwd 경로
code .
# 아래 extramounts 생략 시, myk8s-control-plane 컨테이너 sh/bash 진입 후 직접 git clone 가능
kind create cluster --name myk8s --image kindest/node:v1.23.17 --config - <<EOF
kind: Cluster
apiVersion: kind.x-k8s.io/v1alpha4
nodes:
- role: control-plane
extraPortMappings:
- containerPort: 30000 # Sample Application (istio-ingrssgateway) HTTP
hostPort: 30000
- containerPort: 30001 # Prometheus
hostPort: 30001
- containerPort: 30002 # Grafana
hostPort: 30002
- containerPort: 30003 # Kiali
hostPort: 30003
- containerPort: 30004 # Tracing
hostPort: 30004
- containerPort: 30005 # Sample Application (istio-ingrssgateway) HTTPS
hostPort: 30005
- containerPort: 30006 # TCP Route
hostPort: 30006
- containerPort: 30007 # kube-ops-view
hostPort: 30007
extraMounts: # 해당 부분 생략 가능
- hostPath: /Users/gasida/Downloads/istio-in-action/book-source-code-master # 각자 자신의 pwd 경로로 설정
containerPath: /istiobook
networking:
podSubnet: 10.10.0.0/16
serviceSubnet: 10.200.1.0/22
EOF
# 설치 확인
docker ps
# 노드에 기본 툴 설치
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane sh -c 'apt update && apt install tree psmisc lsof wget bridge-utils net-tools dnsutils tcpdump ngrep iputils-ping git vim -y'
# (옵션) kube-ops-view
helm repo add geek-cookbook https://geek-cookbook.github.io/charts/
helm install kube-ops-view geek-cookbook/kube-ops-view --version 1.2.2 --set service.main.type=NodePort,service.main.ports.http.nodePort=30007 --set env.TZ="Asia/Seoul" --namespace kube-system
kubectl get deploy,pod,svc,ep -n kube-system -l app.kubernetes.io/instance=kube-ops-view
## kube-ops-view 접속 URL 확인
open "http://localhost:30007/#scale=1.5"
open "http://localhost:30007/#scale=1.3"
# (옵션) metrics-server
helm repo add metrics-server https://kubernetes-sigs.github.io/metrics-server/
helm install metrics-server metrics-server/metrics-server --set 'args[0]=--kubelet-insecure-tls' -n kube-system
kubectl get all -n kube-system -l app.kubernetes.io/instance=metrics-server
▶ [실습 환경 구성] istio 1.17.8 설치 - Docs , Install , profile
# myk8s-control-plane 진입 후 설치 진행
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane bash
-----------------------------------
# (옵션) 코드 파일들 마운트 확인
tree /istiobook/ -L 1
혹은
git clone ... /istiobook
# istioctl 설치
export ISTIOV=1.17.8
echo 'export ISTIOV=1.17.8' >> /root/.bashrc
curl -s -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=$ISTIOV sh -
cp istio-$ISTIOV/bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/istioctl
istioctl version --remote=false
# demo 프로파일 컨트롤 플레인 배포
istioctl install --set profile=demo --set values.global.proxy.privileged=true --set meshConfig.accessLogEncoding=JSON -y
# 보조 도구 설치
kubectl apply -f istio-$ISTIOV/samples/addons
# 빠져나오기
exit
-----------------------------------
# 설치 확인 : istiod, istio-ingressgateway, crd 등
kubectl get istiooperators -n istio-system -o yaml
kubectl get all,svc,ep,sa,cm,secret,pdb -n istio-system
kubectl get cm -n istio-system istio -o yaml
kubectl get crd | grep istio.io | sort
# 실습을 위한 네임스페이스 설정
kubectl create ns istioinaction
kubectl label namespace istioinaction istio-injection=enabled
kubectl get ns --show-labels
# istio-ingressgateway 서비스 : NodePort 변경 및 nodeport 지정 변경 , externalTrafficPolicy 설정 (ClientIP 수집)
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 80, "targetPort": 8080, "nodePort": 30000}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 443, "targetPort": 8443, "nodePort": 30005}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway -p '{"spec":{"externalTrafficPolicy": "Local"}}'
kubectl describe svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway
# NodePort 변경 및 nodeport 30001~30003으로 변경 : prometheus(30001), grafana(30002), kiali(30003), tracing(30004)
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system prometheus -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 9090, "targetPort": 9090, "nodePort": 30001}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system grafana -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 3000, "targetPort": 3000, "nodePort": 30002}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system kiali -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 20001, "targetPort": 20001, "nodePort": 30003}]}}'
kubectl patch svc -n istio-system tracing -p '{"spec": {"type": "NodePort", "ports": [{"port": 80, "targetPort": 16686, "nodePort": 30004}]}}'
# Prometheus 접속 : envoy, istio 메트릭 확인
open http://127.0.0.1:30001
# Grafana 접속
open http://127.0.0.1:30002
# Kiali 접속 1 : NodePort
open http://127.0.0.1:30003
# (옵션) Kiali 접속 2 : Port forward
kubectl port-forward deployment/kiali -n istio-system 20001:20001 &
open http://127.0.0.1:20001
# tracing 접속 : 예거 트레이싱 대시보드
open http://127.0.0.1:30004
11.1 컨트롤 플레인의 주요 목표
☞ https://netpple.github.io/docs/istio-in-action/Istio-ch11-performance
▶ 들어가며 : 유령 워크로드와 대응 방안
- 이번 장에서 컨트롤 플레인은 서비스 메시의 두뇌이며 서비스 메시 운영자를 위해 API를 노출한다고 했었다.
- 이 API를 사용하면, 메시의 동작을 조작하고 각 워크로드 인스턴스에 함께 배포된 서비스 프록시를 설정할 수 있다.
- 간결함을 위해 앞서 생략했던 내용이 있는데, 서비스 메시 운영자(즉, 우리)가 이 API에 요청을 하는 것이 메시의 동작과 설정에 영향을 미치는 유일한 방법은 아니라는 점이다.
- 좀 더 일반적으로 말하면 컨트롤 플레인은 런타임 환경의 세부적인 내용들을 추상화하는데, 어떤 서비스가 존재하는지(서비스 디스커버리), 어떤 서비스가 정상인지와 오토스케일링 이벤트 등이 해당된다.
- 이스티오의 컨트롤 플레인은 쿠버네티스의 이벤트를 수신하고, 원하는 새 상태를 반영하고자 설정을 업데이트한다.
- 이 상태 조정 절차는 올바르게 동작하는 메시를 유지하기 위해 계속되며, 시기적절하게 일어나는 것이 중요하다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 상태 조정 절차를 적시에 하지 못할 때마다 예기치 못한 결과로 이어지는데, 워크로드는 이미 바뀐 상태로 설정돼 있기 때문이다.
- 성능 저하될 때 발생하는 흔한 증상을 ‘유령 워크로드 phantom workload’ 라고 하는데, 이미 사라진 엔드포인트로 트래픽을 라우팅하도록 서비스가 설정돼 있으므로 요청이 실패한다.
- 그림 11.1은 유령 워크로드의 개념을 보여준다.
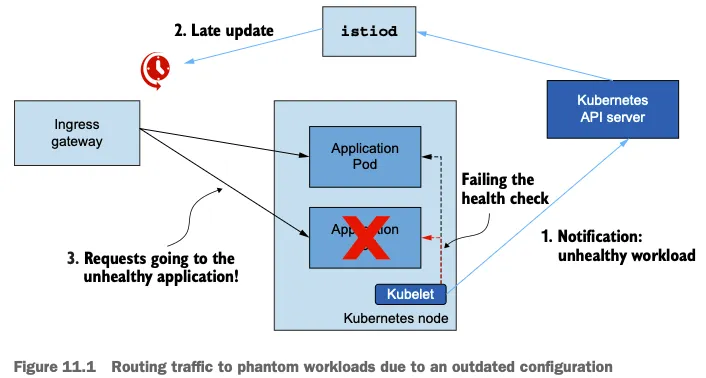
- 비정상이 된 워크로드가 이벤트를 트리거한다.
- 업데이트가 지연되면 서비스가 낡은 설정을 지니게 된다.
- 오래된? 설정 때문에 서비스가 트래픽이 존재하지 않은 워크로드로 라우팅한다.
- 데이터 플레인의 궁극적 일관성 eventually consistent 성질 덕분에 설정이 잠깐 낡은 것은 그리 문제가 되지 않는다.
- 다른 보호 기체를 사용할 수 있기 때문이다. as other protective mechanisms can be employed.
- 예를 들어 네트워크 문제로 요청이 실패하면 요청은 기본적으로 두 번 재시도되므로, 아마도 다른 정상 엔드포인트가 처리할 것이다.
- 또 다른 교정 방법으로는 이상값 감지가 있는데, 엔드포인트로 보낸 요청이 실패했을 때 클러스터에서 엔드포인트를 배제하는 것이다.
- 그러나 지연이 몇 초를 넘어가면 최종 사용자에게 부정적인 영향을 미칠 수 있으므로 반드시 피해야 한다.
- 이 장에서는 바로 이 내용을 주로 다룬다.
11.1.1 데이터 플레인 동기화 단계 이해하기
- Understanding the steps of data-plane synchronization : 디바운스와 스로틀링
- 데이터 플레인을 원하는 상태로 동기화하는 과정은 여러 단계로 수행된다.
- 컨트롤 플레인은 쿠버네티스에서 이벤트를 수신한다.
- 이벤트는 엔보이 설정으로 변환돼 데이터 플레인의 서비스 프록시로 푸시된다.
- 이 과정을 이해하면 컨트롤 플레인 성능을 미세 조정하고 최적화할 때 이뤄지는 의사결정에 도움이 된다.
- 그림 11.2는 들어오는 변경 사항에 맞춰 데이터 플레인을 동기화하는 단계를 순서대로 보여준다.
- 들어오는 이벤트가 동기화 과정을 시작한다. An incoming event triggers the synchronization process.
- istiod 의 DiscoveryServer 구성 요소가 이 이벤트들을 수신한다. The DiscoveryServer component of istiod listens for these events.
- 성능을 향상시키기 위해, 푸시 대기열에 이벤트를 추가하는 작업을 일정 시간 미루고 그 동안의 후속 이벤트를 병합해 일괄 처리한다.
- 이를 ‘디바운스 debounce 한다’고 말하는데, 디바운스는 시간을 잡아먹는 작업이 너무 자주 실행되지 않도록 해준다.
- 지연 시간이 만료되면, DiscoveryServer가 병합된 이벤트를 푸시 대기열에 추가한다. 푸시 대기열은 처리 대기 중인 푸시 목록을 유지 관리한다.
- After the delay period expires, the DiscoveryServer adds the merged events to the push queue, which maintains a list of pushes waiting to be processed.
- istiod 서버는 동시에 처리되는 푸시 요청 개수를 제한 throttle 하는데, 이는 처리 중인 항목이 더 빨리 처리되도록 보장하고 CPU 시간이 작업 간 콘텍스트 스위칭에 낭비되는 것을 방지한다. The istiod server throttles (limits) the number of push requests that are processed concurrently, which ensures that faster progress is made on the items being processed and prevents CPU time from being wasted on context switching between the tasks.
- 처리된 항목은 엔보이 설정으로 변환돼 워크로드로 푸시된다. The items that are processed are converted to Envoy configuration and pushed to the workloads.
- 여기서는 이스티오가 디바운스(디바운싱 debouncing)와 스로틀링 throttling 이라는 두 가지 방법을 사용해 과부하되지 않도록 스스로를 보호하는 방법을 다룬다.
- 추후 살펴보겠지만 디바운스와 스로틀링은 성능을 향상시키기 위해 설정할 수 있는 것이다.
11.1.2 성능을 결정짓는 요소
- Factors that determine performance : 변경 속도, 할당된 리소스, 업데이트할 워크로드 개수, 설정 크기
- 동기화 프로세스를 잘 이해하면, 컨트롤 플레인의 성능에 영향을 미치는 요소를 자세히 설명할 수 있다. (그림 11.3 참조)
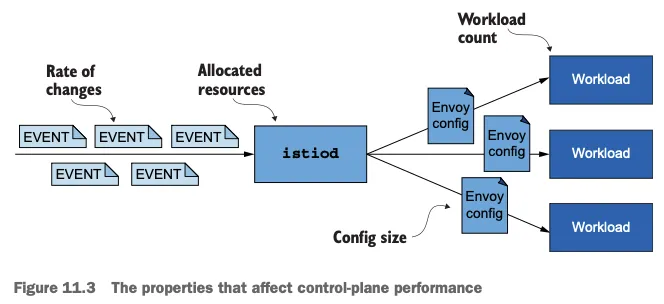
- 변경 속도 The rate of changes
- 변경 속도가 빠를수록 데이터 플레인을 동기화 상태로 유지하는 데 더 많은 처리가 필요하다. A higher rate of changes requires more processing to keep the data plane synchronized.
- 할당된 리소스 Allocated resources
- 수요가 istiod에 할당된 리소스를 넘어서면 작업을 대기열에 넣어야하므로 업데이트 배포가 느려진다. If the demand exceeds the resources allocated to istiod, work has to be queued, which results in a slower distribution of updates.
- 업데이트할 워크로드 개수 Number of workloads to update
- 더 많은 워크로드에 업데이트를 배포하려면 네트워크 대역폭과 처리 능력이 더 많이 필요하다. More processing power and network bandwidth are required to distribute updates to more workloads.
- 설정 크기 Configuration size
- 더 큰 엔보이 구성을 배포하려면 처리 능력과 네트워크 대역폭이 더 많이 필요하다. The distribution of larger Envoy configurations requires more processing power and more network bandwidth.
- 이 요소들에 맞게 성능을 최적화하는 방법을 다룰 것이다.
- 그러니 그 전에 프로메테우스가 istiod에서 수집한 메트릭을 시각화한 그라파나 대시보드(8장에서 준비함)를 사용해 병목 지점을 판단하는 방법을 배워보자.
11.2 컨트롤 플레인 모니터링하기
▶ 들어가며 : Monitoring the control plane
- istiod는 핵심 성능 지표의 지속 시간 및 빈도를 측정하는 메트릭을 노출하는데, 여기에는 리소스 사용률, 수신 또는 발신 트래픽으로 인한 부하, 오류 비율 등이 있다.
- 이런 지표들은 제어 평면의 성능이 어떤지, 어떤 것이 곧 문제를 일으킬지, 이미 올바르게 동작하지 않는 것을 어떻게 트러블슈팅해야 하는지를 밝히는 데 도움을 준다.
- 노출되는 메트릭들은 이스티오 공식 문서에 기술돼 있는데, 메트릭 개수는 방대하다 - Docs
- 여기서는 주목해야 할 핵심 메트릭을 식별하고, 네 가지 황금 신호에 대략 맞도록 메트릭을 정리해볼 것이다
11.2.1 컨트롤 플레인의 네 가지 황금 신호
- The four golden signals of the control plane (실습~)
▶ 들어가며 : 실습환경 초기화
- 구글 SRE 책에서 정의한 네 가지 황금 신호란 서비스가 어떻게 동작하는지에 대한 외부의 시각을 이해하기 위해 모니터링해야 하는 네 가지 주요 메트릭을 말한다.
- 특정 서비스가 자신의 서비스 수준 목표 SLO 에서 벗어난 경우, 황금 메트릭을 통해 원인을 분석하는 통찰력을 얻을 수 있다.
- 네 가지 신호는 지연 시간, 포화도, 오류, 트래픽이다.
- 컨트롤 플레인의 메트릭을 빠르게 살펴보려면 다음 명령어로 쿼리하면 된다.
# 실습 환경 준비
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f services/catalog/kubernetes/catalog.yaml
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f ch11/catalog-virtualservice.yaml
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f ch11/catalog-gateway.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get deploy,gw,vs -n istioinaction
# 반복 설정 해두기
while true; do curl -s http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items ; date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ; sleep 1; echo; done
# 컨트롤 플레인 메트릭 확인
kubectl exec -it -n istio-system deploy/istiod -- curl localhost:15014/metrics
# HELP citadel_server_csr_count The number of CSRs received by Citadel server.
# TYPE citadel_server_csr_count counter
citadel_server_csr_count 3
...- 이 장의 나머지 부분에서는 그라파나 대시보드로 이 메트릭들을 조사한다.
▶ 지연 시간: 데이터 플레인을 업데이트하는 데 필요한 시간
( LATENCY: THE TIME NEEDED TO UPDATE THE DATA PLANE )
- 지연 시간 신호를 사용하면 서비스가 어떻게 동작하는지를 서비스 외부의 최종 사용자 관점으로 알 수 있다.
- 지연 시간이 증가하면 서비스의 성능이 저하된 것이다. 그러나 성능 저하의 원인이 무엇인지는 알 수 없다.
- 원인을 알려면 다른 신호를 조사해야 한다.
- 이스티오 컨트롤 플레인에서 지연 시간은 컨트롤 플레인이 데이터 플레인에 업데이트를 얼마나 빠릴 배포하는지로 측정한다.
- 지연 시간을 측정하는 주요 메트릭은 pilot_proxy_convergence_time 이다.
- 그러나 동기화 절차 중 대부분의 시간을 소비하는 단계의 이해를 돕는 보조 메트릭도 두 가지 있는데, 하나는 pilot_proxy_queue_time 이고 다른 하나는 pilot_xds_push_time 이다.
- 그림 11.4는 동기화 단계 중 이 메트릭이 다루는 부분을 보여준다.
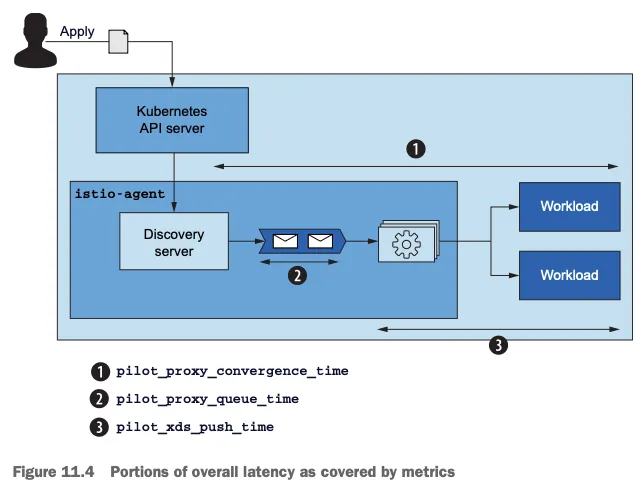
- pilot_proxy_convergence_time 은 프록시 푸시 요청이 대기열에 안착한 순간부터 워크로드에 배포되기까지 전체 과정의 지속 시간을 측정한다.
measures the entire process’s duration from the time a proxy push request lands in the queue until it is distributed to the workloads. - pilot_proxy_queue_time 은 워커가 처리할 때까지 푸시 요청이 대기열에서 기다린 시간을 측정한다. 푸시 대기열에서 상당한 시간이 걸리는 경우, istiod를 수직으로 확장해 동시 처리 능력을 높일 수 있다.
measures the time the push requests wait in the queue until they are processed by a worker. If a considerable amount of time is spent in the push queue, we might scale istiod vertically and increase the concurrent processing power. - pilot_xds_push_time 은 엔보이 설정을 워크로드로 푸시하는 데 필요한 시간을 측정한다. 시간이 늘어나면, 전송되는 데이터양 때문에 네트워크 대역폭이 과부하된 것이다. 설정 업데이트 크기와 워크로드별 변화 빈도를 줄임으로써 이 상황을 상당히 개선할 수 있는 방법을 뒷부분에서 살펴본다.
measures the time required to push the Envoy configuration to workloads. An increase shows that network bandwidth is overloaded by the amount of data being transferred. We see in later sections how sidecars can considerably improve this situation by reducing the size of configuration updates and frequency of changes per proxy.
- pilot_proxy_convergence_time 은 그라파나 대시보드에서 시각화하고 있는데, Istio Control Plane 대시보드의 Proxy Push Time이라는 Pilot Push 정보 부분에 있다.
- 위 그래프는 푸시의 99.9%는 워크로드에 배포하는 데 걸리는 시간이 100ms 미만임. 이상적이다!
histogram_quantile(0.5, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.9, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.99, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.999, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
(참고) 프로메테우스 쿼리 : le (누적 카운트) “less than or equal”
pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket
# le="0.1": 0.1초 이하로 동기화 완료된 프록시가 10개
# le="1": 1초 이하로 완료된 프록시가 누적 20개
# le="+Inf": 모든 프록시 포함 → 누적 41개
...
pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m]
rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])
sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m]))
sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le)
histogram_quantile(0.5, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.9, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
...
☞ 그라파나 대시보드에 2개의 패널(메트릭) 추가 하자 !!
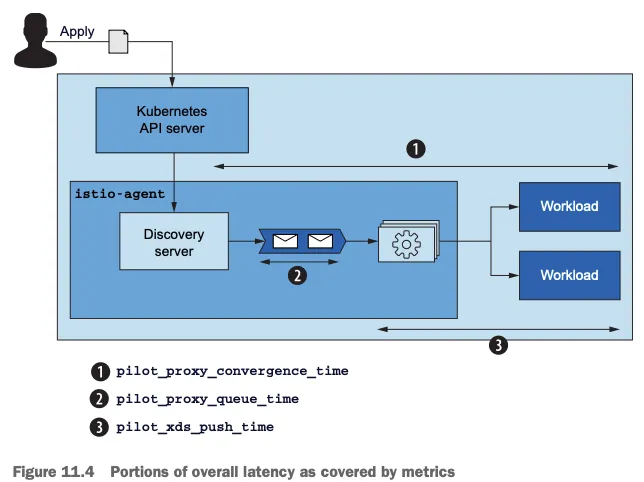
1) 대시보드 편집 설정
2) 기존 Proxy Push Time 패널 복제 하기
- Proxy Queue Time : PromQL - pilot_proxy_queue_time
histogram_quantile(0.5, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_queue_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.9, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_queue_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.99, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_queue_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.999, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_queue_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))- XDS Push Time : PromQL - pilot_xds_push_time_bucket
histogram_quantile(0.5, sum(rate(pilot_xds_push_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.9, sum(rate(pilot_xds_push_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.99, sum(rate(pilot_xds_push_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
histogram_quantile(0.999, sum(rate(pilot_xds_push_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))
- 패널 위치 취향에 따라 배치
☞ 시간이 지나면 , 하기와 같이 데이터가 들어와 그래프 패턴을 확인 할 수 있다!!
- 메시에 워크로드를 추가하면 이런 다양한 메트릭에서 지연 시간이 서서히 증가한다.
- 이는 당연한 일이므로 약간 증가하는 것은 걱정하지 않아도 된다.
- 다만, 허용할 수 있는 임계값은 정의하고 지연 시간이 허용할 수 있는 한계를 넘어가면 얼럿을 트리거해야 한다.
- 다음 기준으로 임계값을 고려하는 것을 권장한다.
- Warning 심각도 severity : 10초 이상 동안 지연 시간이 1초를 초과하는 경우
- Critical 심각도 severity : 10초 이상 동안 지연 시간이 2초를 초과하는 경우
- 첫 번째 얼럿을 받았을 때는 겁 먹을 필요 없다. 단지 서비스 지연 시간이 증가했고 성능 최적화가 필요하다는 조치 요청일 뿐이다.
- 그러나 확인하지 않고 방치하면 성능이 더 저하돼 최종 사용자에게 영향을 미칠 것이다.
- 지연 시간이 늘어났다는 것은 컨트롤 플레인 성능이 저하됐음을 알리는 가장 좋은 지표이지만, 성능 저하 원인에 대한 정보를 더 주지는 않는다.
- 저하 원인을 알아보려면 다른 메트릭을 더 깊이 파고들어야 한다.
▶ 포화도: 컨트롤 플레인이 얼마나(CPU, MEM 리소스) 가득 차 있는가?
( SATURATION: HOW FULL IS THE CONTROL PLANE? )
- 포하도 메트릭은 리소스 사용량을 보여준다.
The saturation metrics show the capacity at which resources are being utilized. - 사용률이 90% 이상이면 서비스는 포화된 것이거나 곧 포화된다.
If utilization is over 90%, the service is saturated or about to become so. - istiod가 포화되면 배포 업데이트가 느려진다. 푸시 요청이 대기열에서 더 오래 처리를 기다리기 때문이다.
When istiod is saturated, the distribution updates slow down as push requests are queued for longer periods, waiting to be processed.
- 포화는 보통 가장 제한적인 리소스 때문에 일어난다. istiod는 CPU 집중적이므로, 보통은 CPU가 가장 먼저 포화되기 때문에 CPU 사용률을 측정한다.
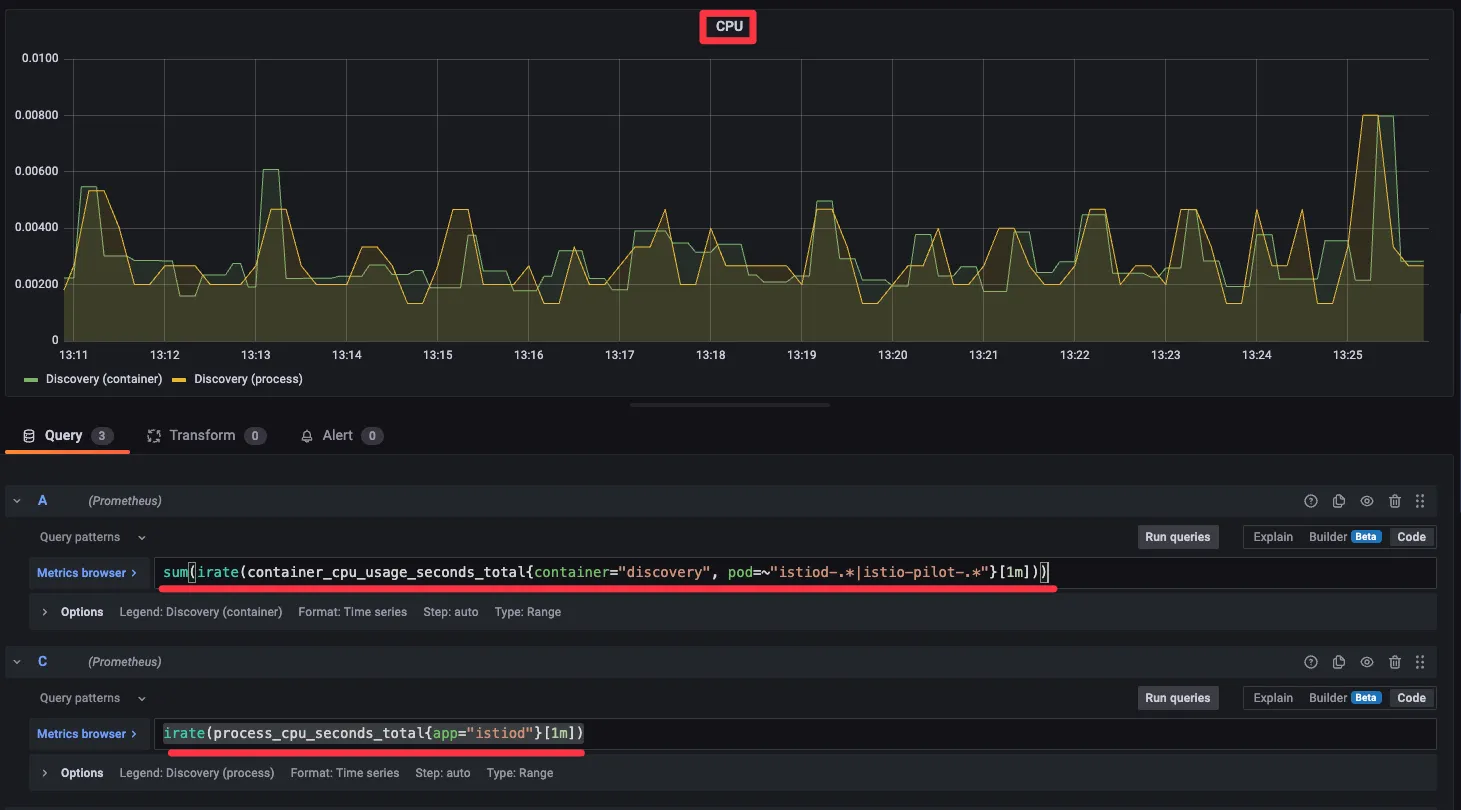
a. container_cpu_usage_seconds_total : 쿠버네티스 컨테이너가 보고하는 (istiod 파드) CPU 사용률을 측정한다 - Docs
# Cumulative cpu time consumed by the container in core-seconds
container_cpu_usage_seconds_total
container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{container="discovery"}
container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{container="discovery", pod=~"istiod-.*|istio-pilot-.*"}
sum(irate(container_cpu_usage_seconds_total{container="discovery", pod=~"istiod-.*|istio-pilot-.*"}[1m]))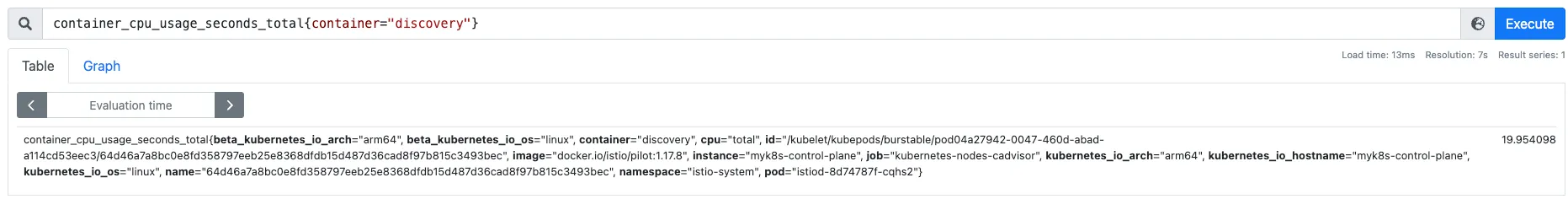
b. process_cpu_seconds_total : istiod 계측이 보고하는 (istiod 파드) CPU 사용률을 측정
# Total user and system CPU time spent in seconds
process_cpu_seconds_total{app="istiod"}
irate(process_cpu_seconds_total{app="istiod"}[1m])
c. (참고) kubectl top 파드/컨테이너 리소스 사용 확인
kubectl top pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod --containers=true
POD NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 discovery 3m 62Mi
kubectl top pod -n istioinaction --containers=true
POD NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
catalog-6cf4b97d-5jtzt catalog 0m 20Mi
catalog-6cf4b97d-5jtzt istio-proxy 6m 46Mi
#
kubectl resource-capacity -n istioinaction -c -u -a
kubectl resource-capacity -n istioinaction -c -u
NODE POD CONTAINER CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS CPU UTIL MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS MEMORY UTIL
myk8s-control-plane * * 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 7m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 67Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane catalog-6cf4b97d-5jtzt * 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 7m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 67Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane catalog-6cf4b97d-5jtzt catalog 0m (0%) 0m (0%) 0m (0%) 0Mi (0%) 0Mi (0%) 21Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane catalog-6cf4b97d-5jtzt istio-proxy 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 7m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 47Mi (0%)
#
kubectl get pod -n istio-system -l istio.io/rev=default
kubectl resource-capacity -n istio-system -c -u
kubectl resource-capacity -n istio-system -c -u -a -l istio.io/rev=default
kubectl resource-capacity -n istio-system -c -u -l istio.io/rev=default
NODE POD CONTAINER CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS CPU UTIL MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS MEMORY UTIL
myk8s-control-plane * * 30m (0%) 4000m (50%) 27m (0%) 180Mi (1%) 2048Mi (17%) 164Mi (1%)
myk8s-control-plane istio-egressgateway-85df6b84b7-m4699 * 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 9m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 49Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane istio-egressgateway-85df6b84b7-m4699 istio-proxy 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 9m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 49Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane istio-ingressgateway-6bb8fb6549-k4ln6 * 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 11m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 50Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane istio-ingressgateway-6bb8fb6549-k4ln6 istio-proxy 10m (0%) 2000m (25%) 11m (0%) 40Mi (0%) 1024Mi (8%) 50Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 * 10m (0%) 0m (0%) 8m (0%) 100Mi (0%) 0Mi (0%) 66Mi (0%)
myk8s-control-plane istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 discovery 10m (0%) 0m (0%) 8m (0%) 100Mi (0%) 0Mi (0%) 66Mi (0%)
☞ https://themapisto.tistory.com/55
[프로메테우스](4) CPU / 메모리 사용률 계산하기
프로메테우스는 PromQL을 사용하여 메트릭을 수집한다. Pod 와 Service 단위의 모니터링을 개발 해야 할 때 , 프로메테우스에서는 쿼리를 통한 가공이 필요하다.container_cpu_seconds_total 데이터와 contai
themapisto.tistory.com
그림 11.6은 CPU 사용률 메트릭을 시각화하는 그래프를 보여준다.
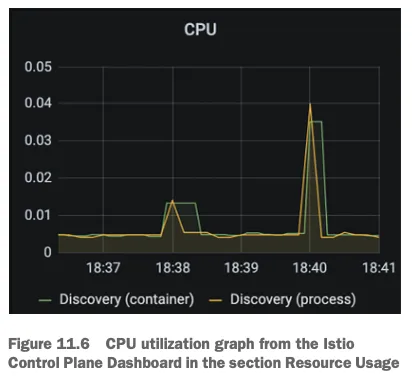
- 이 그래프는 istiod 에서 가장 일반적인 사용 패턴을 나타내는데, 대부분의 시간이 유휴 idle 시간이다.
- 서비스가 배포될 때 컴퓨팅 요청이 급증하는데, istiod가 엔보이 설정을 생성해 모든 워크로드로 푸시하기 때문이다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포하되면 리소스가 부족한 것이므로, 할당량을 다시 생각해야 한다.
- 컨트롤 플레인 동작을 최적화하기 위해 다른 접근법을 시도했었다면, 리소스를 늘리는 것이 최선의 선택일 것이다.
▶ 트래픽: 컨트롤 플레인의 부하는 어느 정도인가?
( TRAFFIC: WHAT IS THE LOAD ON THE CONTROL PLANE? )
- 트래픽은 시스템이 겪는 부하를 측정한다.
The traffic metrics measure the load the system experiences. - 예를 들어, 웹 애플리케이션에서 부하는 초당 요청 수 (rps) 로 정의한다.
for a web application, the load is defined by requests per second - 한편, 이스티오의 컨트롤 플레인에는 수신 트래픽(설정 변경 형태)과 송신 트래픽(데이터 플레인으로 변경 푸시)이 있다. receiving incoming traffic (in the form of configuration changes) outgoing traffic (pushing changes to the data plane)
- 성능을 제한하는 요인을 찾으려면 양방향 트래픽을 모두 측정해야 한다.
- 그리고 그 측정치에 기반해 성능을 개선하는 데 여러 접근 방식을 취할 수 있다.
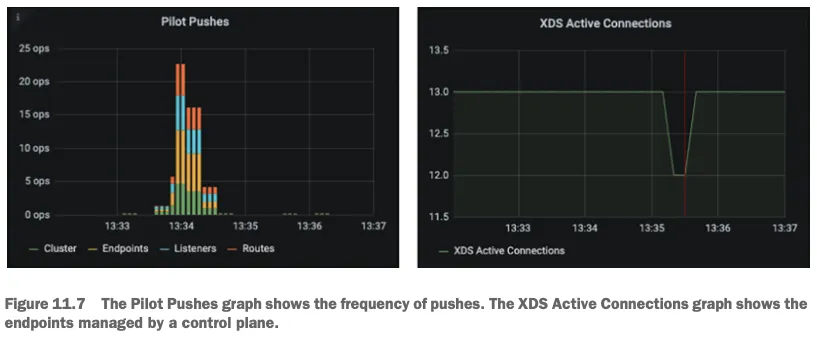
수신 트래픽에 대한 메트릭은 다음과 같다.
- pilot_inbound_updates
- 각 istiod 인스턴스가 설정 변경 수신 횟수를 보여준다. shows the count of configuration updates received per istiod instance
- 해당 메트릭을 사용하는 대시보드와 패널은 어디?
- pilot_push_triggers
- 푸시를 유발한 전체 이벤트 횟수다. the total count of events that triggered a push
- 푸시 원인은 서비스, 엔드포인트, 설정 중 한다. 여기서 설정이란 Gateway나 VirtualService 같은 이스티오 커스텀 리소스를 말한다. service, endpoint, or config, where config represents any Istio custom resource such as Gateway or VirtualService.
- 해당 메트릭을 사용하는 대시보드와 패널은 어디?
- pilot_services
- 파일럿이 인지하고 있는 서비스 개수를 측정한다. measures the number of services known to the pilot.
- 파일럿이 인지하는 서비스 개수가 늘어날수록, 이벤트를 수신할 때 엔보이 설정을 만들어내는 데 필요한 처리가 더 많아진다.
- 따라서, 이 수치는 istiod가 수신 트래픽 때문에 받는 부하량이 결정되는데 중요한 역할을 한다.
# istio vs 개수: kubectl get vs -A --no-headers=true | wc -l
avg(pilot_virt_services{app="istiod"})
# k8s service 개수: kubectl get svc -A --no-headers=true | wc -l
avg(pilot_services{app="istiod"})
발신 트래픽에 대한 메트릭은 다음과 같다.
- pilot_xds_pushes
- 리스너, 루트, 클러스터, 엔드포인트 업데이트와 같이 컨트롤 플레인이 수행하는 모든 유형의 푸시를 측정한다.
- 이 메트릭은 Istio Control Plane 대시보드에서 Pilot Pushes 라는 이름의 그래프(패널)로 표시된다. (그림 11.7 참조)
sum(irate(pilot_xds_pushes{type="cds"}[1m]))
sum(irate(pilot_xds_pushes{type="eds"}[1m]))
sum(irate(pilot_xds_pushes{type="lds"}[1m]))
sum(irate(pilot_xds_pushes{type="rds"}[1m]))
- pilot_xds
- 워크로드로의 전체 커넥션 개수를 파일럿 인스턴스별로 보여준다. total connections to workloads handled per pilot instance.
- 이 메트릭은 Istio Control Plane 대시보드에서 ADS Monitoring 라는 이름의 그래프(패널)로 표시된다.
avg(pilot_virt_services{app="istiod"}) # istio vs 개수: kubectl get vs -A --no-headers=true | wc -l
avg(pilot_services{app="istiod"}) # k8s service 개수: kubectl get svc -A --no-headers=true | wc -l
# docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-status
pilot_xds
pilot_xds{app="istiod"}
sum(pilot_xds{app="istiod"})
sum(pilot_xds{app="istiod"}) by (pod)
- envoy_cluster_upstream_cx_tx_bytes_total
- 네트워크로 전송된 설정 크기를 측정한다. the configuration size that is transferred over the network.
- 대시보드에 XDS Requests Size 패널에 Legend: XDS Request Bytes Average
# rx
max(rate(envoy_cluster_upstream_cx_rx_bytes_total{cluster_name="xds-grpc"}[1m]))
quantile(0.5, rate(envoy_cluster_upstream_cx_rx_bytes_total{cluster_name="xds-grpc"}[1m]))
# tx
max(rate(envoy_cluster_upstream_cx_tx_bytes_total{cluster_name="xds-grpc"}[1m]))
quantile(.5, rate(envoy_cluster_upstream_cx_tx_bytes_total{cluster_name="xds-grpc"}[1m]))- 수신 트래픽과 송신 트래픽을 구분하면 포화의 원인과 사용할 수 있는 완화책이 명확해진다.
- 포화가 수신 트래픽 때문에 생기는 것이면 성능 병목은 변화율 때문이며, 해결책은 이벤트 배치 처리를 늘리거나 스케일 업하는 것이다.
- 만약 포화가 송신 트래픽과 관련 있으면, 해결책은 각 파일럿이 관리하는 인스턴스가 줄어들 수 있도록 컨트롤 플레인을 스케일 아웃하거나 모든 워크로드에 대해 사이드카 리소스를 정의하는 것이다.
▶ 오류: 컨트롤 플레인의 실패율은 어떻게 되는가?
( ERRORS: WHAT IS THE FAILURE RATE IN THE CONTROL PLANE? )
- 오류는 isiotd의 실패율을 나타내며, 보통은 서비스가 포화 상태에 이르러 성능이 저하됐을 때 발생한다.
- 가장 중요한 오류 메트릭들은 표 11.1에 나열했는데, 이들은 Pilot Errors 라는 이름으로 Istio Control Plane 대시보드에 시각화돼 있다.
# 각 쿼리 패턴에 Legend 확인
Legend(Rejected CDS Configs) : sum(pilot_xds_cds_reject{app="istiod"}) or (absent(pilot_xds_cds_reject{app="istiod"}) - 1)
Legend(Rejected EDS Configs) : sum(pilot_xds_eds_reject{app="istiod"}) or (absent(pilot_xds_eds_reject{app="istiod"}) - 1)
Legend(Rejected RDS Configs) : sum(pilot_xds_rds_reject{app="istiod"}) or (absent(pilot_xds_rds_reject{app="istiod"}) - 1)
Legend(Rejected LDS Configs) : sum(pilot_xds_lds_reject{app="istiod"}) or (absent(pilot_xds_lds_reject{app="istiod"}) - 1)
Legend(Write Timeouts) : sum(rate(pilot_xds_write_timeout{app="istiod"}[1m]))
Legend(Internal Errors) : sum(rate(pilot_total_xds_internal_errors{app="istiod"}[1m]))
Legend(Config Rejection Rate) : sum(rate(pilot_total_xds_rejects{app="istiod"}[1m]))
Legend(Push Context Errors) : sum(rate(pilot_xds_push_context_errors{app="istiod"}[1m]))
Legend(Push Timeouts) : sum(rate(pilot_xds_write_timeout{app="istiod"}[1m]))
|
메트릭
|
설명
|
|
pilot_total_xds_rejects
|
설정 푸시 거부 횟수
|
|
pilot_xds_’cds/lds/rds/cds’_reject
|
pilot_total_xds_rejects 메트릭의 부분집합. 어느 API 푸시가 거부됐는지 수사망을 좁히는 데 유용함
|
|
pilot_xds_write_timeout
|
push를 시작할 때 발생한 오류와 타임아웃의 합계
|
|
pilot_xds_push_context_errors
|
엔보이 설정을 생성하는 동안 발생한 이스티오 파일럿 오류 횟수. 주로 이스티오 파일럿의 버그와 관련
|
- 표에서 가장 중요한 메트릭들이 포함돼 있다.
- 이 메트릭들은 컨트롤 플레인 상태는 어떤지, 컨트롤 플레인이 어떻게 동작하는지를 알려줘 성능 병목을 밝히는 데 도움이 된다.
11.3 성능 튜닝하기
▶ 들어가며 : 컨트롤 플레인 성능의 변수
- 컨트롤 플레인의 성능 요인은 클러스터/환경의 변화 속도, 리소스 할당량, 관리하는 워크로드 개수, 그 워크로드로 푸시하는 설정 크기 라는 점을 돌이켜보자.
Recall that the control-plane performance factors are the rate of changes in the cluster/environment, the resources allocated to it, the number of workloads it manages, and the configuration size pushed to those workloads. - 이들 중 하나라도 병목이 되면, 성능을 개선할 수 있는 방법은 그림 11.8처럼 여러 가지가 있다.
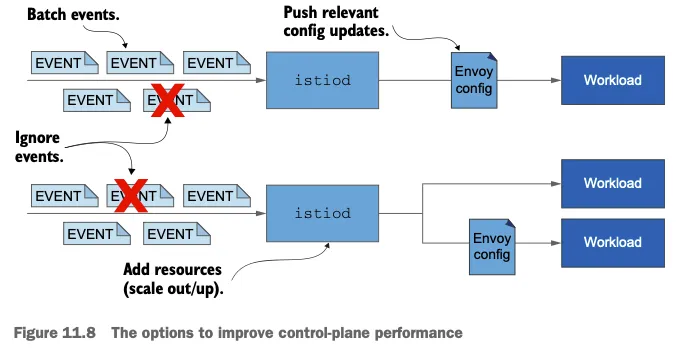
- 컨트롤 플레인 성능의 변수 The knobs of control-plane performance:
- 서비스 메시와 관련 없는 이벤트 무시하기. Ignoring events that are not relevant to the service mesh.
- 이벤트 배치 처리 기간을 좀 더 늘려 데이터 플레인 업데이트에 필요한 푸시 횟수 줄이기 Batching events for a longer period to reduce the number of pushes required to update the data plane.
- 다음 방법으로 리소스 추가 할당 Allocating additional resources by
- istiod 디플로이먼트 스케일 아웃하기 : 관리하는 워크로드를 파일럿 인스턴스들에 나눠 부하를 경감
- istiod 디플로이먼트 스케일 업하기 : 엔보이 설정 생성 속도를 높이고 더 많은 푸시 요청을 동시에 처리
- 워크로드가 관련 있는 설정을 컨트롤 플레인에게 알리는 사이드카 설정을 정의해 관련 있는 업데이트만 워크로드로 푸시하기. 2가지 이점. Pushing only relevant updates to workloads by defining a sidecar configuration that informs the control plane about the relevant configuration for a workload.
- 해당 프로세스에 필요한 최소한의 요청만을 보냄으로써 서비스 프록시에 보내는 설정 크기를 줄인다.
- 이벤트 하나로 업데이트되는 프록시 개수를 줄인다.
☞ 이런 방법으로 어떻게 성능을 개선하는지 보여줄 수 있도록 클러스터에 서비스를 준비하고 성능 테스트를 정의해보자.
11.3.1 워크스페이스 준비하기 : 실습 환경 준비 - 더미 워크로드와 서비스 생성
Step1. istiod에게 관리할 워크로드를 주기 위해 catalog 워크로드와 더미 워크로드 10개를 만들어보자.
# 실습 환경 준비 : 11.2.1 에서 이미 설정함
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f services/catalog/kubernetes/catalog.yaml
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f ch11/catalog-virtualservice.yaml
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f ch11/catalog-gateway.yaml
kubectl get deploy,gw,vs -n istioinaction
# 반복 설정 해두기
while true; do curl -s http://catalog.istioinaction.io:30000/items ; date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ; sleep 1; echo; done
# 모니터링
while true; do kubectl top pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod --containers=true ; date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ; sleep 1; echo; done
POD NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 discovery 7m 65Mi
2025-05-11 15:04:34
POD NAME CPU(cores) MEMORY(bytes)
istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 discovery 27m 82Mi
2025-05-11 15:04:36
...
# 더미 워크로드 10개 생성
cat ch11/sleep-dummy-workloads.yaml
...
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
...
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
name: http
selector:
app: sleep
---
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
...
spec:
serviceAccountName: sleep
containers:
- name: sleep
image: governmentpaas/curl-ssl
command: ["/bin/sleep", "3650d"]
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
...
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f ch11/sleep-dummy-workloads.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get deploy,svc,pod -n istioinaction
...
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-status
NAME CLUSTER CDS LDS EDS RDS ECDS ISTIOD VERSION
catalog-6cf4b97d-5jtzt.istioinaction Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 1.17.8
istio-egressgateway-85df6b84b7-m4699.istio-system Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 1.17.8
istio-ingressgateway-6bb8fb6549-k4ln6.istio-system Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 1.17.8
sleep-6f8cfb8c8f-2nfrm.istioinaction Kubernetes SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED SYNCED NOT SENT istiod-8d74787f-cqhs2 1.17.8
...
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config cluster deploy/catalog.istioinaction --fqdn sleep.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/catalog.istioinaction
10.10.0.16:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||sleep.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
10.10.0.17:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||sleep.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
10.10.0.18:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||sleep.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
10.10.0.19:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||sleep.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
...
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
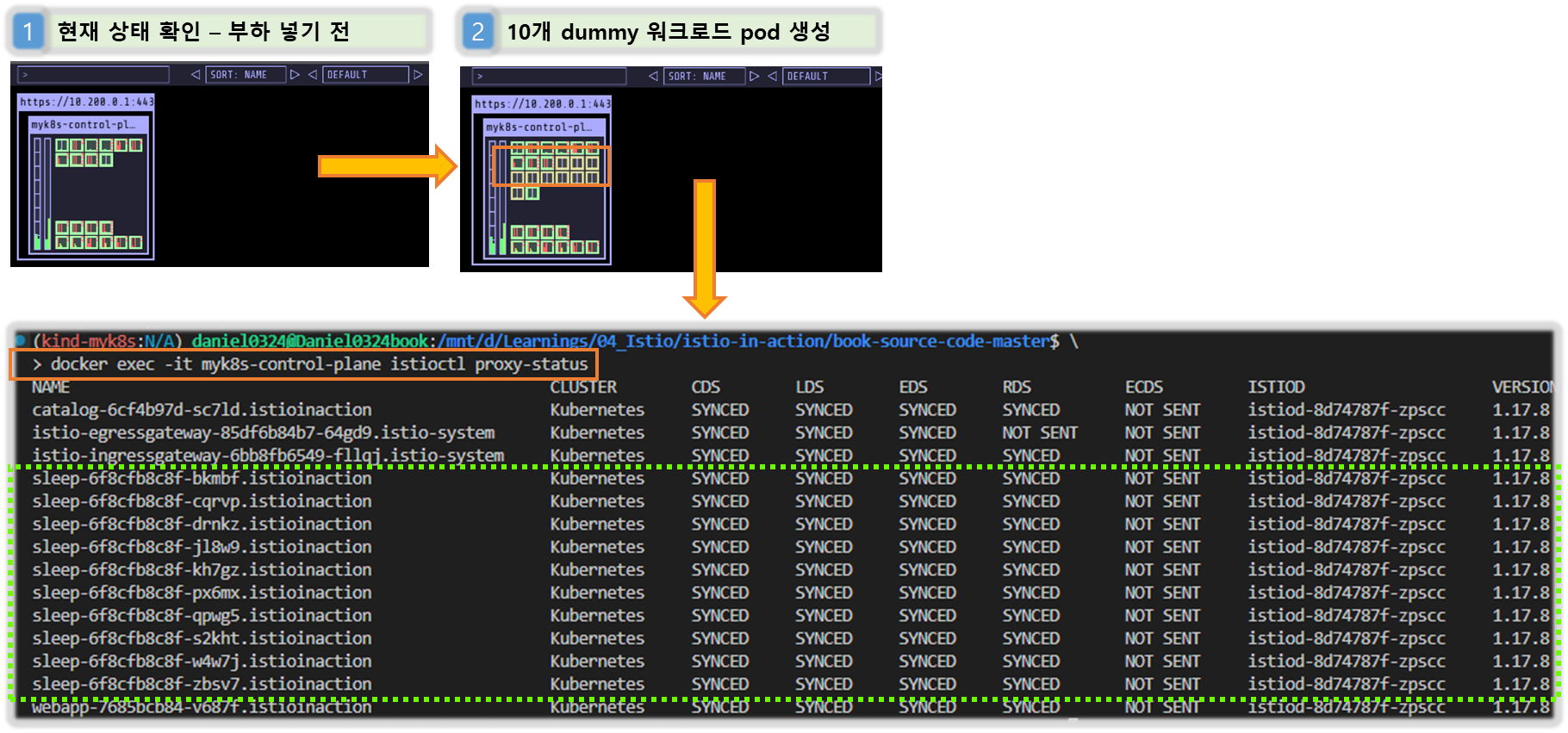
- 그라파나 대시보드 : Last 5 minutes ( Istio-Control plane )
Step2. 이 정도는 파일럿에게 아직도 너무 쉽다. 몇 가지 더미 서비스로 엔보이 설정을 부풀려 상황을 악화시켜보자 : svc 200개, vs 200개, gw 200개
#
cat ch11/resources-600.yaml
cat ch11/resources-600.yaml | wc -l
9200
# 각각 200개
cat ch11/resources-600.yaml | grep 'kind: Service' | wc -l
cat ch11/resources-600.yaml | grep 'kind: Gateway' | wc -l
cat ch11/resources-600.yaml | grep 'kind: VirtualService' | wc -l
200
# 배포 : svc 200개, vs 200개, gw 200개
kubectl -n istioinaction apply -f ch11/resources-600.yaml
# 확인
kubectl get deploy,svc,pod -n istioinaction
...
# k8s service 개수 202개
kubectl get svc -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
202
kubectl get gw,vs -n istioinaction
...
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-status
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config listener deploy/catalog.istioinaction
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config route deploy/catalog.istioinaction
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config cluster deploy/catalog.istioinaction
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/catalog.istioinaction
- 그라파나 대시보드 : Last 15 minutes
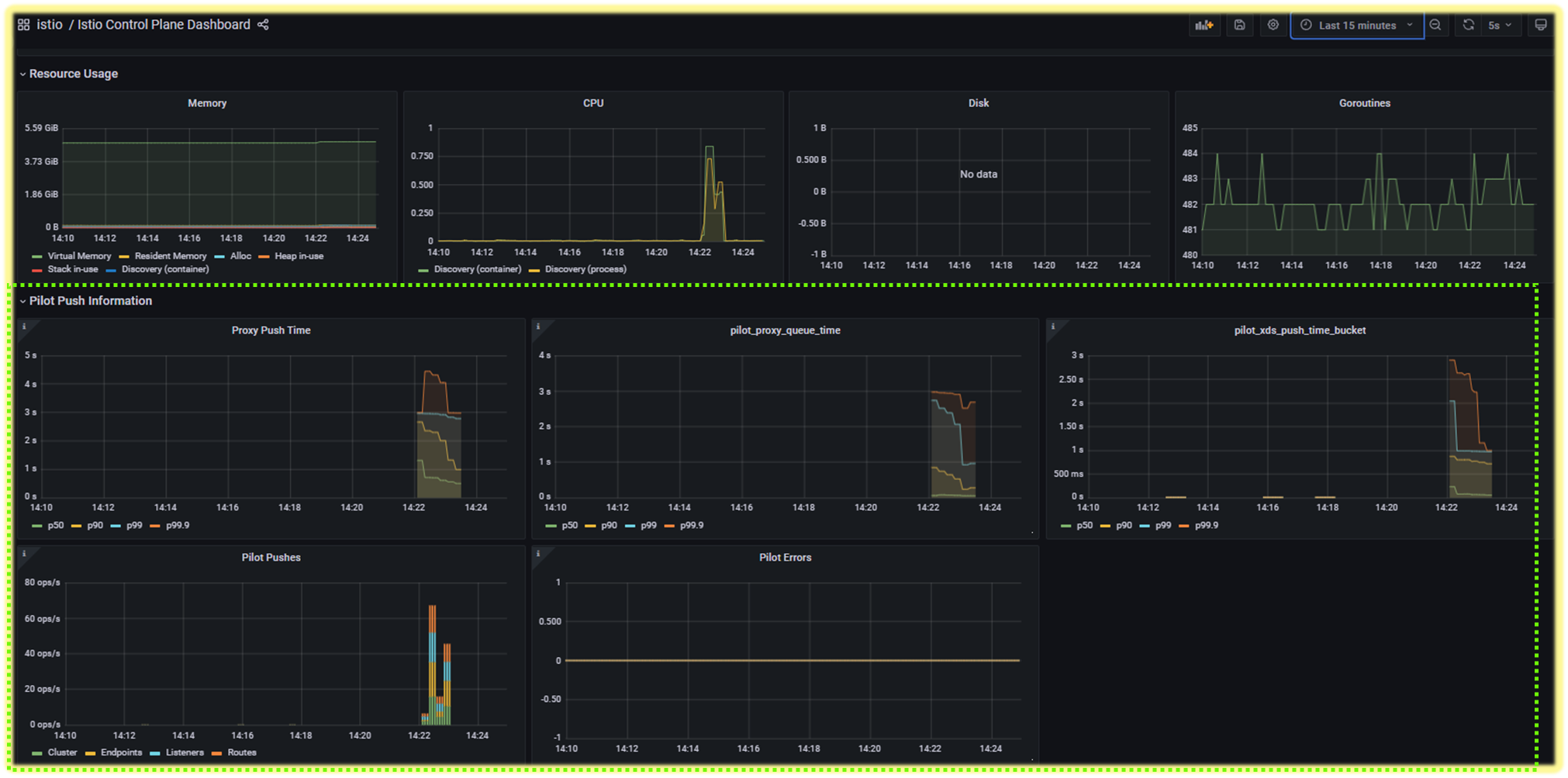
- 그래서 이제 istiod 인스턴스 하나가 인그레스 및 이그레스 게이트웨이를 포함해 워크로드(istio-proxy 동작)를 13개 관리하며, 서비스는 총 600개(svc + vs + gw) 인지하고 있다.
- 서비스 개수는 엔보이 설정을 만드는 데 필요한 처리량을 늘리고, 워크로드로 보내야 하는 설정을 부풀린다.
So now the single istiod instance manages 13 workloads, including ingress and egress gateways, and another 600 total services are known to it, which increases the amount of processing to generate the Envoy configuration and bloats the configuration that has to be pushed to the workloads.
11.3.2 최적화 전 성능 측정하기* Measuring performance before optimizations Sidecar
▶ 들어가며 : 테스트 실행
- 이제 테스트로 컨트롤 플레인 성능을 판단할 것이다.
- 테스트는 서비스를 반복적으로 만들어 부하를 생성하고, 프록시에 설정을 업데이트하는 데 걸리는 지연 시간과 P99 값과 푸시 개수를 측정한다. We’ll determine the control-plane performance with a test that generates load by creating services repeatedly and then measures both the number of pushes and the 99th percentile (P99) latency to distribute the configuration updates to the proxies.
☞ P99 이해하기
P99(또는 percentile 백분위 99)는 업데이트 전파 중 가장 빠른 99%의 최대 지연 시간을 측정한다. 예를 들어 ‘P99 지연 시간이 80ms이다’는 요청 중 99%가 80ms 보다 빠르게 전파됐음을 말한다! 각 요청이 정확히 어떻게 분포하는지는 알지 못하며, 대부분은 수 ms 범위일 수 있다. 그러나 가장 빠른 99%만을 고려할 때 가장 느린 요청도 80ms안에 처리됐음을 알 수 있다.
But we know that even the worst-performing request was served within 80 ms when considering only the fastest 99%.
(첫 번째) 테스트를 10회 반복하되, 반복 사이에 2.5초 간격을 두자.
- Let’s run the test with 10 repetitions and a delay of 2.5 seconds
☞ 이는 변경을 흩뿌려 배치 처리되는 상황을 피하려는 것이다.
between repetitions to spread out the changes and avoid having them batched
☞ bin/performance-test.sh : 파일 수정 해두기! $GATEWAY:30000/items
#!/bin/bash
main(){
## Pass input args for initialization
init_args "$@"
SLEEP_POD=$(kubectl -n istioinaction get pod -l app=sleep -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name} -n istioinaction | cut -d ' ' -f 1)
PRE_PUSHES=$(kubectl exec -n istio-system deploy/istiod -- curl -s localhost:15014/metrics | grep pilot_xds_pushes | awk '{total += $2} END {print total}')
if [[ -z "$PRE_PUSHES" ]]; then
echo "Failed to query Pilot Pushes from prometheus."
echo "Have you installed prometheus as shown in chapter 7?"
exit 1
fi
echo "Pre Pushes: $PRE_PUSHES"
INDEX="0"
while [[ $INDEX -lt $REPS ]]; do
SERVICE_NAME="service-`openssl rand -hex 2`-$INDEX"
create_random_resource $SERVICE_NAME &
sleep $DELAY
INDEX=$[$INDEX+1]
done
## Wait until the last item is distributed
while [[ "$(curl --max-time .5 -s -o /dev/null -H "Host: $SERVICE_NAME.istioinaction.io" -w ''%{http_code}'' $GATEWAY:30000/items)" != "200" ]]; do
# curl --max-time .5 -s -o /dev/null -H "Host: $SERVICE_NAME.istioinaction.io" $GATEWAY/items
sleep .2
done
echo ==============
sleep 10
POST_PUSHES=$(kubectl exec -n istio-system deploy/istiod -- curl -s localhost:15014/metrics | grep pilot_xds_pushes | awk '{total += $2} END {print total}')
echo
LATENCY=$(kubectl -n istioinaction exec -it $SLEEP_POD -c sleep -- curl "$PROM_URL/api/v1/query" --data-urlencode "query=histogram_quantile(0.99, sum(rate(pilot_proxy_convergence_time_bucket[1m])) by (le))" | jq '.. |."value"? | select(. != null) | .[1]' -r)
echo "Push count:" `expr $POST_PUSHES - $PRE_PUSHES`
echo "Latency in the last minute: `printf "%.2f\n" $LATENCY` seconds"
}
create_random_resource() {
SERVICE_NAME=$1
cat <<EOF | kubectl apply -f -
---
kind: Gateway
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
metadata:
name: $SERVICE_NAME
namespace: $NAMESPACE
spec:
servers:
- hosts:
- "$SERVICE_NAME.istioinaction.io"
port:
name: http
number: 80
protocol: HTTP
selector:
istio: ingressgateway
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
app: catalog
name: $SERVICE_NAME
namespace: $NAMESPACE
spec:
ports:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 3000
selector:
app: catalog
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: $SERVICE_NAME
namespace: $NAMESPACE
spec:
hosts:
- "$SERVICE_NAME.istioinaction.io"
gateways:
- "$SERVICE_NAME"
http:
- route:
- destination:
host: $SERVICE_NAME.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local
port:
number: 80
---
EOF
}
help() {
cat <<EOF
Poor Man's Performance Test creates Services, Gateways and VirtualServices and measures Latency and Push Count needed to distribute the updates to the data plane.
--reps The number of services that will be created. E.g. --reps 20 creates services [0..19]. Default '20'
--delay The time to wait prior to proceeding with another repetition. Default '0'
--gateway URL of the ingress gateway. Defaults to 'localhost'
--namespace Namespace in which to create the resources. Default 'istioinaction'
--prom-url Prometheus URL to query metrics. Defaults to 'prom-kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus.prometheus:9090'
EOF
exit 1
}
init_args() {
while [[ $# -gt 0 ]]; do
case ${1} in
--reps)
REPS="$2"
shift
;;
--delay)
DELAY="$2"
shift
;;
--gateway)
GATEWAY="$2"
shift
;;
--namespace)
NAMESPACE="$2"
shift
;;
--prom-url)
PROM_URL="$2"
shift
;;
*)
help
;;
esac
shift
done
[ -z "${REPS}" ] && REPS="20"
[ -z "${DELAY}" ] && DELAY=0
[ -z "${GATEWAY}" ] && GATEWAY=localhost
[ -z "${NAMESPACE}" ] && NAMESPACE=istioinaction
[ -z "${PROM_URL}" ] && PROM_URL="prom-kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus.prometheus.svc.cluster.local:9090"
}
main "$@"
- 여러 개의 임의 서비스 리소스를 생성 → Istio의 xDS Push 횟수 증가량 측정, Prometheus에서 프록시 구성 수렴 시간(latency) 확인 ⇒ 최종적으로 Push 성능과 latency를 평가
# (참고) 호출
curl -H "Host: catalog.istioinaction.io" localhost:30000/items
# 확인
kubectl get svc -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get gw -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get vs -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
# :30000 포트 정보 추가해둘것!
cat bin/performance-test.sh
...
Poor Man's Performance Test creates Services, Gateways and VirtualServices and measures Latency and Push Count needed to distribute the updates to the data plane.
--reps The number of services that will be created. E.g. --reps 20 creates services [0..19]. Default '20'
--delay The time to wait prior to proceeding with another repetition. Default '0'
--gateway URL of the ingress gateway. Defaults to 'localhost'
--namespace Namespace in which to create the resources. Default 'istioinaction'
--prom-url Prometheus URL to query metrics. Defaults to 'prom-kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus.prometheus:9090'
...
# 성능 테스트 스크립트 실행!
./bin/performance-test.sh --reps 10 --delay 2.5 --prom-url prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090
Pre Pushes: 335
...
ateway.networking.istio.io/service-00a9-9 created
service/service-00a9-9 created
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/service-00a9-9 created
==============
Push count: 510 # 변경 사항을 적용하기 위한 푸시 함수
Latency in the last minute: 0.45 seconds # 마지막 1분 동안의 지연 시간
# 확인
kubectl get svc -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get gw -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get vs -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
[ 실행 결과 한 눈에 보기 ]
1) 사전 부하스크립트 수정 ( 포트 추가 )
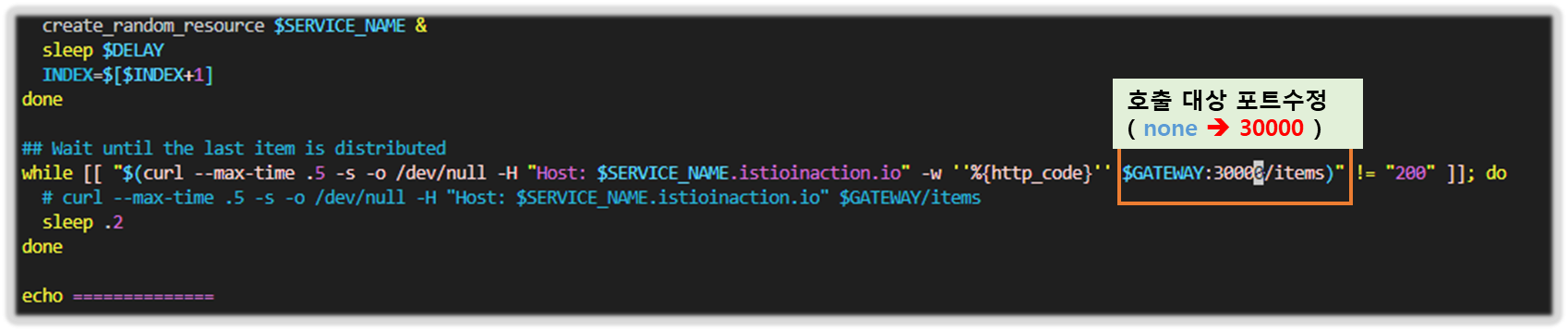
2) 현재 svc, gw, vs 상태 보기
3) 진행상황 및 부하상태 확인
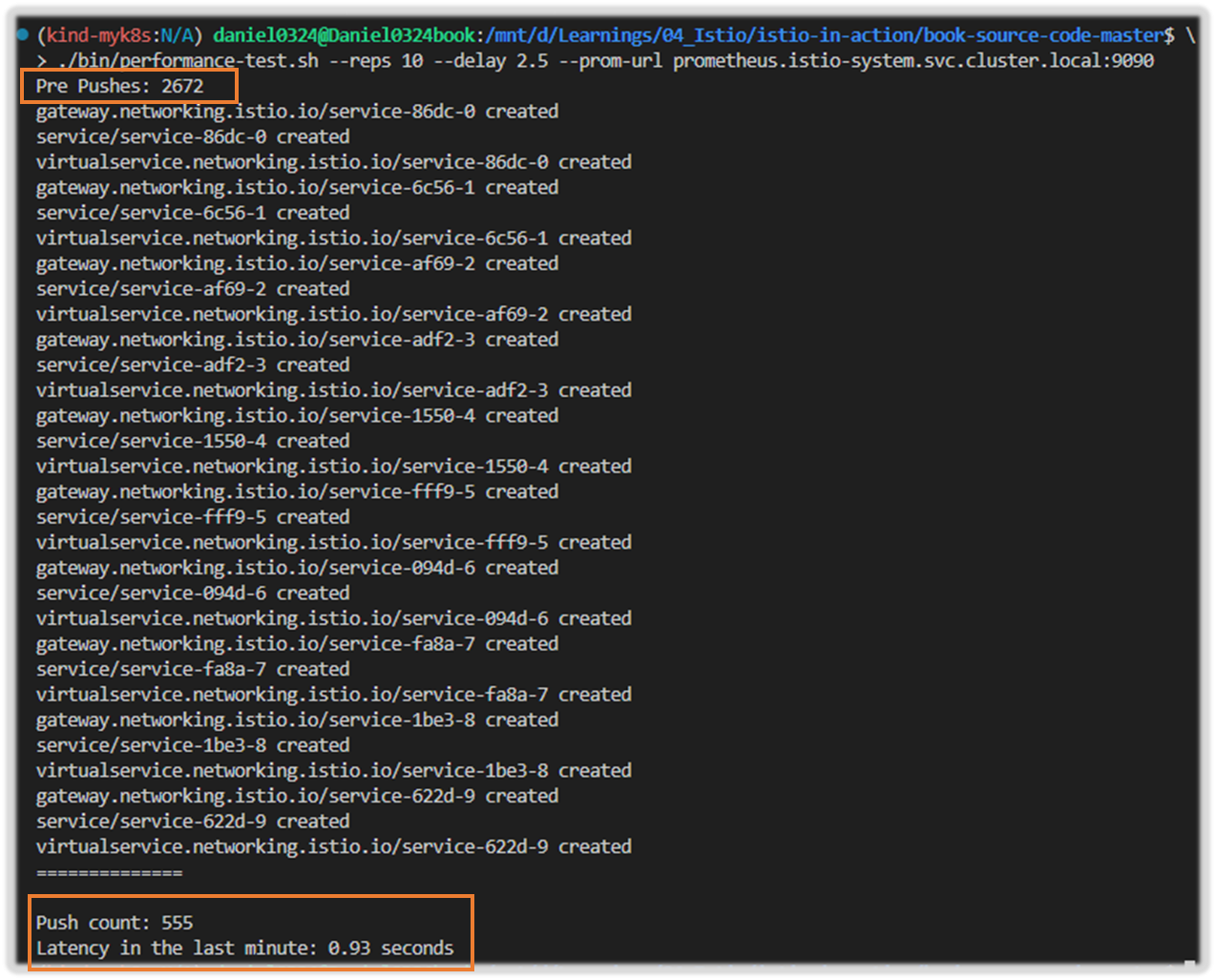
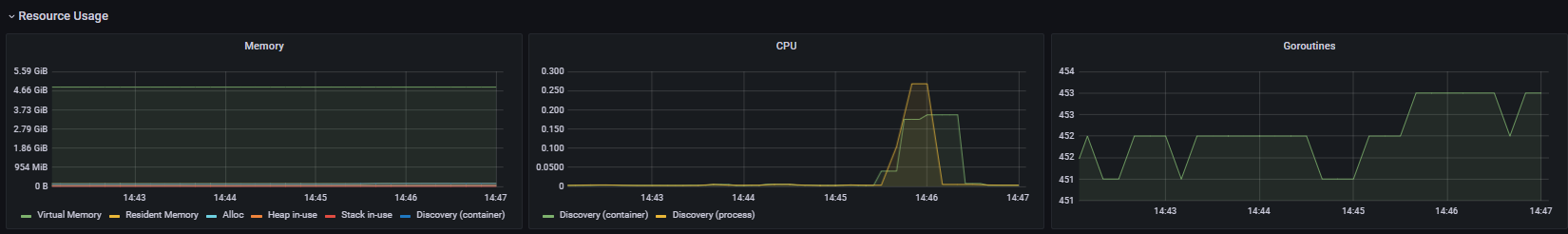
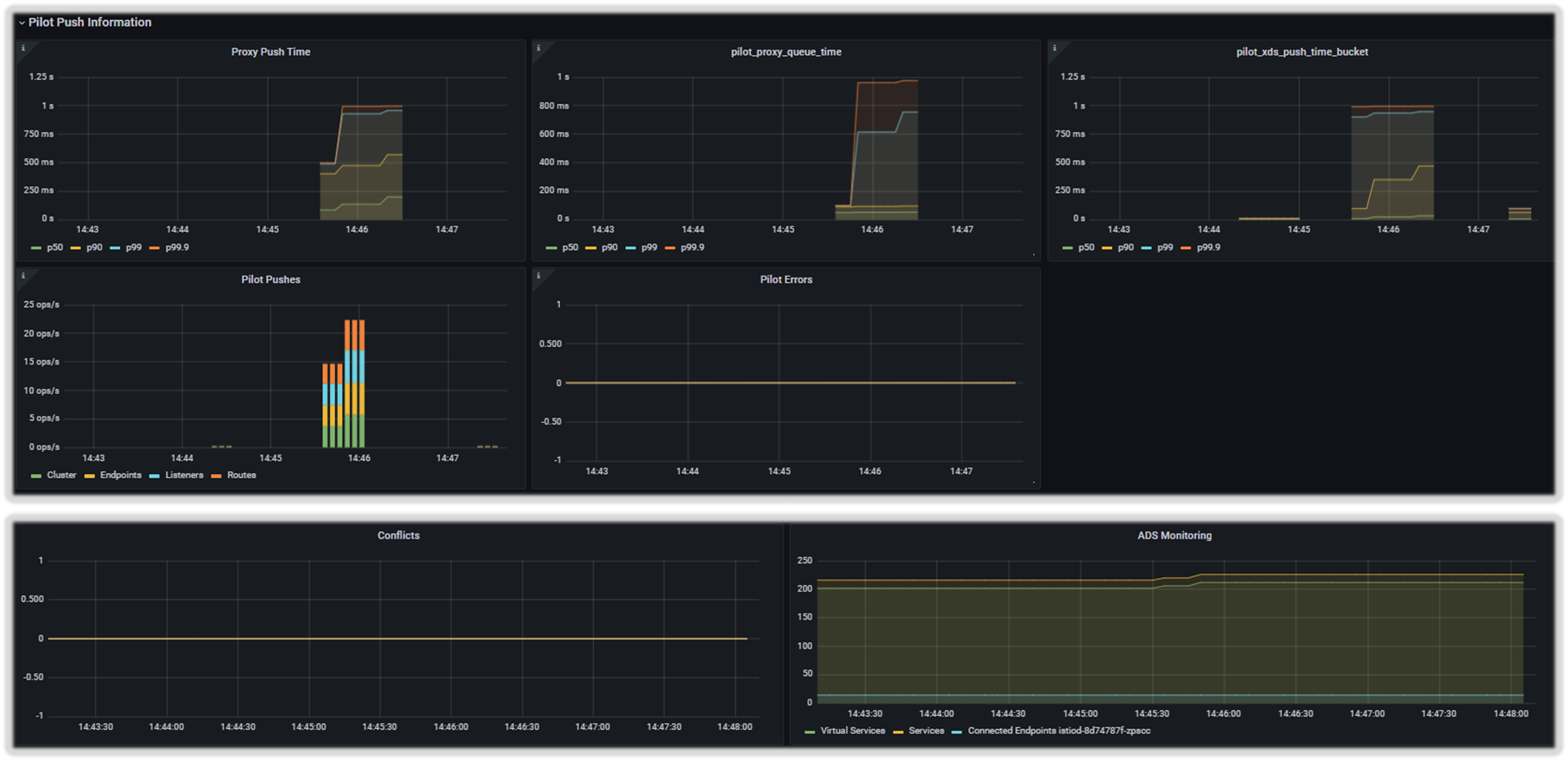
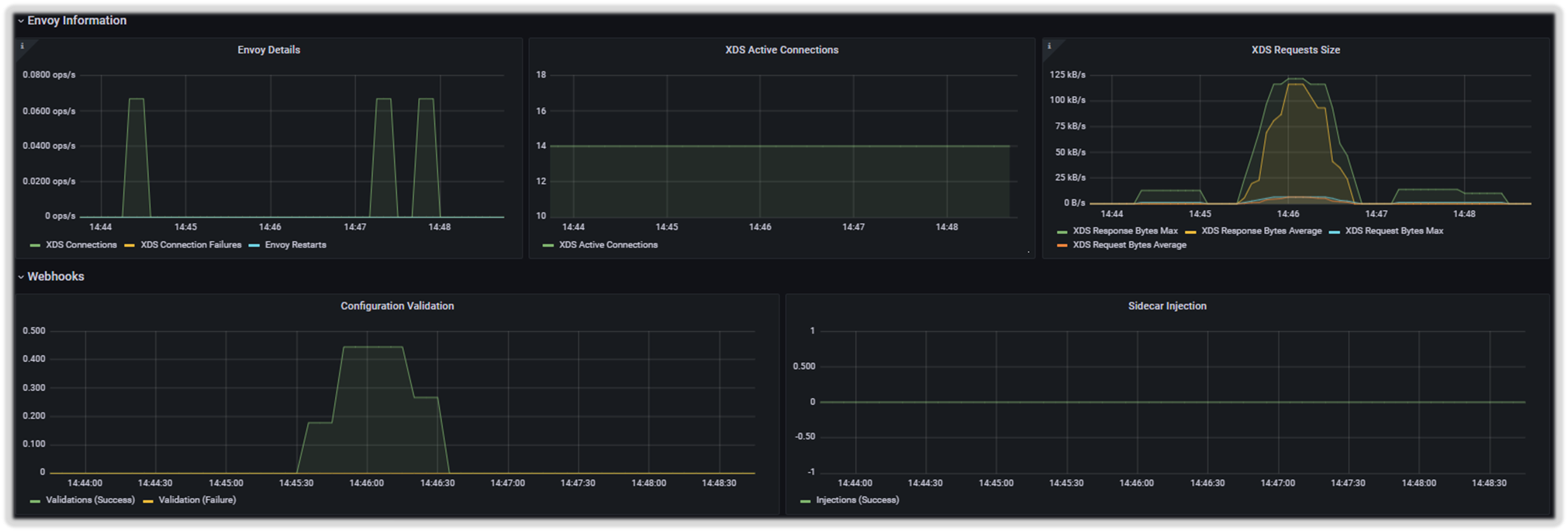
- 그라파나 : Last 5분
(두 번째) 딜레이 없이 실행
# 성능 테스트 스크립트 실행 : 딜레이 없이
./bin/performance-test.sh --reps 10 --prom-url prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090
Push count: 51
Latency in the last minute: 0.47 seconds
# 확인
kubectl get svc -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get gw -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get vs -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
☞ 15:21 분 경 서비스 curl에 대한 부하처리가 '시작 - 완료' 되었다.
- 그라파나
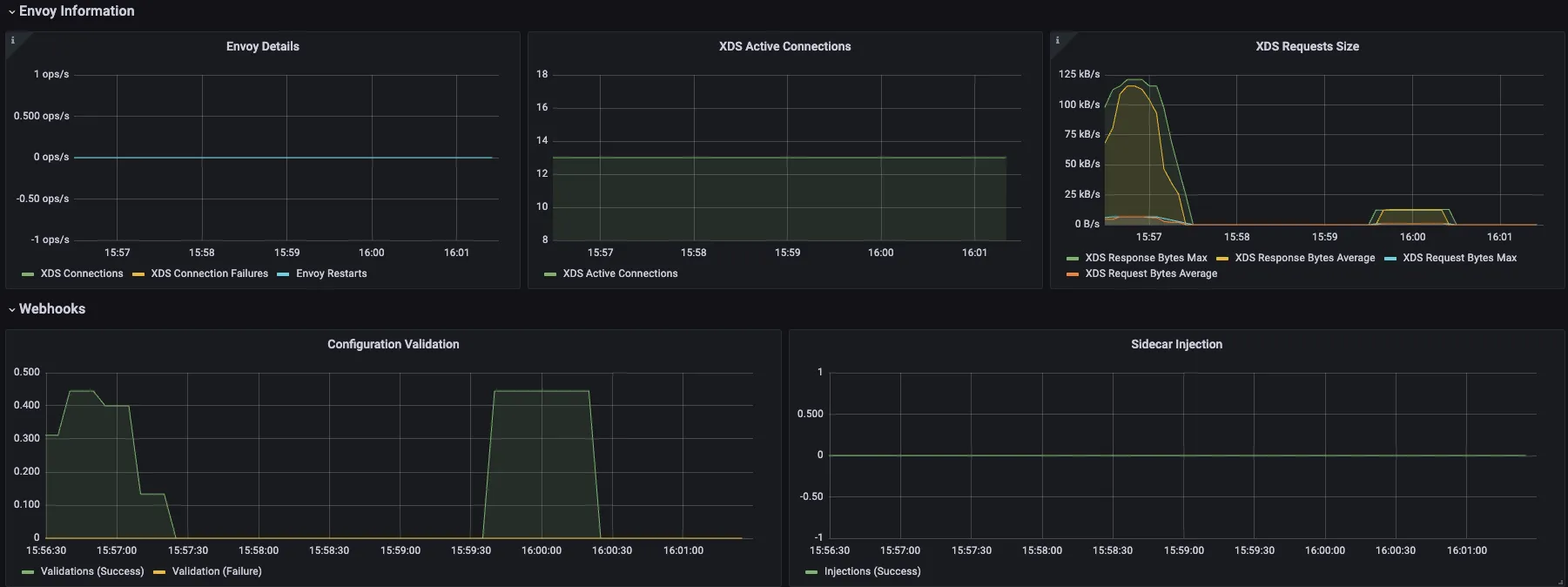
(세 번째) 딜레이 좀 더 늘려서 실행
# 성능 테스트 스크립트 실행 : 딜레이 없이
./bin/performance-test.sh --reps 10 --delay 5 --prom-url prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090
Push count: 510
Latency in the last minute: 0.43 seconds
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
- 그라파나 확인
[ 테스트 정리 ]
- (첫 번째) 테스트에 따르면, 현재 설정으로는 510회의 푸시가 P99 지연 시간 0.45초로 수행됐다.
- 나의 경우는 Push Count가 555 -> 168 -> 550 순으로 측정 되었다.
Push count: 510 # 변경 사항을 적용하기 위한 푸시 함수
Latency in the last minute: 0.45 seconds # 마지막 1분 동안의 지연 시간, 책은 ms로 표기..- (두 번째) 테스트에 따르면, 서비스 간의 간격을 없애면, 푸시 횟수와 지연 시간 모두 떨어지는 것을 볼 수 있다. 이는 이벤트가 배치 처리돼서 더 적은 작업량으로 처리되기 때문이다.
Push count: 51
Latency in the last minute: 0.47 seconds
- 당신의 측정값은 다를 수 있지만, 괜찮다.
- 이 테스트의 목표는 후속 절들에서 최적화를 실행한 후의 성능 향상을 검증할 수 있는 ‘충분히 좋은’ 측정을 하는 것이다.
▶ 사이드카를 사용해 푸시 횟수 및 설정 크기 줄이기
- REDUCING CONFIGURATION SIZE AND NUMBER OF PUSHES USING SIDECARS
- 마이크로서비스 환경에서 한 서비스가 다른 서비스에 의존하는 것은 흔한 일이다.
- 그러나 한 서비스가 다른 모든 가용 서비스에 접근해야 하는 것도 드믄 일이다 (아니면 적어도 이런 상황을 피하려고는 한다)
- 기본적으로 이스티오는 각 서비스가 어떤 접근이 필요한지 알 수 없으므로, 기본값은 모든 서비스 프록시가 메시의 모든 워크로드를 알도록 한다!
- 이로 인해 프록시의 설정이 쓸데없이 부풀려진다는 점은 쉽게 알 수 있다.
- 예를 들어 catalog 워크로드의 설정 크리를 계산해보자.
#
CATALOG_POD=$(kubectl -n istioinaction get pod -l app=catalog -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name} | cut -d ' ' -f 1)
kubectl -n istioinaction exec -ti $CATALOG_POD -c catalog -- curl -s localhost:15000/config_dump > /tmp/config_dump
du -sh /tmp/config_dump
1.8M /tmp/config_dump
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config listener deploy/catalog.istioinaction
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config route deploy/catalog.istioinaction
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config cluster deploy/catalog.istioinaction
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/catalog.istioinaction
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/catalog.istioinaction | wc -l
275- 지금 설정 크키가 대략 2MB 인데, 이는 엄청 많은 것이다!
- 워크로드가 200개인 중간 클러스터만 돼도 엔보이 설정이 400MB로 늘어나며, 이로 인해 연산 성능, 네트워크 대역폭, 메모리가 더 많이 필요하다.
- 이 설정이 모든 사이드카 프록시에 저장되기 때문이다.
[ 실행결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
1. catalog POD 로 curl 테스트

2. control-plane 내 proxy-config 자원 확인 ( listener, route, cluster )
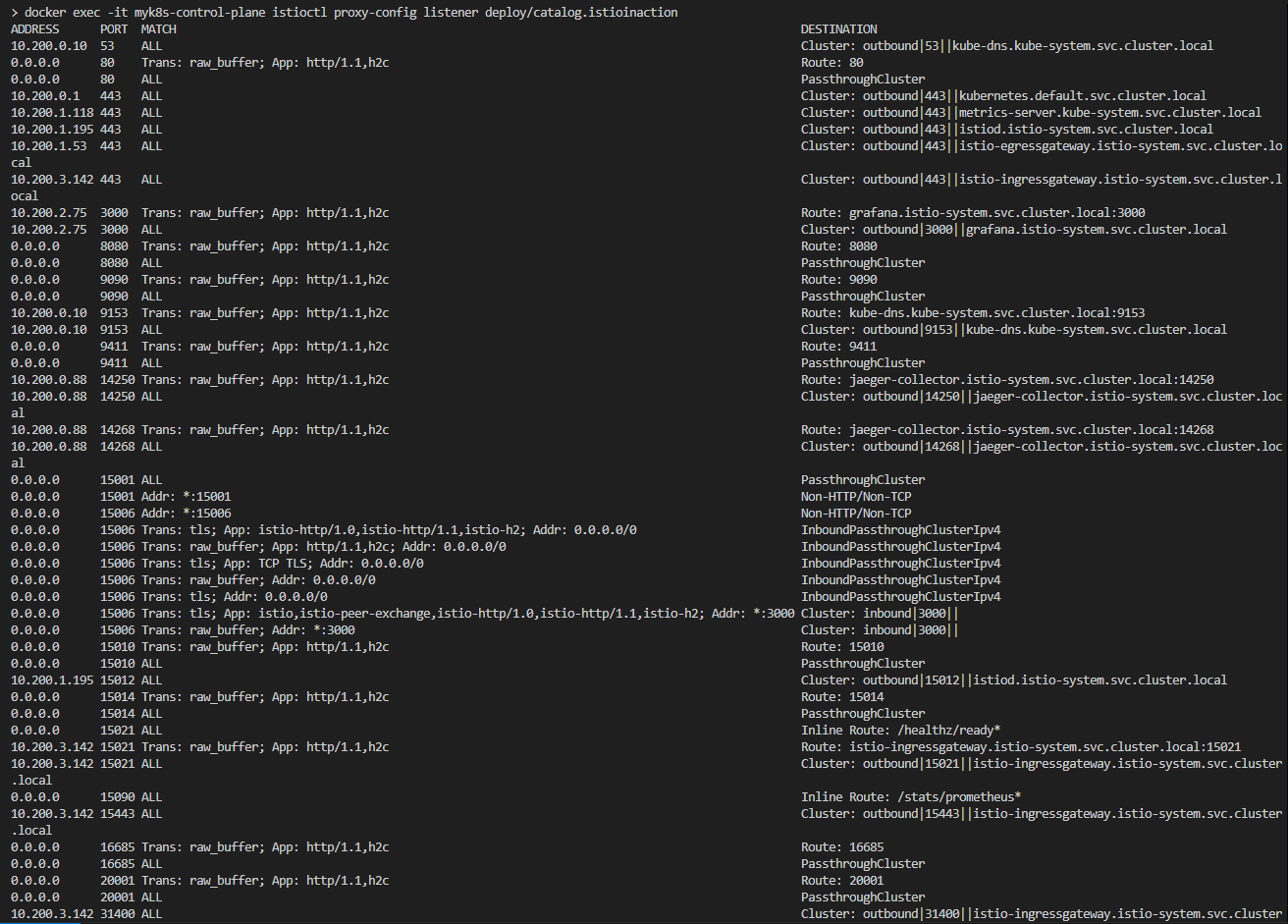
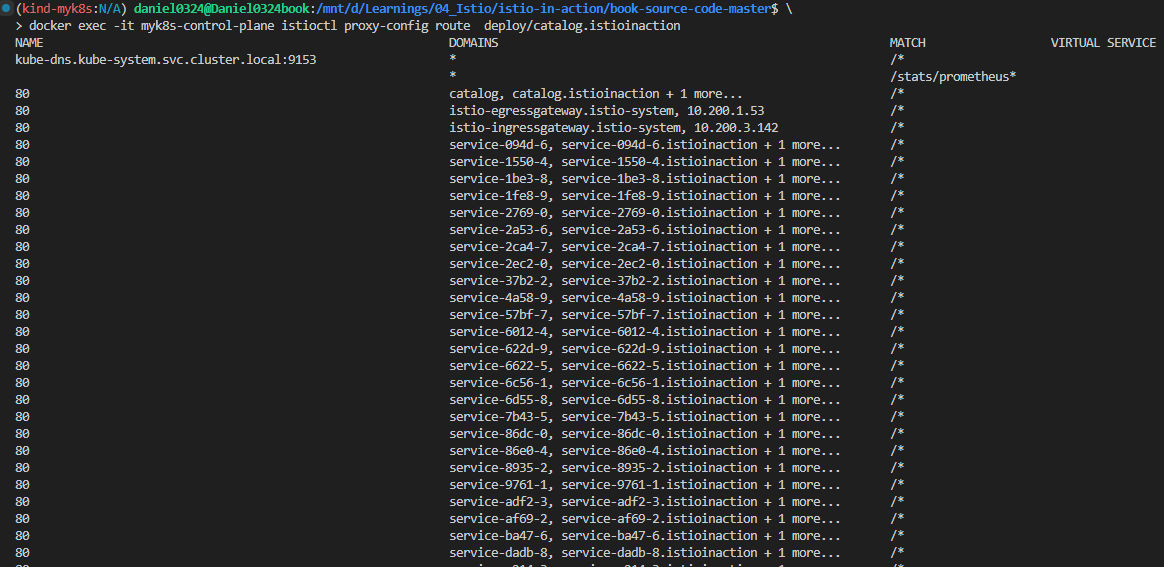
중간 생략 ...
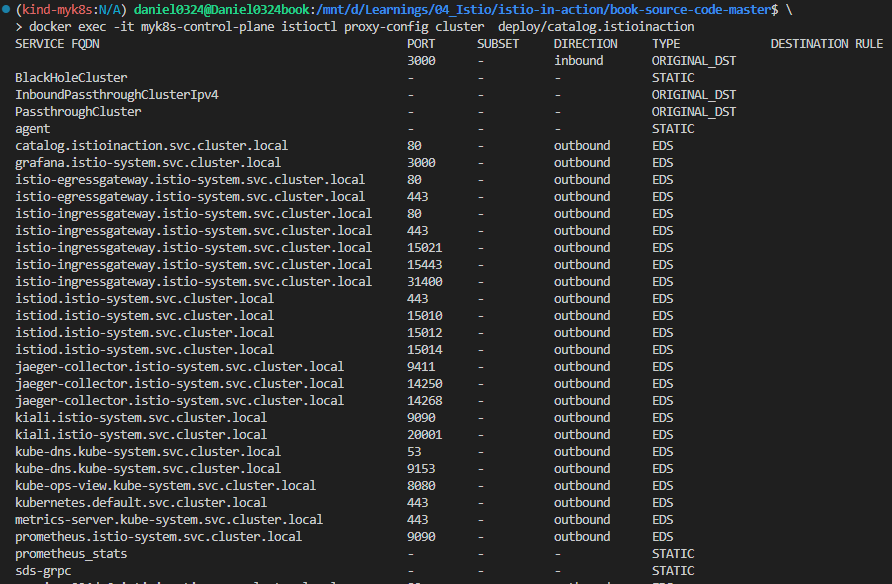
3) End-point 갯수 확인 : 워크로드 수가 200이 넘는다.
▶ Sidecar 리소스
- 이런 문제를 해결하기 위해 Sidecar 리소스를 사용해 사이드카 프록시에 드나드는 트래픽의 설정을 세밀하게 조정할 수 있다.
- 이 작업을 수행하는 방법을 이해하기 위해 예시 리소스를 살펴보자.
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Sidecar
metadata:
name: default
namespace: istioinaction
spec:
workloadSelector:
labels:
app: foo
egress:
-hosts:
- "./bar.istioinaction.svc.cluster.local"
- "istio-system/*"
outboundTrafficPolicy:
mode: REGISTRY_ONLY- workloadSelector
- 사이드카 설정을 적용할 워크로드를 제한한다. limits the workloads to which the sidecar configuration applies.
- ingress
- 애플리케이션에 들어오는 트래픽 처리를 지정한다. specifies the handling of inbound traffic to the application.
- 생략하면, 이스티오는 파드 정의를 조회해 서비스 프록시를 자동으로 설정한다. If omitted, Istio configures the service proxy automatically by looking up the Pod definition.
- egress
- 사이드카를 거치는 외부 서비스로의 송신 트래픽 처리를 지정한다. specifies the handling of the application’s outbound traffic to an external service through the sidecar.
- 생략되면, 설정은 좀 더 일반적인 사이드카에서 egress 설정을 상속한다 (있는 경우).
- 없으면, 다른 모든 서비스에 접근할 수 있도록 설정하는 기본 동작으로 대처한다. If omitted, the configuration inherits the egress configuration from a more generic sidecar, if present; otherwise, it falls back on the default behavior of configuring access to all other services.
- outboundTrafficPolicy : 송신 트래픽 처리 시 모드 지정. specifies the mode for handling outbound traffic.
- REGISTRY_ONLY 모드 : 워크로드가 설정한 서비스에만 트래픽을 보낼 수 있게 한다.
- ALLOW_ANY 모드 : 어디로든 트래픽 송신을 허용한다.
- Sidecar 리소스를 워크로드에 적용하면, 컨트롤 플레인은 egress 필드를 사용해 워크로드가 어떤 서비스들에 접근해야 하는지 판단한다. When a Sidecar resource applies to a workload, the control plane uses the egress field to determine which services the workload requires access to.
- 덕분에 컨트롤 플레인은 관련 있는 설정과 업데이트를 파악하고 해당 프록시로만 보낼 수 있다.
- 그 결과, 다른 모든 서비스에 도달하는 방법에 대한 설정을 모두 생성하고 배포하는 일을 방지해 ‘CPU, 메모리, 네트워크 대역폭 소모’를 줄일 수 있다.
▶ 메시 범위 사이드카 설정으로 더 나은 기본값 정의하기
- DEFINING BETTER DEFAULTS WITH A MESH-WIDE SIDECAR CONFIGURATION
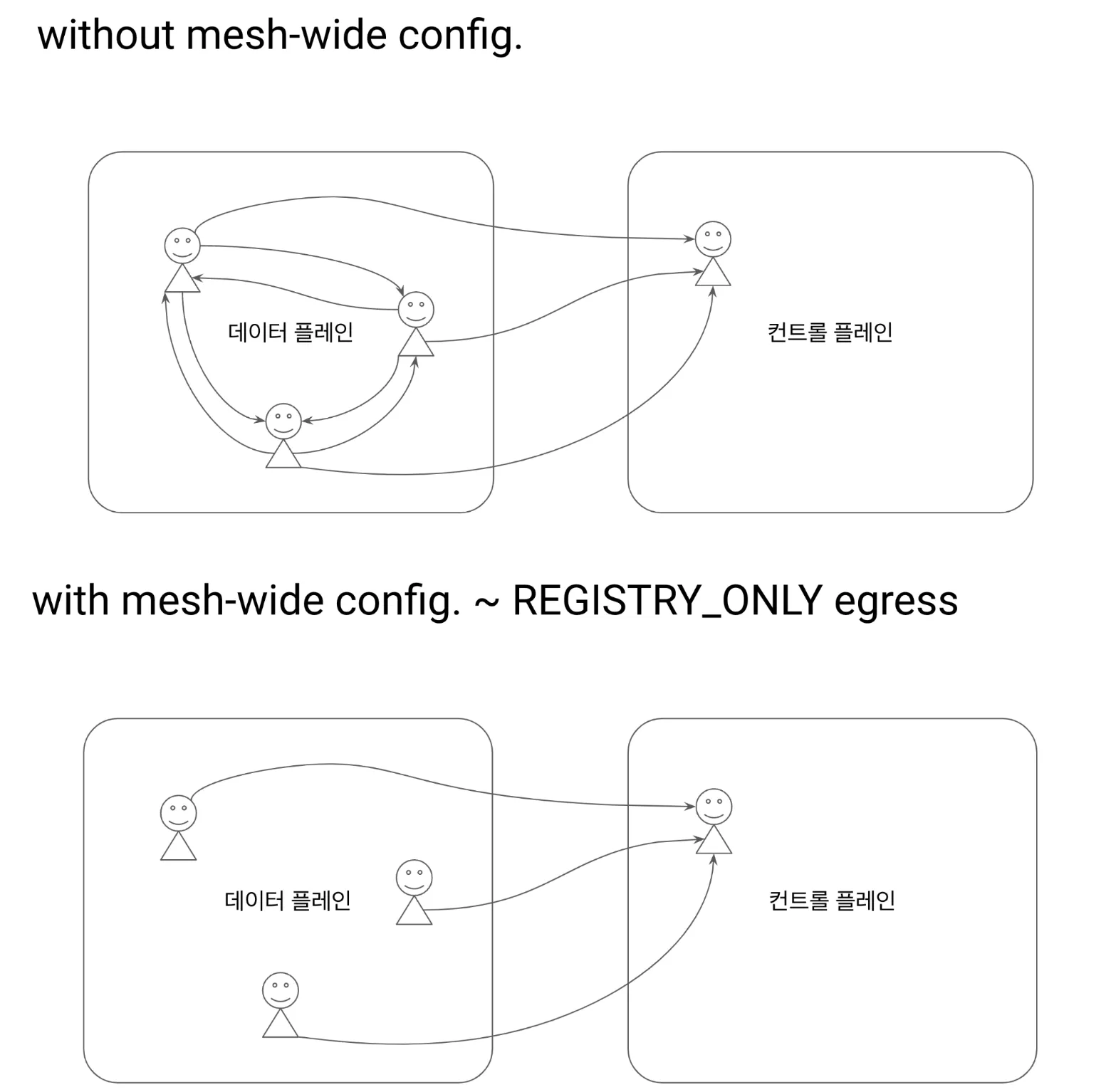
- 모든 서비스 프록시로 전송되는 엔보이 설정을 줄여 컨트롤 플레인 성능을 개선할 수 있는 가장 쉬운 방법은 트래픽 송신을 istio-system 네임스페이스의 서비스로만 허용하는 사이드카 설정을 메시 범위로 정의하는 것이다.
- 기본값을 이렇게 정의하면, 최소 설정으로 메시 내 모든 프록시가 컨트롤 플레인에만 연결하도록 하고 다른 서비스로의 연결 설정은 모두 삭제할 수 있다.
- 이 방식은 서비스 소유자를 올바른 길로 유도하는데, 워크로드용 사이드카 정의를 좀 더 구체적으로 정의하고 서비스에 필요한 트래픽 송신을 모두 명시적으로 기술함게 함(강제 유도?)으로써 워크로드가 프로세스에 필요한 관련 설정을 최소한으로 수신할 수 있게 한다.
- 다음 사이드카 정의를 사용하면, 메시 내 모든 서비스 사이트가가 istio-system 네임스페이스에 있는 이스티오 서비스로만 연결하도록 설정할 수 있다. (메트릭을 수집할 수 있드록 프로메테우스 네임스페이스도 연결한다)
- 이제 컨트롤 플레인은 서비스 프록시가 istio-system / prometheus 네임스페이스의 서비스로 연결할 수 있는 최소한의 설정만 갖도록 업데이트 한다.
- 우리의 가설이 맞다면, catalog 워크로드의 엔보이 설정 크기는 현저히 줄어야 한다. 확인해보자.
# cat ch11/sidecar-mesh-wide.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Sidecar
metadata:
name: default # istio-system 네임스페이스의 사이드카는 메시 전체에 적용된다.
namespace: istio-system # 위 설명 동일.
spec:
egress:
- hosts:
- "istio-system/*" # istio-system 네임스페이스의 워크로드만 트래픽 송신을 할 수 있게 설정한다.
- "prometheus/*" # 프로메테우스 네임스페이스도 트래픽 송신을 할 수 있게 설정한다.
outboundTrafficPolicy:
mode: REGISTRY_ONLY # 모드는 사이드카에 설정한 서비스로만 트래픽 송신을 허용한다# 테스트를 위해 샘플 nginx 배포
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
EOF
# catalog 에서 nginx 서비스 접속 확인
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config route deploy/catalog.istioinaction | grep nginx
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config cluster deploy/catalog.istioinaction | grep nginx
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/catalog.istioinaction | grep nginx
10.10.0.26:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||nginx.default.svc.cluster.local
kubectl exec -it deploy/catalog -n istioinaction -- curl nginx.default | grep title
<title>Welcome to nginx!</title>
# istio-system, prometheus 네임스페이스만 egress 허용 설정
kubectl -n istio-system apply -f ch11/sidecar-mesh-wide.yaml
kubectl get sidecars -A
# catalog 에서 nginx 서비스 접속 확인
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config route deploy/catalog.istioinaction | grep nginx
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config cluster deploy/catalog.istioinaction | grep nginx
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/catalog.istioinaction | grep nginx
kubectl exec -it deploy/catalog -n istioinaction -- curl nginx.default | grep title
# envoy config 크기 다시 확인!
CATALOG_POD=$(kubectl -n istioinaction get pod -l app=catalog -o jsonpath={.items..metadata.name} | cut -d ' ' -f 1)
kubectl -n istioinaction exec -ti $CATALOG_POD -c catalog -- curl -s localhost:15000/config_dump > /tmp/config_dump
du -sh /tmp/config_dump
520K /tmp/config_dump- 설정 크기가 2MB에서 520KB로 대폭 줄었다. 게다가 이점은 그것만이 아니다. 이제부터 컨트롤 플레인은 푸시를 더 적게 할 것이다.
- 어느 워크로드는 업데이트가 필요하고, 어느 워크로드는 그렇지 않은지 판단하기 때문이다.
- 성능 테스트로 확인해보자.
# 성능 테스트 스크립트 실행!
./bin/performance-test.sh --reps 10 --delay 2.5 --prom-url prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090
...
Push count: 88 # 변경 사항을 적용하기 위한 푸시 함수
Latency in the last minute: 0.10 seconds # 마지막 1분 동안의 지연 시간
# 확인
kubectl get svc -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get gw -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l
kubectl get vs -n istioinaction --no-headers=true | wc -l- 예상대로 푸시 횟수와 지연 시간 모두 줄어들었다. As expected, both the push count and latency have dropped.
- 이 성능 향상은 메시 범위 Sidecar 리소스를 정의하는 것이 얼마나 중요한지 보여준다.
- 이렇게 하면 메시의 운영 비용을 절감하고, 성능을 개선하고, 플랫폼의 사용자(테넌트 tenant)들에게 워크로드에 송신 트래픽을 명시적으로 정의하는 좋은 습관을 심어줄 수 있다.
- 기존 클러스터에서는 서비스 중단을 방지하기 위해 플랫폼의 사용자들과 신중히 협의해야 하는데, 구체적으로는 그들이 좀 더 구체적인 Sidecar 리소스로 워크로드의 송신 트래픽을 먼저 정의하도록 해야 한다.
- 그러고 나서야 메시 범위에 디폴트 사이드카 설정을 적용할 수 있다.
- 항상 스테이징 환경에서 변경 사항을 테스트해야 한다.
☞ 사이드카 설정 범위 Sidecar configuration scopes
사이드카 설정은 PeerAuthentication 리소스와 비슷하게 다양한 범위에서 적용할 수 있다.
- mesh-wide 메시 범위 사이드카는 메시 내 모든 워크로드에 적용돼 기본값을 정의할 수 있다. 다른 규칙을 명시적으로 지정하지 않는 한 트래픽 송신을 제한하는 식이다. 메시 범위 사이트카 설정을 만들려면, 이스티오를 설치한 네임스페이스(우리의 경우 istio-system)에 적용하면 된다. 메시 범위 사이드카의 이름 컨벤션은 default이다.
By convention, mesh-wide sidecars are named default.
- namespace-wide 네임스페이스 범위 사이드카 설정은 좀 더 구체적이며 메시 범위 설정을 덮어 쓴다. 네임스페이스 범위 사이드카 설정을 만들려면, workloadSelector 필드를 정의하지 않고 원하는 네임스페이스에 적용하자. 네임스페이스 범위 사이드카의 이름 컨벤션은 default이다.
- workload-specific 워크로드별 사이트카 설정은 workloadSelector 속성에 부합하는 특정 워크로드를 목표로 한다. 가장 구체적인 설정으로, 메시 범위와 네임스페이스 범위 설정 모두를 덮어 쓴다.
Being the most specific, it overrides both mesh-wide and namespace-wide configurations.
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
1. NginX 배포 및 접속 테스트
2. 사이드 카 형식의 Traffic 처리규칙 적용
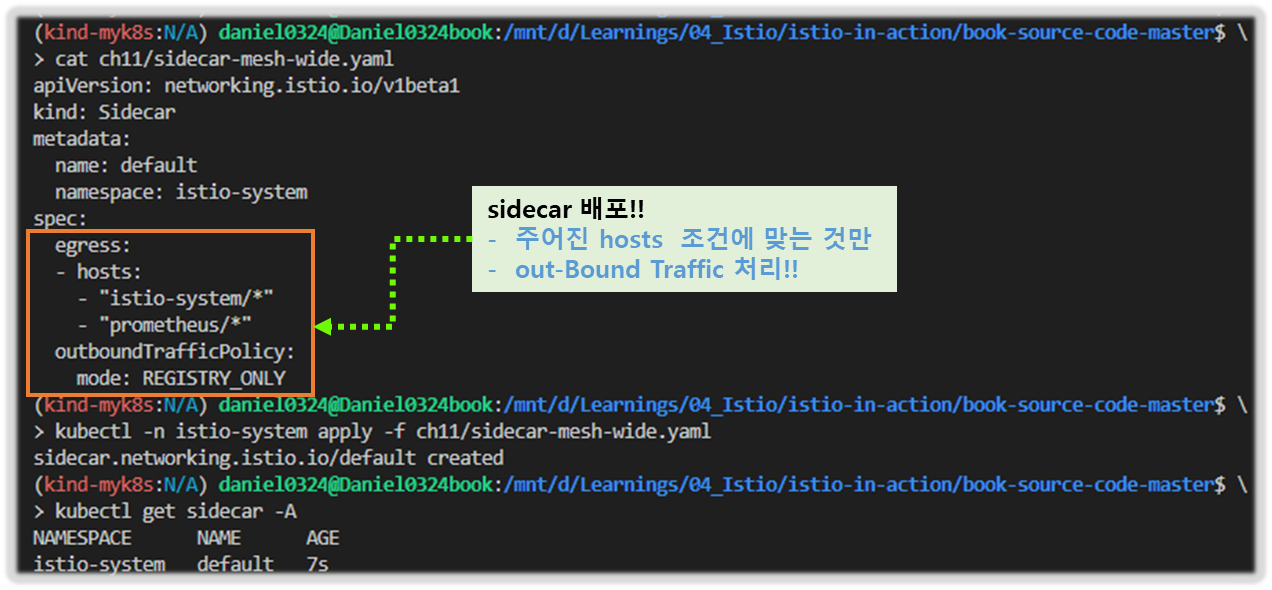
3. 처리양의 차이 비교 ( Traffic 처리 로그 크기 )
4. '2.5초 delay' 준 Traffic 처리 패턴을 10회 반복 후, 결과 확인해 보자.
( 이전 테스트와 비교 시, Push Count : 550 ==> 74, 마지막 1분 동안 지연 시간 : 0.1sec )
☞ https://youtu.be/4sJd6PIkP_s?si=xEMYgy7YC5TsOAJg&t=466
11.3.3 이벤트 무시하기*: 디스커버리 셀렉터로 디스커버리 범위 줄이기 meshConfig.discoverySelectors
- 이스티오 컨트롤 플레인이 기본적으로 K8S 모든 네임스페이스의 파드, 서비스와 기타 리소스의 생성 이벤트를 감지한다는 것은 놀라운 일이다! It may come as a surprise that the Istio control plane by default watches events for the creation of Pods, services, and other resources in all namespaces!
- 대규모 클러스터에서 이런 동작은 컨트롤 플레인에 부담을 줄 수 있다.
- 데이터 플레인을 최신 상태로 유지하기 위해 모든 이벤트마다 엔보이 설정을 처리하고 생성하기 때문이다.
- 이런 부담을 줄이기 위해 Istio 1.10에는 네임스페이스 디스커비리 셀렉터 discovery selector 라는 기능이 새로이 추가돼 istiod 컨트롤 플레인이 감시할 이벤트를 세밀하게 조정할 수 있다.
- 이 기능을 사용하면 워크로드와 엔드포인트를 감시할 네임스페이스를 명시적으로 지정할 수 있다.
- 네임스페이스 셀렉터 접근법을 사용하면 동적으로 네임스페이스와 해당 네임스페이스의 각 워크로드를 포함하거나, 메시에서 처리하지 않도록 제외할 수 있다.
- K8S 클러스터에 메시 내 워크로드가 절대 라우팅하지 않을 워크로드가 많거나, 계속 변하는 워크로드가 있는 경우(스파크 잡 spark job 이 계속 생성되고 종료되는 등) 특히 유용한다.
- 이 경우 컨트롤 플레인이 이 워크로드들에서 만들어지는 이벤트를 무시하게 만들고 싶을 것이다.
- 다음과 같이 IstioOperator 파일을 사용해 시작 시 디스커버리 설렉터 기능을 활성화할 수 있다.
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
namespace: istio-system
spec:
meshConfig:
discoverySelectors: # 디스커버리 셀렉터 활성화
- matchLabels:
istio-discovery: enabled # 사용할 레이블 지정
☞ 컨트롤 플레인이 처리할 네임스페이스를 istio-discovery: enabled 레이블이 있는 것으로 한정한다. 네임스페이스에 이 레이블이 없으면 무시한다.
- 네임스페이스 대부분을 포함하고 소규모만 제외하려는 경우에는 레이블 비교 표현식을 사용해 어떤 네임스페이스를 포함하지 않을 수 있다.
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
namespace: istio-system
spec:
meshConfig:
discoverySelectors:
- matchExpressions:
- key: istio-exclude
operator: NotIn
values:
- "true"
(참고) discoverySelectors - Docs
- A list of Kubernetes selectors that specify the set of namespaces that Istio considers when computing configuration updates for sidecars.
- 모든 항목을 살피는 기존 동작을 방해하지 않고 istio-exclude: true 레이블이 있는 네임스페이스만 제외 하도록 다음과 같이 업데이트할 수 있다.
#
cat ch11/istio-discovery-selector.yaml
#
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane \
cat /istiobook/book-source-code-master/ch11/istio-discovery-selector.yaml
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl install -y \
-f /istiobook/book-source-code-master/ch11/istio-discovery-selector.yaml
#
kubectl get istiooperators.install.istio.io -A -o json
...
"meshConfig": {
"accessLogEncoding": "JSON",
"accessLogFile": "/dev/stdout",
"defaultConfig": {
"proxyMetadata": {}
},
"discoverySelectors": [
{
"matchExpressions": [
{
"key": "istio-exclude",
"operator": "NotIn",
"values": [
"true"
...
▶ 간단히 테스트 해 보자!!
#
kubectl create ns new-ns
kubectl label namespace new-ns istio-injection=enabled
kubectl get ns --show-labels
# 테스트를 위해 샘플 nginx 배포
cat << EOF | kubectl apply -n new-ns -f -
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:alpine
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
type: ClusterIP
EOF
# 확인
kubectl get deploy,svc,pod -n new-ns
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system | grep nginx
10.10.0.26:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||nginx.default.svc.cluster.local
10.10.0.27:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||nginx.new-ns.svc.cluster.local
# 설정
kubectl label ns new-ns istio-exclude=true
kubectl get ns --show-labels
# 다시 확인
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane istioctl proxy-config endpoint deploy/istio-ingressgateway.istio-system | grep nginx
10.10.0.26:80 HEALTHY OK outbound|80||nginx.default.svc.cluster.local[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
1) istio-injection 옵션 적용 : "istio-injection=enabled"
2) Labeling : "istio-exclude=true"
- discoverySelectors를 사용해 디스커버리 범위를 관련 있는 네임스페이스로 줄였는데도 컨트롤 플레인이 여전히 포화 상태인 경우, 다음으로 고려해 볼 방법은 각 이벤트를 개별적으로 해결하는 대신 이벤트를 배치 처리해 묶음으로 해결하는 것이다.
11.3.4 이벤트 배치 처리 및 푸시 스로틀링 속성 Event-batching and push-throttling properties
▶ 들어가며 : 디바운스 기반
- 데이터 플레인 설정을 바꾸는 런타임 환경 이벤트는 보통 운영자가 제어할 수 없는 것이다.
Events in the run-time environment that cause changes to the data-plane configurations are usually outside the operator’s control. - 새로운 서비스가 온라인 상태가 되는 것, 복제본 스케일 아웃, 서비스가 비정상이 되는 것 같은 이벤트들은 모두 컨트롤 플레인이 감지해 데이터 플레인 프록시를 조정한다.
Events such as new services coming online, scaling up replicas, or services becoming unhealthy are all detected by the control plane and reconciled for the data-plane proxies. - 그래도 업데이트를 얼마나 지연해서 배치 처리할지 정도는 어느 정도 제어할 수 있다.
However, we have some control when determining how long we may delay updates and batch those events. - 배치 처리하면, 이벤트를 한 묶음으로 처리함으로써 엔보이 설정을 한 번만 만들어 데이터 플레인 프록시로 한 번에 푸시할 수 있다는 이점이 있다.
This has the benefit that the batched events are processed as a group and generate an Envoy configuration that is pushed to the data plane proxies as a single unit.
- 그림 11.9의 순서도는 이벤트 수신이 서비스 프록시로 변경 사항을 푸시하는 작업을 어떻게 **지연시키는지(디바운스)**를 보여준다.
- 디바운스 기반을 더 늘리면, 지연 기간에서 제외됐던 마지막 이벤트도 배치에 포함시켜 모든 이벤트를 하나의 배치로 합침으로써 하나의 요청으로 푸시할 수 있게된다.
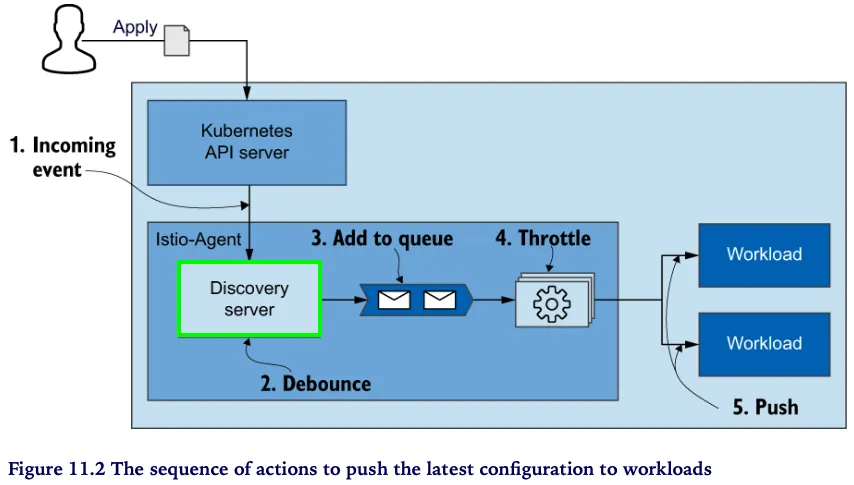
- 그러나 푸시를 너무 미루면 데이터 플레인 설정이 오래돼 최신 상태가 아니게 될 수 있는데, 상술한 것처럼 이런 상황 역시 원하는 바가 아니다.
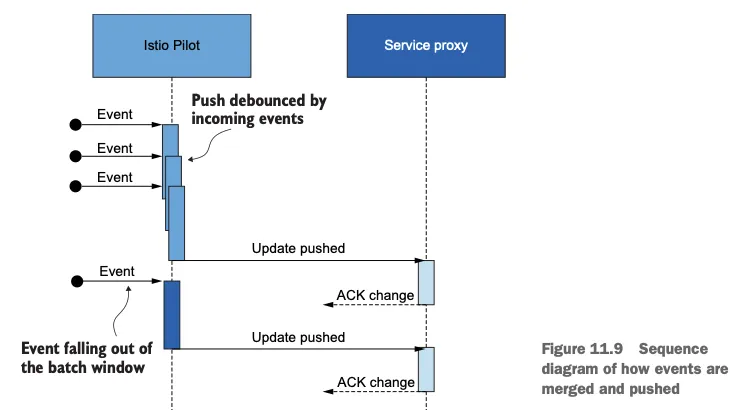
- 한편, 반대로 기간을 줄이면 업데이트가 더 빠르게 수행되는 것이 보장된다.
- 그러나 그렇게 하면 컨트롤 플레인이 미처 배포할 수 없을 정도로 푸시 요청이 많아진다.
- 이런 요청들은 푸시 대기열에서 스로틀링돼 대기 시간 증가로 이어지게 될 것이다.
▶ 배치 기간과 푸시 스로틀링을 정의하는 환경 변수
- ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES THAT DEFINE THE BATCHING PERIOD AND PUSH THROTTLING
- 배치 기간을 정의하는 환경 변수는 다음과 같다 ****- Docs
- PILOT_DEBOUNCE_AFTER
- 이벤트를 푸시 대기열에 추가하는 디바운스할 시간을 지정한다. Specifies the time to debounce, adding an event to the push queue.
- 기본값은 100ms인데, 그 의미는 컨트롤 플레인이 이벤트를 받았을 때 푸시 대기열에 추가하는 행동을 100ms 디바운스한다는 것이다.
- 이 기간 동안에 추가로 발생하는 이벤트는 앞서 발생한 이벤트에 통합돼 작업이 다시 디바운스한다.
- 이 기간 동안 이벤트가 발생하지 않으면, 결과 배치가 푸시 대기열에 추가돼 처리할 준비가 된다. Whenever no events occur in this period, the resulting batch is added to the push queue and is ready for processing.
- 예) 100ms (기본값) 이내에 새로운 이벤트가 없으면 queue에 추가하고, 있으면 merge 후 다시 100ms 동안 대기 + 단, 최대 PILOT_DEBOUNCE_MAX 이내에서 허용
- PILOT_DEBOUNCE_MAX
- 이벤트 디바운스를 허용할 최대 시간을 지정한다. Specifies the maximum time in which debouncing of events is allowed.
- 이 시간이 지나면 현재 병합된 이벤트가 푸시 대기열에 추가된다. 이 변수의 기본값은 10초다.
- PILOT_ENABLE_EDS_DEBOUNCE
- 엔드포인트 업데이트가 디바운스 규칙을 준수할지, 우선권을 줘 푸시 대기열에 즉시 배치할지를 지정한다. Specifies if endpoint updates comply with the debounce rules or have priority and land immediately in the push queue.
- 이 변수의 기본값은 true이며, 엔드포인트 업데이트도 디바운스된다는 의미다.
- PILOT_PUSH_THROTTLE
- istiod가 동시에 처리하는 푸시 요청 개수를 지정한다. Specifies push requests that istiod processes concurrently.
- 이 변수의 기본값은 100개의 동시 푸시다. CPU 사용률이 낮은 경우, 스로틀 값을 높여서 업데이트를 더 빠르게 할 수 있다.
- PILOT_DEBOUNCE_AFTER
- 다음은 이런 설정 옵션을 사용할 때의 일반적인 지침 general guidance 이다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태이고 수신 트래픽이 성능 병목을 야기하는 경우 이벤트 배치 처리를 늘린다.
- 목표가 업데이트 전파를 더 빠르게 하는 것이면 이벤트 배치 처리를 줄이고 동시에 푸시하는 개수를 늘린다. 단, 이 방식은 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태가 아닐 때만 권장한다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태이고 송신 트래픽이 성능 병목인 경우 동시에 푸시하는 개수를 줄인다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태가 아니거나, 스케일 업을 했고 빠른 업데이트를 원하는 경우 동시에 푸시하는 개수를 늘린다.
▶ 배치 기간 늘리기
- INCREASING THE BATCHING PERIOD
- 배치의 효과를 보여주기 위해 PILOT_DEBOUNCE_AFTER 값을 말도 안 되게 높은 값인 2.5초로 지정하자. (기본값은 100ms == 0.1초)
- 여기서 ‘말도 안 되게’라는 수식어는 운영 환경에서는 이렇게 하면 안된다는 것이다. 학습을 위한 실습용 설정임.
# myk8s-control-plane 진입 후 설치 진행
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane bash
-----------------------------------
# demo 프로파일 컨트롤 플레인 배포 시 적용
istioctl install --set profile=demo --set values.pilot.env.PILOT_DEBOUNCE_AFTER="2500ms" --set values.global.proxy.privileged=true --set meshConfig.accessLogEncoding=JSON -y
exit
-----------------------------------
#
kubectl get deploy/istiod -n istio-system -o yaml
...
- name: PILOT_DEBOUNCE_AFTER
value: 2500ms
...
# 성능 테스트 스크립트 실행!
./bin/performance-test.sh --reps 10 --delay 2.5 --prom-url prometheus.istio-system.svc.cluster.local:9090
Push count: 28 # 변경 사항을 적용하기 위한 푸시 함수
Latency in the last minute: 0.10 seconds # 마지막 1분 동안의 지연 시간- PILOT_DEBOUNCE_MAX 로 정의한 한계값을 넘지 않는 한 모든 이벤트는 병합돼 푸시 큐에 더해지는데, 덕분에 푸시 횟수가 현저히 줄어들었다.
- 푸시 횟수가 겨우 28회로 줄었다!
- 엔보이 설정을 만들고 워크로드로 푸시하는 추가 작업을 모두 피해 CPU 사용률과 네트워크 대역폭 소모가 줄어든다.
- 이 예제는 이벤트 디바운스 효과를 설명하기 위한 것이지 일반적으로 사용할 수 있는 istiod 설정이 아니라는 점을 명심하자.
- 이스티오 컨트롤 플레인 설정은 관찰한 메트릭과 환경에 맞춰 조정할 것을 권장한다.
- 그리고 설정을 변경할 때는 컨트롤 플레인의 성능에 부정적인 영향을 줄 수 있는 큰 변화 대신에 조금씩 조절하는 것이 더 안전하다.
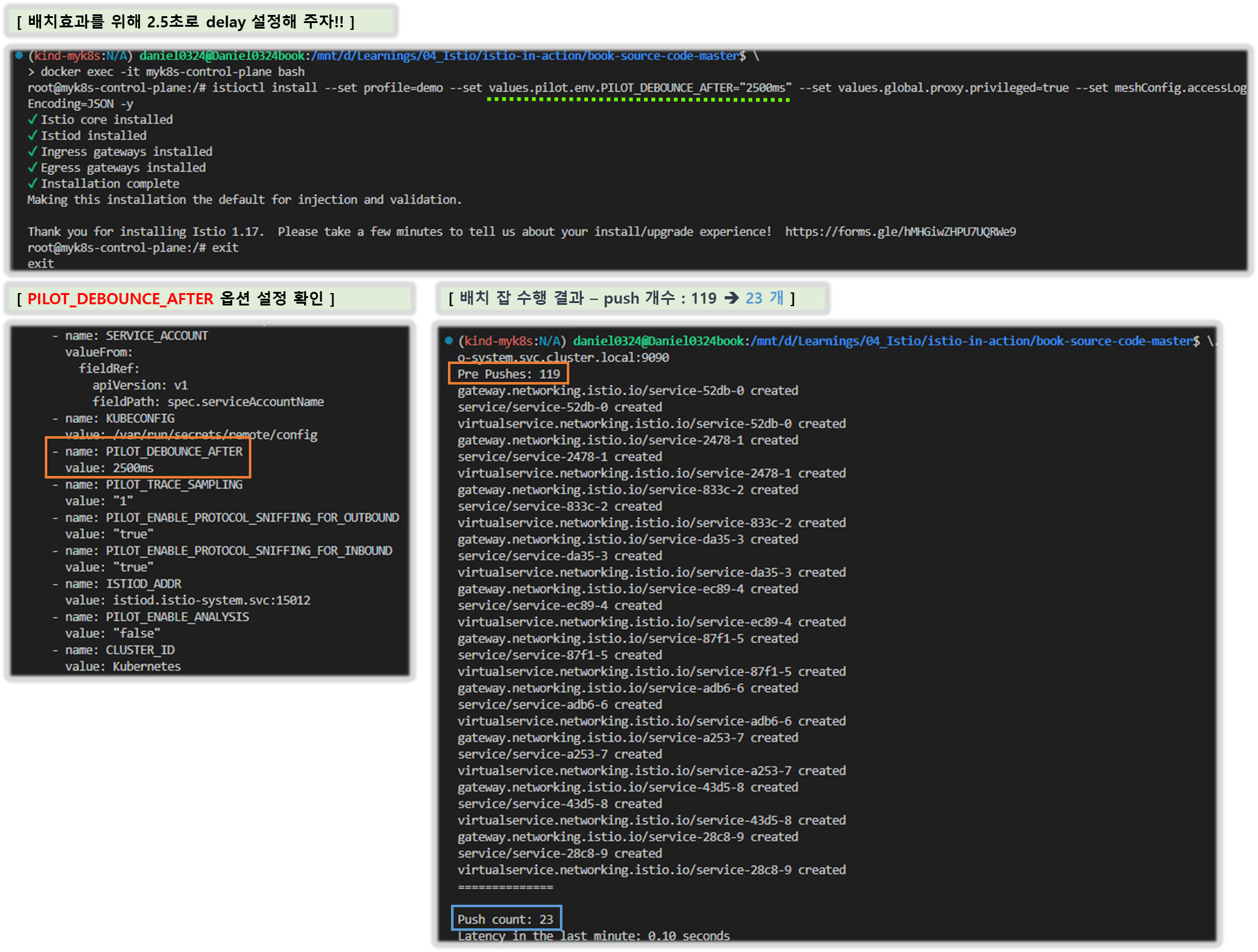
▶ 지연 시간 메트릭은 디바운스 기간을 고려하지 않는다!
- LATENCY METRICS DO NOT ACCOUNT FOR THE DEBOUNCE PERIOD!
- 디바운스 기간을 늘린 후 지연 시간 메트릭에 푸시 배포가 10ms 걸린 것으로 나타났지만, 사실은 그렇지 않다.
- 지연 시간 메트릭이 측정하는 기간은 푸시 요청이 푸시 대기열에 추가된 시점부터 시작됨을 기억하자.
- 즉, 이벤트들이 디바운드되는 동안 업데이트는 전달되지 않았다.
- 따라서 업데이트를 푸시하는 시간은 늘어났지만, 이는 지연 시간 메트릭에서는 나타나지 않는다! And thus, the time of pushing updates increased, but this didn’t appear in the latency metrics!
- 이렇게 이벤트를 너무 오래 디바운스해 지연 시간이 늘어나면 성능이 낮을 때와 마찬가지로 설정이 낡게(오래되게) 된다. This increased latency caused by debouncing events for too long leads to stale configurations, just as low performance would.
- 따라서 배치 속성을 조정할 때는 한 번에 너무 크게 변경하는 것보다는 조금씩 변경하는 것이 좋다.
☞ 데이터 플레인은 보통 늦은 엔드포인트 업데이트에 영향을 받는다. The data plane is commonly affected by late endpoint updates. 환경 변수 PILOT_ENABLE_EDS_DEBOUNCE를 false로 설정하면 엔드포인트 업데이트가 디바운스 기간을 건너뛰어 지연되지 않음을 보장할 수 있다. Setting the environment variable PILOT_ENABLE_EDS_DEBOUNCE to false ensures that endpoint updates are not delayed and skip the debouncing period.
▶ 컨트롤 플레인에 리소스 추가 할당하기
- LOCATING ADDITIONAL RESOURCES TO THE CONTROL PLANE
- Sidecar 리소스를 정의하고 discovery selectors를 사용하고 배치를 설정한 후, 성능을 향상 시킬 수 있는 유일한 방법은 컨트롤 플레인에 리소스를 더 할당하는 것이다.
- 리소스를 더 할당할 때는 istiod 인스턴스를 추가해 스케일 아웃하거나, 모든 istiod 인스턴스에 리소스를 추가로 제공해 스케일 업할 수 있다. When allocating additional resources, we can either scale out by adding more istiod instances or scale up by providing more resources to every instance.
- 스케일 아웃을 할지 스케일 업을 할지는 성능 병목 원인에 따라 결정된다.
- 송신 트래픽이 병목일 때는 스케일 아웃하자. Scale out when the outgoing traffic is the bottleneck.
- 이는 istiod 인스턴스당 관리하는 워크로드가 많을 때만 일어난다. This occurs only when there are many workloads managed per istiod instance.
- 스케일 아웃은 istiod 인스턴스가 관리하는 워크로드 개수를 줄인다.
- 수신 트래픽이 병목일 때는 스케일 업하자. Scale up when the incoming traffic is the bottleneck.
- 이는 엔보이 설정을 생성하는 데 리소스(Service, VS, DR 등)을 많이 처리할 때만 일어난다.
- 스케일 업하면 istiod 인스턴스에 처리 능력을 더 제공한다.
- 송신 트래픽이 병목일 때는 스케일 아웃하자. Scale out when the outgoing traffic is the bottleneck.
- 다음 명령으로 복제본 2 스케일 아웃과 리소스 스케일 업 해보자 !!
#
kubectl get pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod
kubectl describe pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod
...
Requests:
cpu: 10m
memory: 100Mi
...
kubectl resource-capacity -n istio-system -u -l app=istiod
NODE CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS CPU UTIL MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS MEMORY UTIL
myk8s-control-plane 10m (0%) 0m (0%) 8m (0%) 100Mi (0%) 0Mi (0%) 90Mi (0%)
# myk8s-control-plane 진입 후 설치 진행
docker exec -it myk8s-control-plane bash
-----------------------------------
# demo 프로파일 컨트롤 플레인 배포 시 적용
istioctl install --set profile=demo \
--set values.pilot.resources.requests.cpu=1000m \
--set values.pilot.resources.requests.memory=1Gi \
--set values.pilot.replicaCount=2 -y
exit
-----------------------------------
#
kubectl get pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istiod-5485dd8c48-6ngdc 1/1 Running 0 11s
istiod-5485dd8c48-chjsz 1/1 Running 0 11s
kubectl resource-capacity -n istio-system -u -l app=istiod
NODE CPU REQUESTS CPU LIMITS CPU UTIL MEMORY REQUESTS MEMORY LIMITS MEMORY UTIL
myk8s-control-plane 2000m (25%) 0m (0%) 119m (1%) 2048Mi (17%) 0Mi (0%) 107Mi (0%)
kubectl describe pod -n istio-system -l app=istiod
...
Requests:
cpu: 1
memory: 1Gi
...- 컨트롤 플레인 성능 최적화의 요점은 다음과 같다.
- 항상 워크로드에 사이드카 설정을 정의하자. 이것만으로도 대부분의 이점을 얻을 수 있다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태인데 이미 리소스를 많이 할당한 경우에만 이벤트 배치를 수정하자.
- 병목이 송신 트래픽일 때 istiod 스케일 아웃하자.
- 병목이 수신 트래픽일 때 istiod 스케일 업하자.
[ 실행 결과 - 한 눈에 보기 ]
* krew 명령어로 resource-capacity 플러그인 설치
1) control plane 내 istiod 에 할당된 자원 확인
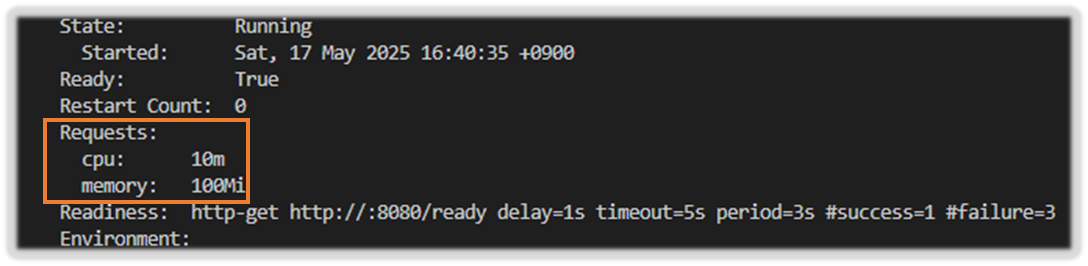
2) control-plane 노드에 접속하여 pilot.replicaCount=2 로 패치한다.
3) 생성된 자원 및 총 할당된 자원량 확인 ( replicas=1 ☞ 2 , 자원 량 : 2배 )
▶ Istiod 디플로이먼트 오토스케일링 Autoscaling istiod deployment
- 오토스케일링은 일반적으로 리소스 소모를 최적화할 수 있는 좋은 아이디어다. 이스티오 컨트롤 플레인과 같이 부하가 급증할 수 있는 워크로드의 경우에는 특히 그렇다.
- 그러나 현재로서는 istiod에 효과적이지 않은데, isiotd가 워크로드와 30분 커넥션을 시작하기 때문이다???. 이 커넥션은 ADS로 프록시를 설정하고 업데이트하는 데 사용하는 것이다. But as of now, this isn’t effective for istiod because it initiates a 30-minute connection with the workloads, which is used to configure and update the proxies using the Aggregated Discovery Service (ADS).
(참고) MaxServerConnectionAge by GPT - Github
- MaxServerConnectionAge는 Istio에서 Envoy 프록시가 오래된 연결을 자동으로 종료시키도록 설정하는 값입니다. 이 값은 gRPC Keepalive 정책에 가까운 기능으로, 연결의 수명 최대치를 정의합니다.
Step1. Sidecar ProxyConfig 설정에 적용
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: ProxyConfig
metadata:
name: example-proxy-config
namespace: istio-system
spec:
proxyMetadata:
ISTIO_META_PROXY_CONFIG: |
concurrency: 2
terminationDrainDuration: 5s
tracing:
sampling: 100
connectionPool:
tcp:
maxServerConnectionAge: 30m- 이 설정은 Envoy가 수신한 TCP 연결을 최대 30분까지만 유지하도록 제한합니다.
- 그 후에는 연결을 graceful 하게 종료하여 새 연결이 만들어지게 유도합니다.
Step2. DestinationRule에서 설정
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:
name: my-service-dr
namespace: my-namespace
spec:
host: my-service.my-namespace.svc.cluster.local
trafficPolicy:
connectionPool:
tcp:
maxServerConnectionAge: 300s # 연결 최대 수명 300초 (5분)
☞ 왜 사용 하나요?
- L7 프록시의 연결 수를 주기적으로 리셋해 리소스 누수 방지
- 장시간 열린 연결로 인한 부하 집중을 해소
- 로드밸런서/업스트림 변경 시 새 연결 유도
- 가비지 커넥션, idle 상태 유지 문제를 방지
- 따라서 새로이 생성된 istiod 복제본은 서비스 프록시와 종전 파일럿 사이의 커넥션이 만료될 때까지는 아무런 부하를 받지 않는다.
- 아무런 부하를 받지 않으니 새 istiod 복제본은 축소된다.
- 이론 인해 아래 그림과 같이 디플로이먼트가 반복적으로 확장됐다가 축소되는 퍼덕거림(flapping)이 일어나게 된다.
- 현재로서 오토스케일링을 구성하는 가장 좋은 방법은 점진적인 부하 증가에 맞추는 것이다.
- 며칠, 몇주, 심지어는 몇 달 단위에 걸쳐서 말이다.
- 이렇게 하면 성능을 지속적으로 모니터링하고 디폴리어먼트 스케일링 결정을 내려야 하는 인적 자원의 부담을 줄일 수 있다.
11.4 성능 튜닝 가이드라인
▶ 들어가기
- 성능을 튜닝하기 전에 이스티오는 성능이 정말 좋다는 것을 명심하자.
- 이스티오 팀은 다음과 같은 파라미터로 모든 릴리스를 테스트한다.
- 엔보이 설정을 부풀리는 쿠버네티스 서비스 1,000개 Kubernetes services that bloat the Envoy configuration
- 동기화해야 하는 워크로드 2,000개 workloads that need to be synchronized
- 서비스 메시 전체에서 초당 요청 70,000개 requests per second in the entire service mesh
- 이 정도 부하로도 메시 전체를 동기화하는 이스티오 파일럿 인스턴스 하나가 겨우 가상 코어 하나와 메모리 1.5GB만을 사용한다.
- 대부분의 운영 환경 클러스터에는 복제본 셋에 vCPU 2개와 2GB 정도쯤되는 적당한 할당으로도 충분하다.
▶ 컨트롤 플레인 성능 튜닝 가이드라인 Performance tuning guidelines
- 이것이 성능 문제인지 확인하자. 다음과 같은 질문에 답하자.
- 데이터 플레인에서 컨트롤 플레인으로 연결이 제대로 이뤄지고 있는가?
- 플랫폼 문제인가? 이를테면 쿠버네티스에서 API 서버가 정상인가?
- 변경 범위를 지정하도록 Sidecar 리소스를 정의했는가?
- 성능 병목 지점을 파악하자. 수집된 지연 시간, 포화도, 트래픽에 대한 메트릭을 사용해 튜닝 결정을 내리자.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태도 아닌데 지연 시간이 증가하면 리소스가 최적으로 활용되지 않고 있다는 것을 나타낸다.
- 더 많은 푸시가 동시에 처리되도록 동시 푸시 임계값을 늘릴 수 있다.
- 사용률은 낮지만 부하가 걸렸을 때 빠르게 포화 상태가 되면 변경 사항이 매우 폭발적임을 나타낸다.
- 즉, 변경 사항이 없는 기간이 길다가 짧은 시간에 이벤트가 급증하는 것이다.
- 이스티오 파일럿의 복제본 수를 늘리거나, 업데이트를 미룰 여지가 있는 경우 배치 속성을 조정한다.
- 변경은 점진적으로 수행하자. 병목을 파악한 후 점진적으로 변경하자.
- 예를 들어, 컨트롤 플레인이 긴 시간 동안 계속해서 이벤트를 받는 경우에는 디바운스 기간을 두배, 심지어는 네 배로 늘리고 싶은 유혹이 있을 수 있다.
- 하지만 그렇게 하면 데이터 플레인이 낡기 쉽다. 대신 설정을 10~30% 범위에서 늘리거나 줄이는 등 조금만 바꾸자.
- 그런 다음, 며칠 동안 이점(또는 성능 저하)를 지켜보고 새로운 데이터를 바탕으로 결정을 내리자.
- 안전은 최우선으로 생각하자.
- 이스티오 파일럿은 메시 전체의 네트워크를 관리하므로, 다운타임은 중단으로 이어지기 십상이다.
- 컨트롤 플레인에 할당하는 리소스는 항상 관대하게 잡고, 복제본을 절대 2개 밑으로 내리지 말자.
- 또한 안전을 최우선으로 생각하자.
- 버스트 가능한 burstable 가상머신을 사용하는 것을 고려하자.
- 이스티오 파일럿은 CPU 리소스가 계속 필요하지 않으므로 버스트성 성능 요구 사항이 있다.
- 컨트롤 플레인이 포화 상태도 아닌데 지연 시간이 증가하면 리소스가 최적으로 활용되지 않고 있다는 것을 나타낸다.
- 다음 장에서는 조직에서 이스티오를 확장하는 방법을 배운다.
- 게이트웨이 여러 대 사용하기, 쿠버네티스가 아닌 워크로드 지원하기, 기존 인증 기관 사용하기, 서비스 메시 내에서 컨트롤 플레인 가용성 패턴 구현하기 등을 다룬다.
▶ Summary
- 컨트롤 플레인의 주요 목표는 데이터 플레인을 원하는 상태로 동기화하는 것이다.
- 이스티오 파일럿 성능에 영향을 주는 요소에는 변경 속도, 파일럿에 할당한 리소스양, 파일럿이 관리하는 워크로드 개수, 설정 크기가 있다.
- 기반 플랫폼에서 받는 변경 속도는 우리가 제어할 수 없다. 그러나 이벤트를 배치 처리할 기간을 정의해 데이터 플레인을 업데이트할 작업량을 줄일 수는 있다.
- istiod에는 리소스를 관대하게 할당하자. default 운영 환경 프로필은 좋은 출발점이다.
- 항상 sidecar 커스텀 리소스를 사용해 변경 범위를 지정하자. 그렇게 하면 다음과 같은 효과를 얻는다.
- 한 이벤트에서 업데이트하는 워크로드가 적어진다.
- 관련 설정만 보내기 때문에 엔보이 설정 크기가 줄어든다.
- discovery selectors 를 사용해 메시와 성관없는 네임스페이스의 이벤트는 무시하자.
- 컨트롤 플레인 튜닝 방법을 결정하는 데 그라파나의 Istio Control Plane 대시보드를 사용하자.
[ 장애 해결 케이스 모음 ]
▶ 멈춰버린 세계: 네트워크 통신 불가를 해결하기 위한 여정(feat. Istio) | 2024 당근 테크 밋업 : istio-proxy 에 CPU Limit 제거하기 - Link
▶ Isito 환경에서 MSA 서비스 간 호출시 Connection Reset 이슈 해결 사례 : tcp max_connect_attempts 1 → 5 시도 증가 - Blog
{{- if .Capabilities.APIVersions.Has "networking.istio.io/v1alpha3/EnvoyFilter" }}
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: EnvoyFilter
metadata:
name: max-connect-attempts
namespace: istio-system
spec:
configPatches:
- applyTo: NETWORK_FILTER
match:
listener:
filterChain:
filter:
name: envoy.filters.network.tcp_proxy
patch:
operation: MERGE
value:
name: envoy.filters.network.tcp_proxy
typed_config:
'@type': type.googleapis.com/envoy.extensions.filters.network.tcp_proxy.v3.TcpProxy
max_connect_attempts: 5
{{- end }}
▶ Istio 도입시 겪었던 Error : holdApplicationUntilProxyStarts: true - Blog
- Pod 시작시 Network Error ⇒ holdApplicationUntilProxyStarts: true 설정 - Docs
- Pod 종료시 Network Error ⇒ terminationDrainDuration 설정 혹은 EXIT_ON_ZERO_ACTIVE_CONNECTIONS 설정
- terminationDrainDuration
- he amount of time allowed for connections to complete on proxy shutdown. On receiving SIGTERM or SIGINT, istio-agent tells the active Envoy to start gracefully draining, discouraging any new connections and allowing existing connections to complete. It then sleeps for the terminationDrainDuration and then kills any remaining active Envoy processes. If not set, a default of 5s will be applied.
- EXIT_ON_ZERO_ACTIVE_CONNECTIONS
- When set to true, terminates proxy when number of active connections become zero during draining
- terminationDrainDuration
- Pod가 종료될 때 커넥션이 비정상적으로 종료되는 경우 : EXIT_ON_ZERO_ACTIVE_CONNECTIONS - Blog
- Istio를 통한 header기반 API 라우팅/호출 시 cors preflight request 이슈 트러블슈팅 : http.corsPolicy - Blog
- Istio xDS로 인한 connection 끊김 이슈 : excludeEgressPorts - Blog
[ 중요 - 실습 후 자원정리 ]
## 1. cluster 삭제
kind delete cluster --name myk8s
## 2. /etc/hosts 파일에 추가했던 도메인 제거
vi /etc/hosts
[ 참고 링크 모음 ]
[ 도전 과제 모음 ]
'ISTIO' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Istio 8주차 - 13장 : VM Support & Istio Traffic Flow (0) | 2025.05.27 |
|---|---|
| 7주차 - 12장, 14장 이스티오 스케일링, 데이터 플레인 확장 (0) | 2025.05.18 |
| Istio 5주차 - 마이크로서비스 통신 보안 (3) | 2025.05.04 |
| ISTIO 4주차 - Observability (2) | 2025.04.28 |
| Istio-3주차 Istio Traffic 제어 및 복원력 (0) | 2025.04.19 |